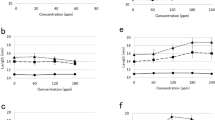
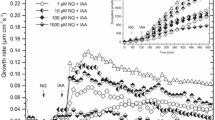
Abstract
Brefeldin A (BFA), a fungal metabolite causing dysfunction of the Golgi apparatus in plant and animal cells, was used to investigate the role of secretory processes at the plasma membrane in auxin-mediated elongation growth of maize (Zea mays L.) coleoptiles. In abraded coleoptile segments BFA produced, within less than 30 min, a decrease in the incorporation of [3H]leucine into tightly bound cell-wall proteins, accompanied by an increased incorporation into the intracellular pool of putative cell-wall glycoproteins. Total protein synthesis was not affected. Electron micrographs revealed striking morphological changes in dictyosomes (especially vesiculation of trans-cisternae), accumulation of Golgi vesicles and dilation of the endoplasmic reticulum. These effects are taken as indication that BFA interferes with the secretion of cell-wall components. Elongation growth of coleoptile segments in the presence and absence of auxin was inhibited by 80% in 20 mg·l−1 BFA. If BFA was applied to segments growing in the presence of auxin, maximum inhibition was reached after about 30 min, indicating that the growth response depends on an uninterrupted supply of a cell-wall or plasma-membrane component (“wall-loosening factor”) delivered by the secretory pathway. After its secretion, this factor has a rather short growth-effective life time. The inhibition of auxin-mediated growth by BFA was accompanied by an elimination of auxin-induced cell-wall extensibility and by an inhibition of auxin-induced proton excretion. Fusicoccin-induced proton excretion was similarly affected by BFA. It is concluded that both the wall-loosening process underlying elongation growth as well as proton excretion depend on an intact secretory pathway from the Golgi apparatus to the cell wall; however, a causal relationship between these processes is not warranted by the data.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- BFA:
-
brefeldin A
- FC:
-
fusicoccin
- TCA:
-
trichloroacetic acid
- WLF:
-
wall-loosening factor
References
Chrispeels, M.J. (1991) Sorting of proteins in the secretory system. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. Plant Mol. Biol. 42, 21–53
Cleland, R.E. (1975) Auxin-induced hydrogen ion excretion: correlation with growth, and control by external pH and water stress. Planta 127, 233–242
Driouich, A., Zhang, G.F., Staehelin, L.A. (1993) Effect of brefeldin A on the structure of the Golgi apparatus and on the synthesis and secretion of proteins and polysaccharides in sycamore maple (Acer pseudoplatanus) suspension-cultured cells. Plant Physiol. 101, 1363–1373
Edelmann, H., Schopfer, P. (1989) Role of protein and RNA synthesis in the initiation of auxin-mediated growth in coleoptiles of Zea mays L. Planta 179, 475–485
Edelmann, H., Bergfeld, R., Schopfer P. (1989) Role of cell-wall biogenesis in the initiation of auxin-mediated growth in coleoptiles of Zea mays L. Planta 179, 486–494
Hager, A., Debus, G., Edel, H.-G., Stransky, H., Serrano, R. (1991) Auxin induces exocytosis and the rapid synthesis of a highturnover pool of plasma-membrane H+-ATPase. Planta 185, 527–537
Hohl, M., Schopfer, P. (1991) Water relations of growing maize coleoptiles. Comparison between mannitol and polyethylene glycol 6000 as external osmotica for adjusting turgor pressure. Plant Physiol. 95, 716–722
Hohl, M., Schopfer, P. (1992a) Growth at reduced turgor: irreversible and reversible cell-wall extension of maize coleoptiles andits implications for the theory of cell growth. Planta 187, 209–217
Hohl, M., Schopfer, P. (1992b) Physical extensibility of maize coleoptile cell walls: apparent plastic extensibility is due to elastic hysteresis. Planta 187, 498–504
