Abstract
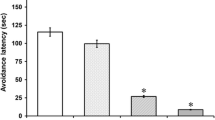
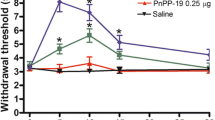
An analogue of sendide, [DTrp7]sendide, was newly synthetized and evaluated as a putative NK1 receptor antagonist in a mouse behavioural test. Effects of [DTrp7]sendide on the scratching, biting and licking response induced by substance P (SP), neurokinin A (NK A) and neurokinin B (NK B) was studied after intrathecal injections. When administered simultaneously with SP, an endogenous agonist for NK1 receptors, [DTrp7]sendide inhibited the behavioural response to this tachykinin in a dose-dependent manner with ID50 value of 1 t.0 pmol/mouse. The behavioural response elicited by other NK1 receptor agonists, septide and physalaemin, was reduced significantly by a small dose (32.0 pmol) of [DTrp7]sendide. Large doses (nmol order) of [DTrp7]sendide were needed to reduce the characteristic behaviour of NK A, an NK2 agonist, NK B, an NK3 agonist and eledoisin, an NK2/NK3 agonist. The duration of the antagonistic effect of [DTrp7]sendide was relatively longer. In a [3H]labeled SP binding assay using mouse spinal cord membranes, [DTrp7]sendide potently displaced [3H] labeled SP binding with a Ki value of 0.023 ± 0.007 nM, which was approximately 140 and 9400 times more potent than that of unlabeled SP and CP-96,345, respectively. These findings suggest that [DTrp7]sendide interacts selectively with the NK1 receptor in the mouse spinal cord as assayed by the receptor binding and SP-induced behavioural tests.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bereford IJM, Birch PJ, Hagan RM, Ireland SJ (1991) Investigation into species variants in tachykinin NK1 receptors by use of the nonpeptide antagonist, CP-96,345. Br J Pharmacol 104:292–293
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254
Buck SH, Burcher E (1986) The tachykinins: a family of peptides with a “brood” of receptors. Trends Pharmacol Sci 7:65–68
Chang K-J, Cuatrecasas (1979) Multiple opiate receptors. J Biol Chem 254:2610–2618
Chang MM, Leeman SE, Niall HD (1971) Amino acid sequence of substance P. Nature New Biol 232:86–87
Cheng YC, Prusoff WH (1973) Relationship between the inhibition constant (Ki) and the concentration of inhibitor which causes 50 per cent inhibition (ID50) of an enzymatic reaction. Biochem Pharmacol 22:3099–3108
Garces YI, Rabito SF, Minshall RD, Sagen J (1992) Lack of potent antinociceptive activity by substance P antagonist CP-96,345 in the rat spinal cord. Life Sci 52:353–360
Gitter BD, Waters DC, Bruns RF, Mason NR, Nixon JA, Howbert JJ (1991) Species differences in affinities of non-peptide antagonists for substance P receptors. Eur J Pharmacol 197:237–238
Guard S, Watson SP (1991) Tachykinin receptor subtypes: classification and membranes signalling mechanisms. Neurochem Int 18:149–165
Harmar A, Schofield JG, Keen P (1980) Cycloheximide-sensitive synthesis of substance P by isolated dorsal root ganglia. Nature 284:267–269
Helke CJ, Charlton CG, Wilwy RG (1986) Studies on the cellular localization of spinal cord substance P receptors. Neuroscience 19:523–533
Hylden JLK, Wilcox GL (1980) Intrathecal morphine in mice: A new technique. Eur J Pharmacol 67:313–316
Jacques L, Couture R, Drapeau G, Regoli D (1989) Capillary permeability induced by intravenous neurokinins. Recpetor characterization and mechanism of action. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 340:170–179
Laneuville O, Dorais J, Couture R (1988) Characterization of the effects produced by nerokinins and three agonists selective for neurokinin receptor subtypes in a spinal nociception reflex of the rat. Life Sci 42:1295–1305
Lavielle S, Chassaing G, Julien S, Besseyre J, Marquet A (1986) Influence of the amino acids of substance P in the recognition of its receptor: affinities of synthesized SP analogues for the specific 125I-BHSP binding site on rat brain synaptosomes. Neuropeptides 7:191–200
Lecci A, Giuliani S, Patacchini R, Viti G, Maggi CA (1991) Role of NK1 tachykinin receptors in thermonociception: effect of (t)-CP 96,345, a non-peptide substance P antagonist, on the hot plate test in mice. Neurosci Lett 129:299–302
Litchfield IT, Wilcoxon F (1949) A simplified method of evaluating dose-effect experiments. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 96:99–113
