Abstract
In a single-blind, randomized, two-way crossover study with 12 healthy male volunteers, 60 μg of prostaglandin E1 (PGE1) or placebo was administered by intravenous infusion during a 120-min period. PGE1, 13,14-dihydro-PGE1 (PGE0) and 15-keto-PGE0 plasma concentrations were measured by a highly specific and sensitive GC-MS/MS method.
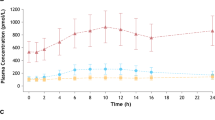
Endogenous PGE1 plasma concentrations ranged between 1.2 and 1.8 pg·ml−1. Endogenous PGE0 and 15-keto-PGE0 plasma concentrations varied from 0.8 to 1.3 pg·ml−1 and from 4.2 to 6.0 pg/ml respectively. During intravenous infusion of PGE1, plasma PGE1 concentrations rose to a level twice as high as during the placebo infusion. In contrast, PGE0 plasma concentrations were 8 times higher during PGE1 infusion than during placebo infusion, and 15-keto-PGE0 plasma concentrations were 20 times higher.
The new analytical method has thus been useful to describe the pharmacokinetics of PGE1 and its metabolites PGE0 and 15-keto-PGE0, during and after intravenous infusion of PGE1.
Similar content being viewed by others

References
Sinzinger H, Virgolini I, O'Grady J (1989). Clinical trials of PGE1, PGI2 and mimetics in patients with peripheral vascular disease. In: Schrör K, Sinzinger H (eds) Postaglandins in clinical research. Liss, New York, pp 85–96
Schweer H, Meese CO, Watzer B, Seyberth HW (1994) Determination of prostaglandin E1 and its main plasma metabolites 15-keto-prostaglandin E0 and prostaglandin E0 by gas chromatography/negative ion chemical ionization triple stage quadrupole mass spectrometry. Biol Mass Spectrom 23: 221–227
Westwick J (1976) The effect of pulmonary metabolites of prostaglandins E1, E2 and F2 on ADP-induced aggregation of human and rabbit platelets. Br J Pharmacol 58: 297
Anggard E (1966) The biological activities of three metabolites of prostaglandin E1. Acta Physiol Scand 66: 509–510
Braun M, Ney P, Szymanski Ch, Bruch L, Schrör K (1991) 13,14-Dihydro-PGE1, a potent inhibitor of human platelet and neutrophil activation. Br J Pharmacol 102: 90
Yamaoko K, Tanigawara Y, Nakagowa T, Uno T (1981) A pharmacokinetic analysis program (Multi) for microcomputer. J Pharm Dyn 4: 876–885
Fleishaker JC, Smith RB (1987) Compartmental Model Analysis in Pharmacokinetics. J Clin Pharmacol 27: 922–926
Gibaldi M, Perrier D (eds) (1975) Pharmacokinetics. Dekker, New York
Leonhardt A, Schweer H, Wolff D, Seyberth HW (1992). Formation of biologically active 13,14-dihydro-prostaglandin E1 during intravenous infusion of prostaglandin E1 in newborns with ductus arteriosus-dependent congenital heart disease. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 33: 323–325
Peskar BA, Hesse WH, Rogatti W, Diehm C, Rudofsky G, Schweer H, Seyberth HW (1991) Formation of 13,14-dihydroprostaglandin E1 during intravenous infusions of prostaglandin E1 in patients with peripheral arterial occlusive disease. Prostaglandins 41: 225–228
Rosenkranz B, Fischer C, Boeynaems JM, Frölich J (1983) Metabolic disposition of prostaglandin E1 in man. Biochim Biophs Acta 750: 231–236
Bothwell W, Verburg M, Wynalda M, Daniels EG, Fitzpatrick FA (1982) A radioimmunoassay for the unstable pulmonary metabolites of prostaglandin E1 and E2: an indirect index of their in vivo disposition and pharmacokinetics. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 220: 229–235
Peskar BA, Cawello W, Rogatti W, Rudofsky G (1991) On the metabolism of prostaglandin E1 administered intravenously to human volunteers. J Physiol Pharmacology 6: 327–331
Simmet TH, Peskar BA (1988) Prostaglandin E1 and arterial occlusive disease: pharmacological considerations. Eur J Clin Invest 18: 549–554
Hamberg M, Samuelsson B (1971) On the metabolism of prostaglandins E1 and E2 in man. J Biol Chem 246: 6713–6721
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cawello, W., Schweer, H., Müller, R. et al. Metabolism and pharmacokinetics of prostaglandin E1 administered by intravenous infusion in human subjects. Eur J Clin Pharmacol 46, 275–277 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00192562
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00192562