Abstract
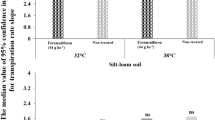
The absorption and translocation of fenoxaprop-ethyl and imazamethabenz-methyl were investigated in wild oat (Avena fatua L.) plants grown under different temperature and light intensity conditions by using 14C tracer techniques. The phytotoxicity of both herbicides, applied as individual droplets, was also determined under similar environments. The absorption of fenoxaprop-ethyl and imazamethabenz-methyl was increased by high temperature (30/20°C) and to a lesser extent by 70% shading; low temperature (10/5°C) had limited effect on the absorption. The basipetal translocation of fenoxaprop-ethyl was not affected by high temperature, and the increase in imazamethabenz-methyl translocation at high temperature was likely the result of the increased absorption. Low temperature decreased total translocation and translocation efficiency in both fenoxaprop-ethyl and imazamethabenz-methyl. Low light intensity tended to reduce the efficiency of basipetal translocation of both herbicides. Fenoxaprop-ethyl phytotoxicity was reduced by high temperature but not by low temperature. Temperature had little effect on imazamethabenz-methyl effectiveness. Under 70% shading, the phytotoxicity of both herbicides was enhanced.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- S.E.D.:
-
standard errors of difference
References
Blair AM, Richardson WG, West TM (1983) The influence of climatic factors on metoxuron activity on Bromus sterilis L. Weed Res 23:259–265
Chandrasena JPNR, Sagar GR (1986) Some factors affecting the performance of fluazifop-butyl against Elymus repens (L.) Gould (= Agropyron repens (L.) Beauv.). Weed Res 26:139–148
Chandrasena NR, Sagar GR (1987) The effect of site of application of 14C-fluazifop on its uptake and translocation by quackgrass (Agropyron repens). Weed Sci 35:457–462
Chandrasena NR, Sagar GR (1989) Fluazifop toxicity to quackgrass (Agropyron repens) as influenced by some application factors and site of application. Weed Sci 37:790–796
Chow PNP (1978) Selectivity and site of action in relation to field performance of herbicides in Manitoba, Proceedings of the 1976 Manitoba Agron Conference Winnipeg, Manitoba, pp 131–139
Coupland D (1986) The effect of environmental factors on the performance of fluazifop-butyl against Elymus repens. Ann Appl Biol 108:353–363
Coupland D (1989a) Pre-treatment environmental effects on the uptake, translocation, metabolism and performance of fluazifop-butyl in Elymus repens. Weed Res 29:289–297
Coupland D (1989b) Factors affecting the phloem translocation of foliage-applied herbicides. In: Atkin RK, Clifford DR (eds) British Plant Growth Regulation Group, Monograph 18, Parchments Ltd., Oxford, pp. 85–112
Devine MD, Bandeen JD, McKersie BD (1983) Temperature effects on glyphosate absorption, translocation, and distribution in quackgrass (Agropyron repens). Weed Sci 31:461–464
Donn G, Bieringer H (1980) The influence of temperature on the herbicidal activity of diclofop-methyl against different weed grass species. Proc Br Crop Prot Conf Weeds 1:283–288
Farahbakhsh A, Murphy KJ, Dominy PJ (1988) Effects of tralkoxydim on cereals and grass weeds with reference to nitrogen and light interactions. Aspects Appl Biol 18:167–176
Grafstorm LD Jr, Nalewaja JD (1988) Uptake and translocation of fluazifop in green foxtail (Setaria viridis). Weed Sci 36:153–158
Hoagland DR, Arnon DI (1939) The water culture method of growing plants without soil. Calif Agric Exp Stn Circ 347
Jeffcoat B, Harries WN, Thomas DB (1977) Factors favoring the choice of flamprop-methyl (±)-2-(N-(3-chloro-4-fluorophenyl) benzamido)propionate for control of Avena species in wheat. Pest Sci 8:1–12
Kells JJ, Meggitt WF, Penner D (1984) Absorption, translocation, and activity of fluazifop-butyl as influenced by plant growth stage and environment. Weed Sci 32:143–149
