Summary
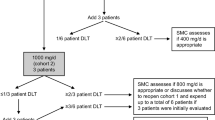
A phase I study with recombinant human tumor necrosis factor α (rhuTNF-α; Knoll AG, Ludwigshafen, FRG) in patients with advanced malignant disease was undertaken to evaluate drug toxicity (organ specifity, time course, predictability, reversibility, maximal tolerated dose), effectiveness, antigenicity and pharmacokinetics. TNF was administered as a test dose followed by daily i.v. infusions for 5 days, every 3 weeks (single i.v. infusion lasting 10 min, TNF dissolved in 50 ml 5% human albumin). Dosage was increased in groups of 3 or 4 patients from 0.04 mg/m2 to 0.28 mg/m2. A total of 19 patients with different cancers, including seven large-bowel carcinomas, three chronic myelogenous leukemias, three hypernephromas, two small-cell lung cancers, one malignant melanoma, one malignant lymphoma, one rhabdomyosarcoma and one fibrosarcoma were treated. Major side-effects were chills and fever (maximum 40.4°C, median 38.7°C, 19/19), headache (12/19), nausea and vomiting (12/19) and pronounced (>20%) hypotension (4/19). Acute side-effects could be diminished by paracetamol or indomethacin pretreatment, and with one possible exception no tachyphylaxis to TNF was noted. Mild renal toxicity was seen during TNF treatment. Pharmacokinetic studies showed a serum half-life (t 1/2) ranging from 11 min to 17 min for doses from 0.04 mg/m2 to 0.16 mg/m2 and prolonged clearance with t 1/2 ranging from 54 min to 70 min in the 0.20–0.28 mg/m2 dose range. No objective antitumor effects were observed in this phase I study.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Balkwill FR, Lee A, Aldam G, Moodie E, Thomas JA, Tavernier J, Fiers W (1986) Human tumor xenografts treated with recombinant human tumor necrosis factor alone or in combination with interferons. Cancer Res 46:3990
Bertolini DR, Nedwin GE, Bringman TS, Smith DD, Mundy GR (1986) Stimulation of bone resoption and inhibition of bone formation in vitro by human tumor necrosis factor. Nature 319:516
Beutler B, Cerami A (1987) Cachectin: more than a tumor necrosis factor. N Engl J Med 316:379
Beutler B, Milsark IW, Cerami AC (1985) Passive immunization against cachectin / tumor necrosis factor protects mice from lethal effects of endotoxin. Science 229:869
Broudy VC, Kaushnansky K, Segal GM, Harlan JM, Adamson JW (1986) Tumor necrosis factor type alpha stimulates human endothelial cells to produce granulocyte/macrophage colony-stimulating factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 83:7467
Carswell EA, Old LA, Kassel RL, Green S, Fiore N, Williamson B (1975) An endotoxin-induced serum factor that causes necrosis of tumors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 72:3666
Chapman PB, Lester TJ, Casper ES, Gabrilove JL, Wong GY, Kempin SJ, Gold PJ, Welt S, Warren RS, Starnes HF, Sherwin SA, Old LJ, Oettgen HF (1987) Clinical pharmacology of recombinant human tumor necrosis factor in patients with advanced cancer. J Clin Oncol 5:1942
Creaven PJ, Plager JE, Dupere S, Huben RP, Takita H, Mittelman A, Proefrock A (1987) Phase I clinical trial of recombinant human tumor necrosis factor. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 20:137
Dinarello CA, Cannon JG, Wolff SM, Bernheim HA, Beutler B, Cerami A, Figari IS, Palladino MA Jr, O'Connor JV (1986) Tumor necrosis factor (cachectin) is an endogenous pyrogene and induces production of interleukin 1. J Exp Med 163:1433
Gamble JR, Harlan JM, Klebanoff SJ, Vadas MA (1985) Stimulation of the adherence of neutrophils to umbilical vein endothelium by human recombinant tumor necrosis factor. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 82:8667
Gray PW, Aggerwal BB, Benton CV, Bringman TS, Henzel WJ, Jarrett JA, Leung DW, Moffat B, Ng P, Svedersky LP, Palladino MA, Nedwin GE (1984) Cloning and expression of c-DNA for human lymphotoxin, a lymphokine with tumor necrosis activity. Nature 312:721
