Abstract
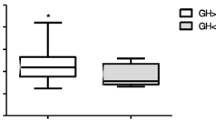
We studied the growth hormone (GH) response to GH-releasing hormone (GHRH) and the thyroid-stimulating hormone (TSH) response to thyrotropin-releasing hormone (TRH) in four groups of patients with dementia and examined whether GH and TSH secretion is altered in patients with Alzheimer's disease. The four groups included those with Alzheimer's disease (n=28), parkinsonism with dementia (n=10), progressive supranuclear palsy with dementia (n=10), and dementia of vascular origin (n=28). The results showed no differences among the four groups in GH response to GHRH (12.2 ± 2, 10.7 ± 2, 8.9 ±1.1, and 9.9 ± 1.9 μg/ml, respectively); there was no correlation between GH response to GHRH and sex, stage of the disease, or cerebral atrophy. The proportion of patients with exaggerated, normal, or lower GH response was similar in the four groups. There were also no differences among the groups in terms of TSH response to TRH (9.2 ±0.9, 11.1 ± 1, 11.1 ± 1, and 10.3 ± 1 mU/ml, respectively), nor was there a correlation between TSH response to TRH and sex, stage of the disease, cerebral atrophy, or GH response to GHRH. The proportion of those with exaggerated, normal, or lower TSH response was similar in the four groups. Cerebrospinal somatostatin levels were similar in Alzheimer's disease and vascular dementia patients. These findings indicate that neither GH response to GHRH nor TSH response to TRH provides a useful diagnostic adjunt in Alzheimer's disease patients.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- AD:
-
Alzheimer's disease
- PD:
-
parkinsonism with dementia
- PSP:
-
progressive supranuclear palsy
- VD:
-
dementia of vascular origin
- GH:
-
growth hormone
- GHRH:
-
growth hormone releasing hormone
- TRH:
-
thyrotropin releasing hormone
- TSH:
-
thyroid stimulating hormone
References
Adolfsson R, Gottfriess CG, Roos BE (1981) Monoamines in the human brain in normal aging and in senile dementia. In: Marois M (ed) Aging a challenge to science and social policy, vol 2. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 238–247
Beal F, Grovidon JH, Mazurek MF, Martin JB (1986) CSF somatostatin-like immunoreactivity in dementia. Neurology 36:294–297
Blessed G, Tomlinsson BE, Roth z (1968) The association between quantitative measures of dementia and of senile change in the cerebral grey matter of elderly subjects. Br J Psychiatry 114:797–811
Cacabelos R, Niigawa H, Ikemura Y, Yanagi Y, Tanaka S, Rodríguez-Arnao MD, Gómez Pan A, Nishimura T (1988) GHRH-induced GH response in patients with senile dementia of the Alzheimer type. Acta Endocrinol (Copenh) 117:295–301
Davidson M, Bastiaens L, Davis BM, Shab MD, Davis KL (1988) Endocrine changes in Alzheimer's disease. Endocr Metab Clin North Am 17:149–157
Davies P, Maloney AJF (1976) Selective loss of cholinergic neurons in Alzheimer's disease. Lancet II:1403
Devesa J, Lima L, Lois C, Fraga C, Lechuga MJ, Arce V, Tresguerres JAF (1989) Reasons for the variability in growth hormone responses to GHRH challenge: the endogenous hypothalamic-somatotroph rhythm (HSR). Clin Endocrinol (Oxf) 30:367–378
Folstein MF, Folstein SE, McHugh PR (1975) Mini-mental state. J Psychiatr Res 12:189–198
Gómez S, Davous P, Rondot P, Faivre-Bauman A, Valade D, Puymirat J (1986) Somatostatin-like immunoreactivity and acetylcholinesterase activities in cerebrospinal fluid in patients with Alzheimer disease and senile dementia of the Alzheimer type. Psychoneuroendocrinol 11:69–73
Gottfries CG (1986) Nosological aspects of differential typology of dementia of Alzheimer type. In: Bergener M (ed) Dimensions in aging. Academic Press, London, pp 207–219
Hachinski VC, Lassen NA, Marshall J (1974) Multi-infarct dementia. A cause of mental deterioration in the elderly. Lancet 11: 207–210
Hardy J, Adolfsson R, Alufuzoff I (1985) Review. Transmitter deficits in Alzheimer's disease. In: Critique: Gottfries CG, Rossor MN, Yates CM (eds) Neurochem Intern 7:545–563
McKhann G, Drachman D, Folstein M, Katzman R, Price D, Standla EM (1984) Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease: report of the NINCDS-ADRDA work group under the auspices of Department of Health and Human Services Task Force on Alzheimer's disease. Neurology 34:485–490
Minton L, Edvinsson L, Ekman R, Gustafson L (1991) Reduced lumbar cerebrospinal fluid somatostatin levels in Alzheimer's disease and dementia with frontotemporal degeneration. Dementia 2:273–277
Navarro MA, Morató J, Rosel P, Gómez JM (1983) Somatostatin in diabetes. Clin Chem 29:2118–2119
Navarro MA, Morath J, Rosel P, Castell C, Bonnin R, Novials A, Marigó M (1984) Somatostatin en individuos intolerantes a la glucosa y diabéticos tipo II. Rev Diag Biol 33:20–26
Nemeroff CA, Krishanan RR, Belkin BM, Ritchie JC, Clark C, Vale WC, Rivier JE, Thorner MO (1989) Growth hormone response to growth hormone releasing factor in Alzheimer's disease. Neuroendocrinol 50:663–666
Perry EK, Blessed G, Tomlinson BE, Perry RH, Crow TJ, Cross AJ, Dockray GJ, Dimaline R, Arregui A (1981) Neurochemical activities in human-temporal lobe related to aging and Alzheimer-type changes. Neurobiol Aging 2:251–256
Raskind MA, Reskind ER, Lampe TH, Rizze SC, Taborsky GJ, Dorsa D (1986) Cerebrospinal fluid vasopressin, oxytocin, somatostatin, and β-endorphin in Alzheimer's disease. Arch Gen Psychiatry 43:382–388
Reischlin S (1983) Somatostatin. N Engl J Med 309:1495–1500
Soinen HS, Jolkkonen JT, Reinikaimen HJ, Halonen TO, Rikkinen PJ (1984) Reduced cholinesterase activity and somatostatin-like immunoreactivity in the cerebrospinal fluid of patients with dementia of the Alzheimer type. J Neurol Sci 63:167–172
Sparks DL, DeKosky ST, Markesbery WR (1988) Alzheimer's disease. Aminergic-cholinergic alterations in hypothalamus. Arch Neurol 45:994–999
Thorner MO, Spiess J, Vance ML, Rogol AD, Kaiser DL, Welster JD, Rivier J, Borges JLC, Bloom SR, Cronin MJ, Evans WS, McLeod RM, Vale W (1983) Human pancreatic growth hormone-releasing factor selectivity stimulates growth hormone secretion in man. Lancet 1:2428
Wade JPH, Mirsen TR, Hatchinski VC, Fisman M, Lan C, Merskey H (1987) The clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer's disease. Arch Neurol 44:2429
Whitehouse PJ (1987) Neurotransmitter receptor alterations in Alzheimer's disease: a review. Alzheimer's Dis Ass Dis 1:9–18
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Correspondence to: J.M. Gomez
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gómez, J.M., Aguilar, M., Navarro, M.A. et al. Secretion of growth hormone and thyroid-stimulating hormone in patients with dementia. Clin Investig 72, 489–493 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00207475
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00207475