Klevorn TB, Wyse DL (1984) Effect of soil temperature and moisture on glyphosate and photoassimilate distribution in quackgrass (Agropyron repens). Weed Sci 32:402–407
Kloppenburg DJ, Hall JC (1990) Effects of formulation and environment on absorption and translocation of clopyralid in Cirsium arvense (L.) Scop. and Polygonum convolvulus L. Weed Res 30:9–20
Malefyt T, Quakenbush LS (1991) Influences of environmental factors on the biological activity of the imidazolinone herbicides. In: Shaner DL, O'Connor SL (eds) The imidazolinone herbicides. CRC Press, Boca Raton, FL, pp 103–117
Morrison IN (1983) Environmental factors influencing the response of wild oats to herbicides. In: Smith AE (ed) Wild oat symposium: Proceeding. Can Plains Research Centre, Regina, SK, pp 67–79
Nalewaja JD, Woznica Z (1988) Effect of environment and adjuvants on asulam phytotoxicity. Weed Sci 36:367–372
Olson W, Nalewaja JD (1982) Effect of MCPA on 14C-diclofop uptake and translocation. Weed Sci 30:59–63
Pillmoor JB (1985) Influence of temperature on the activity of AC 222,293 against Avena fatua L. and Alopecurus myosuroides Huds. Weed Res 25:433–442
Price CE (1982) A review of the factors influencing the penetration of pesticides through plant leaves. In: Cutler DF, Alvin KL, Price CE (eds) The plant cuticle. Academic Press, London, pp 237–252
Price C, Ipor I (1992) The influence of sun and shade on herbicide activity and translocation. Proc 1st Intl Weed Control Cong 2:403–406
Sharma MP, Vanden Born WH, Friesen HA, McBeath DK (1976) Penetration, translocation, and metabolism of 14C-difenzoquat in wild oat and barley. Weed Sci 24:379–384
Smeda RJ, Putnam AR (1990) Influence of temperature, rainfall, grass species, and growth stage on efficacy of fluazifop. Weed Technol 4:349–355
Walter H, Koch W, Muller F (1980) Effect of the type of application on the penetration and translocation of diclofop-methyl in wild oats (Avena fatua L.). Weed Res 20:325–331
Whitehouse P, Holloway PJ, Caseley JC (1982) The epicuticular wax of wild oats in relation to foliar entry of the herbicides diclofopmethyl and difenzoquat. In: Cutler DF, Alvin KL, Price CE(eds) The plant cuticle. Academic Press, London, pp 315–330
Wills GD (1984) Toxicity and translocation of sethoxydim in bermudagrass (Cynodon dactylon) as affected by environment. Weed Sci 32:20–24
Wills GD, McWhorter CG (1983) Effect of environment and adjuvants on the translocation and toxicity of fluazifop in Cynodon dactylon and Sorghum halepense. Aspects Appl Biol 4:283–290
Xie HS, Caldwell BC, Hsiao AI, Quick WA, Chao JF (1995) Spray deposition of fenoxaprop and imazamethabenz on wild oat (Avena fatua) as influenced by environmental factors. Weed Sci 43:179–183
Xie HS, Hsiao AI, Quick WA (1994a) Effect of temperature on the phytotoxicity of imazamethabenz and fenoxaprop to wild oat (Avena fatua). Crop Prot 13:376–380
Xie HS, Hsiao AI, Quick WA (1994b) Effect of shading on activity of imazamethabenz and fenoxaprop in wild oat (Avena fatua). Weed Sci 42:66–69
Xie HS, Hsiao AI, Quick WA, Hume J (1996) Influence of water stress on absorption, translocation and phytotoxicity of fenoxaprop-ethyl and imazamethabenz-methyl in Avena fatua. Weed Res36:65–71
Xie HS, Quick WA, Hsiao AI (1994c) Spring cereal response to imazamethabenz and fenoxaprop-p-ethyl as influenced by environment. Weed Technol 8:713–716
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xie, H.S., Hsiao, A.I. & Quick, W.A. Influence of temperature and light intensity on absorption, translocation, and phytotoxicity of fenoxaprop-ethyl and imazamethabenz-methyl in Avena fatua . J Plant Growth Regul 15, 57–62 (1996). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00192932
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00192932