Haranaka K, Satomi N, Sakurai A (1984) Antitumor activity of murine tumor necrosis factor (TNF) against transplanted murine tumors and heterotransplanted human tumors in nude mice. Int J Cancer 34:263
Helson L, Green S, Carswell E, Old LJ (1975) Effects of tumor necrosis factor on cultured human melanoma cells. Nature 258:731
Kettelhut IC, Fiers W, Goldberg AL (1987) The toxic effects of tumor necrosis factor in vivo and their prevention by cyclooxygenase inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 84:4273
Kimura K, Taguchi T, Urushizaki J, Ohno R, Abe O, Furue H Hattori T, Ichizaki H, Inoguchi K, Majima H, Niitani H, Ota K, Saito T, Suga S, Suzuoki Y, Wakui A, Yamada K, The TNF Cooperative Study Group (1987) Phase I study of recombinant human tumor necrosis factor. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol 20:223
Lu L, Welte K, Gabrilove JL, Hangoc C, Bruno E, Hoffman R, Broxmeyer HE (1986) Effects of recombinant human tumor necrosis factor alpha, recombinant human interferon gamma and prostaglandin E on colony formation of human hematopoietic progenitor cells stimulated by natural human pluripotent colony-stimulating factor, pluripoietin alpha and recombinant erythropoietin in serum-free cultures. Cancer Res 46:4357
Marmenout A, Fransen L, Tavernier J, von der Heiden J, Tizard R, Kawashima E, Shaw A, Johnson MJ, Semon D, Müller R, Ruysschaert MR, Van Vliet A, Fiers W (1985) Molecular cloning and expression of human tumor necrosis factor and comparison with mouse tumor necrosis factor. Eur J Biochem 152:515
Mestan J, Digel W, Mittnacht S, Hillen H, Bloem D, Möller A, Jacobsen H, Kirchner H (1986) Antiviral effects of recombinant tumor necrosis factor in vitro. Nature 323:816
Niederle N, Kloke O, Osieka R, Wandl U, Opalka B, Schmidt CG (1987) Interferon alfa-2b in the treatment of chronic myelogenous leukemia. Semin Oncol 14, Suppl 2:29
Old LJ (1985) Tumor necrosis factor. Science 230:630–632
Pennica D, Nedwin GE, Hayflick JS, Seeburg PH, Derynck R, Palladino MA, Kohr WJ, Aggerwal BB, Goeddel DV (1984) Human tumour necrosis factor: precursor structure, expression and homology to lymphotoxin. Nature 312:724
Sato N, Goto T, Haranaka K, Satoni N, Nariuchi H, Mano-Hirano Y, Sawasaki Y (1986) Actions of tumor necrosis factor on cultured vascular endothelial cells: morphologic modulation, growth inhibition and cytotoxicity. J Natl Cancer Inst 76:1113
Selby P, Hobbs S, Viner C, Jackson E, Jones A, Newell D, Calvert AH, McElwain T, Fearon K, Humphreys J, Shiga T (1987) Tumour necrosis factor in man: clinical and biological observations. Br J Cancer 56:803
Taverne J, Matthews N, Depledge P, Playfair JHL (1984) Malarian parasites and tumour cells are killed by the same component of tumour necrosis serum. Clin Exp Immunol 57:293
Torti FM, Dieckmann B, Beutler B, Cerami A, Ringgold GH (1985) A macrophage factor inhibits adipocyte gene expression: an in vitro model of cachexia. Science 229:867
Vilcek J, Palombella VJ, Henriksen-De Stefano D, Swenson C, Feinman R, Hirai M, Tsujimoto M (1986) Fibroblast growth enhancing activity of tumor necrosis factor and its relationship to other polypeptide growth factors. J Exp Med 163:632
Waage A, Halstensen A, Espevik T (1987) Association between tumour necrosis factor in serum and fatal outcome in patients with meningococcal disease. Lancet 1:355
Williamson BD, Carswell EA, Rubin BY, Prendergast JS, Old LJ (1983) Human tumor necrosis factor produced by human B-cell lines. Synergistic cytotoxic interaction with human interferon. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 80:5397
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Moritz, T., Niederle, N., Baumann, J. et al. Phase I study of recombinant human tumor necrosis factor α in advanced malignant disease. Cancer Immunol Immunother 29, 144–150 (1989). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00199290
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00199290