Jones, R.L., Robinson, D.G. (1989) Protein secretion in plants. New Phytol. 111, 567–597
Klausner, R.D., Donaldson, J.G., Lippincott-Schwartz, J. (1992) Brefeldin A: insights into the control of membrane traffic and organelle structure. J. Cell Biol. 116, 1071–1080
Kutschera, U., Schopfer, P. (1985a) Evidence against the acidgrowth theory of auxin action. Planta 163, 483–493
Kutschera, U., Schopfer, P. (1985b) Evidence for the acid-growth theory of fusicoccin action. Planta 163, 494–499
Kutschera, U., Schopfer, P. (1986) Effect of auxin and abscisic acid on cell wall extensibility in maize coleoptiles. Planta 167, 527–535
Kutschera, U., Bergfeld, R., Schopfer, P. (1987) Cooperation of epidermis and inner tissues in auxin-mediated growth of maize coleoptiles. Planta 170, 168–180
Laemmli, U.K. (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 227, 680–685
Lippincott-Schwartz, J., Yuan, L., Tipper, C., Amherdt, M., Orci, L., Klausner, R.D. (1991) Brefeldin A's effects on endosomes, lysosomes, and the TGN suggest a general mechanism for regulating organelle structure and membrane traffic. Cell 67, 601–616
Marrè, E. (1979) Fusicoccin, a tool in plant physiology. Annu. Rev. Plant Physiol. 30, 273–288
Miller, S.G., Carnell, L., Moore, H.-P.H. (1992) Post-Golgi membrane traffic: brefeldin A inhibits export from distal Golgi compartments to the cell surface but not recycling. J. Cell Biol. 118, 267–283
Mollenhauer, H.H., Morré, D.J., Rowe, L.D. (1990) Alteration of intracellular traffic by monensin; mechanism, specificity and relationship to toxicity. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 1031, 225–246
Moore, P.J., Swords, K.M.M., Lynch, M.A., Staehelin, L.A. (1991) Spatial organization of the assembly pathways of glycoproteins and complex polysaccharides in the Golgi apparatus of plants. J. Cell Biol. 112, 589–602
Ray, P. (1977) Auxin-binding sites of maize coleoptiles are localized on membranes of the endoplasmic reticulum. Plant Physiol. 59, 594–599
Rayle, D.L., Cleland, R.E. (1992) The acid growth theory of auxin-induced cell elongation is alive and well. Plant Physiol. 99, 1271–127
Satiat-Jeunemaître, B., Hawes, C. (1992a) Reversible dissociation of the plant Golgi apparatus by brefeldin A. Biol. Cell 74, 325–328
Satiat-Jeunemaître, B., Hawes, C. (1992b) Redistribution of a Golgi glycoprotein in plant cells treated with brefeldin A. J. Cell Sci. 103, 1153–1166
Satiat-Jeunemaître, B., Hawes, C. (1993) The distribution of secretory products in plant cells is affected by brefeldin A. Cell Biol. Inter. 17, 183–193
Schopfer, P. (1990) Cytochemical identification of arabinogalactan protein in the outer epidermal wall of maize coleoptiles. Planta 183, 139–142
Schopfer, P. (1993) Determination of auxin-dependent pH changes in coleoptile cell walls by a null-point method. Plant Physiol. 103, 351–357
Wong, D.H., Brodsky, F.M. (1992) 100-kD proteins of Golgi and trans-Golgi network-associated coated vesicles have related but distinct membrane binding properties. J. Cell Biol. 117, 1171–1179
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Supported by Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (SFB 206). We thank Ms. B. Huvermann and Mrs. C. Plachy for conducting growth and proton excretion measurements.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Schindler, T., Bergfeld, R., Hohl, M. et al. Inhibition of Golgi-apparatus function by brefeldin A in maize coleoptiles and its consequences on auxin-mediated growth, cell-wall extensibility and secretion of cell-wall proteins. Planta 192, 404–413 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00198577
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00198577