Summary
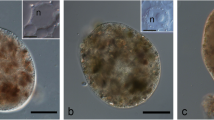
The cytochemical localization of the lysosomal marker enzyme acid phosphatase was studied in the chloragogenous tissue of earthworms. The Gomori lead technique and the cerium capture technique were utilized. Both techniques demonstrated the chloragosomal location of this enzyme. Only a small proportion of chloragosomes presented reactivity, which suggests that these organelles are distinctly heterogeneous. The reaction product was localized in the periphery of chloragosomes, suggesting a membrane-bound compartmentalization of acid phosphatase. In addition, degenerating mitochondria and membrane whorls were observed in some chloragosomes, indicating the possibility that these organelles perform autophagosomal functions.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
agius, c. & agbede, s. a. (1984) An electron microscopical study on the genesis of lipofuscin, melanin and haemosiderin in the haemopoietic tissues of fish. J. Fish Biol. 24, 471–88.
fischer, e. (1972) Uber die pigmente der chloragosomen und ihre histochemischen eigenschafter bei Lumbricus terrestris L. Acta Histochem. 42, 10–4.
fischer, e. (1973a) Histochemische untersuchungen uber die metabolische aktivitat der chloragosomen von Lumbricus terrestris L. Acta Histochem. 46, 1–9.
fischer, e. (1973b) The chloragosomes of lumbricidae as cation exchangers (in vitro investigations). Acta Acad. Sci. Hung. 24, 157–63.
fischer, e. (1975) Chloragosomes of lumbricidae as specific electron acceptors (in vitro investigations). Acta Acad. Sci Hung. 26, 135–40.
fischer, e. (1976) Chloragocyte-eleocyte transformation induced by benomyl and carbofuran toxication of earthworms (Oligochaeta). Zool. Anz. 197, 225–33.
fischer, e. (1977) The function of chloragosomes, the specific age-pigment granules of annelids — a review. Exp. Geront. 12, 69–74.
ghadially, f. n. (1988) Ultrastructural Pathology of the Cell and Matrix, Vol. 2, 3rd edn. London: Butterworths.
george, s. g., pirie, b. j. s. & coombs, t. s. (1980) Isolation and elemental analysis of metal-rich granules from the kidney of the scallop, Pecten maximus (L.). J. Exp. Mar. Biol. Ecol. 42, 143–56.
gomori, g. (1952) Microscopic Histochemistry: Principles and Practice. Chicago: University of Chicago Press.
heath, m. f., gandy, g. & jacobson, w. (1976) Lysosomes in the lung. In Lysosomes in Biology and Pathology 5 (edited by dingle, j. t. & dean, r. t.), pp. 33–58. Amsterdam: North Holland Publishing Company.
holtzman, e. (1989) Lysosomes. New York: Plenum Press.
ireland, m. p. (1978) Heavy metal binding properties of earthworm chloragosomes. Acta Biol. Acad. Sci. Hung. 29, 385–94.
ireland, m. p. & richards, k. s. (1977) The occurrence and localisation of heavy metals and glycogen in the earthworms Lumbricus rubellus and Dendrobaena rubida from a heavy metal site. Histochemistry 51, 153–66.
jamieson, b. g. m. (1981) The Ultrastructure of the Oligochaeta. Edinburgh: Oliver and Boyd.
jamieson, b. g. m. (1992) Oligochaeta. In Microscopic Anatomy of Invertebrates. 7, Annelida (edited by harrison, f. w. & gardiner, s. l.). pp. 217–322. New York: Wiley-Liss inc.
jones, g. w. & bowen, i. d. (1979) The fine structural localization of acid phosphatase in pore cells of embryonic and newly hatched Deroceras reticulatum (Pulmonata: Stylommatophora). Cell Tiss. Res. 204, 253–65.
moment, g. b. (1974) The possible roles of coelomic cells and their yellow pigment in annelid regeneration and aging. Growth 38, 209–18.
morgan, a. j. (1982) The elemental composition of the chloragosomes of nine species of British earthworms in relation to calciferous gland activity. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 73A, 207–16.
morgan, j. e. & morgan, a. j. (1988a) Earthworms as biological monitors of cadmium, copper, lead and zinc in metalliferous soils. Environ. Pollut. 54, 123–38.
morgan, j. e. & morgan, a. j. (1988b) Calcium-lead interactions involving earthworms. Part II: the effect of accumulated lead on endogenous calcium in Lumbricus rubellus. Environ. Pollut. 55, 41–54.
morgan, j. e. & morgan, a. j. (1989) The effect of lead incorporation on the elemental composition of earthworm (Annelida, Oligochaeta) chloragosome granules. Histochemistry 92, 237–41.
prentø, p. (1979) Metals and phosphate in the chloragosomes of Lumbricus terrestris and their possible physiological significance. Cell Tiss. Res. 196, 123–34.
prentø, p. (1986) Cellular and intracellular localization of catalase and acid phosphatase in the midgut of Lumbricus terrestris L. a cell fractionation study. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 83B, 385–90.
prentø, p. (1987) Distribution of 20 enzymes in the midgut region of the earthworm, Lumbricus terrestris L., with particular emphasis on the physiological role of the chloragogenous tissue. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 87A, 135–42.
richards, k. s. & ireland, m. p. (1978) Glycogen-lead relationship in the earthworm Dendrobaena rubida from a heavy metal site. Histochemistry 56, 55–64.
robinson, j. m. (1991) A simple method for ultrastructural enzyme cytochemistry on small volumes and numbers of isolated cells. Histochem. J. 23, 10–2.
robinson, j. m. & karnovsky, m. j. (1983) Ultrastructural localization of several phosphatases with cerium. J. Histochem. Cytochem. 31, 1197–208.
robinson, j. m., okada, t., castellot, j. J. J. & karnovsky, m. j. (1986) Unusual lysosomes in aortic smooth muscle cells: presence in living and rapidly frozen cells. J. Cell Biol. 102, 1615–25.
roots, b. i. (1957) Some observations on the chloragogenous tissue of earthworms. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 1, 216–26.
roots, b. i. & johnston, p. v. (1966) The lipids and pigments of the chloragosomes of the earthworm Lumbricus terrestris L. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 17, 285–8.
skepper, j. n. & navaratnam, v. (1987) Lipofuscin formation in the myocardium of juvenile golden hamsters: an ultrastructural study including staining for acid phosphatase. J. Anat. 150, 155–67.
vannoorden, c. j. f. & frederiks, w. m. (1993) Cerium methods for light and electron microscopical histochemistry. J. Microsc. 171, 3–16.
varute, a. t. & more, n. k. (1972) Are chloragosomes in earthworm chloragogen cells lysosomes? Acta Histochem. 44S, 144–51.
varute, a. t. & more, n. k. (1973) Lysosomal acid hydrolases in the chloragogen cells of earthworms. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. 45A, 607–35.
whitehouse, r. h. & grove, a. j. (1943) Dissection of the Earthworm. London: University Tutorial Press.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cancio, I., ap Gwynn, I., Ireland, M.P. et al. Lysosomal origin of the chloragosomes in the chloragogenous tissue of the earthworm Eisenia foetida: cytochemical demonstration of acid phosphatase activity. Histochem J 27, 591–596 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00173095
Received:
Revised:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00173095