McLean S, Ganong AH, Seeger TF, Bryce DK, Pratt KG, Reynolds LS, Siok CJ, Lowe III JA, Heym J (1991) Activity and distribution of binding sites in brain of a nonpeptide substance P (NK1) receptor antagonist. Science 25:437–439
Otsuka M, Yanagisawa M (1987) Does substance P act as a pain transmitter? Trends Pharmacol Sci 8:506–510
Papir-Kricheli D, Frey J, Laufer R, Gilon C, Cherev M, Selinger Z, Devor M (1987) Behavioural effects of receptor-specific substance P analogues. Pain 31:263–276
Post C, Folkers K (1985) Behavioural and antinociceptive effects of intrathecally injected substance P analogues in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 113:335–343
Radhakrishnan V, Henry JL (1991) Novel substance P antagonist, CP-96,345, blocks response of cat spinal dorsal horn neurons to noxious cutaneous stimulation and to substance P. Neurosci Lett 132:39–43
Regoli D, Drapeau G, Dion S, D'Orleans-Juste P (1987) Pharmacological receptors for substance P and neurokinins. Life Sci 40:109–117
Rouissi N, Gitter BD, Waters DC, Howbert JJ, Nixon JA, Regoli D (1991) Selectivity and specificity of new, non-peptide, quinuclidine antagonists of substance P. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 176:894–901
Sakurada T, Yamada T, Sakurada S, Kisara K, Ohba M (1989) Substance P analogues containing D-histidine antagonize the behavioural effects of intrathecally co-administered substance P in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 174:153–160
Sakurada T, Yamada T, Tan-No K, Manome Y, Sakurada S, Kisara K, Ohba M (1991) Differential effects of substance P analogs on neurokinin 1 receptor agonists in the mouse spinal cord. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 259:205–210
Sakurada T, Manome Y, Katsumata K, Uchiumi H, Tan-No K, Sakurada S, Kisara K (1992a) Naloxone-reversible effect of spantide on the spinally mediated behavioural response induced by neurokinin-2 and -3 receptor agonists. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 346:69–75
Sakurada T, Manome Y, Tan-No K, Sakurada S, Kisara K, Ohba M, Terenius L (1992b) A selective and extremely potent antagonist of the neurokinin-1 receptor. Brain Res 593:319–322
Sakurada T, Katsumata K, Manome Y, Tan-No K, Sakurada S, Kisara K, Ohba M (1993) Antinociceptive effects in the formalin and capsaicin tests after intrathecal administration of substance P analogues in mice. Eur J Pharmacol 242:47–52
Sakurada T, Yogo H, Tan-No K, Sakurada S, Kisara K, Ohba M (1994) Opioid activity of sendide, an NK1 receptor antagonist, in the mouse spinal cord. Jpn J Pharmacol [Suppl I] 64:173P
Scatchard G (1949) The attractions of proteins for small molecules and ions. Ann NY Acad Sci 51:660–672
Snider RM, Constantine JW, Lowe JA III, Longo KP, Lebel WS, Woody HA, Drozda SE, Desai MC, Vinick C, Spencer RW, Hess HJ (1991) A potent nonpeptide antagonist of the substance P (NK1) receptor. Science 251:435–437
Stoessl AJ, Dourish CT, Young SC, Williams BJ, Iversen SD, Iversen LL (1987) Senktide, a selective neurokinin B-like agonist, elicits serotonin-mediated behaviour following intracisternal administration in the mouse. Neurosci Lett 80:32–326
Vaught JL, Scott R (1986) Species differences in the behavioral toxicity produced by intrathecal substance P antagonists: Relationship to analgesia. Life Sci 40:175–181
Wiesenfeld-Hallin Z, Xu X-J, Kristensson K, Håkanson R, Feng D-M, Folkers K (1990) Antinociceptive and substance P antagonistic effects of intrathecally injected spantide II in rat: no signs of motor impairment or neurotoxicity. Regul Peptides 29:1–11
Yamamoto T, Yaksh TL (1991) Stereospecific effects of a nonpeptidic NK1 selective antagonist, CP-96,345: Antinociception in the absence of motor dysfunction. Life Sci 49:1955–1963
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Correspondence to: T. Sakurada at the above address
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Sakurada, T., Yogo, H., Manome, Y. et al. Pharmacological characterisation of NK1 receptor antagonist, [D-Trp7]sendide, on behaviour elicited by substance P in the mouse. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 350, 387–392 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00178956
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00178956