Summary
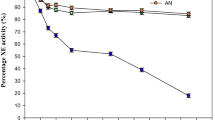
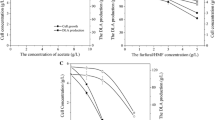
The possible effects of lignocellulose substrate on lignocellulolytic activity of the fungus Pleurotus pulmonarius was studied in submerged culture. This study included fungal growth rates, nitrogen and carbon consumption, and enzymatic activity rates, with and without added cotton-wheat straw (CWS) mixtures. Addition of CWS to the media caused increased consumption of glucose and NH sup+inf4 by the fungal mycelium, induced carboxymethylcellulase (CMC-ase), increased poly-B decolourization, and enhanced the activity of laccase tenfold, while β-glucosidase activity was also enhanced: its first peak was higher and second peak earlier. Lignin peroxidase, however, was not detected. These results give some indication that the lignocellulolytic activity of P. pulmonarius in liquid culture is enhanced by the presence of lignocellulosic substrates such as CWS.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ander P, Eriksson KE (1978) The importance of phenol oxidase activity in lignin degradation by the white rot fungus sporotrichum pulverulentum. Arch Microbiol 109:1–8
Bollag JM, Leonowicz A (1984) Comparative studies of extra-cellular fungal laccases. Appl Environ Microbiol 48:849–854
Bourbonnais R, Paice MG (1990) Oxidation of non-phenolic substrates: an expanded role for laccase in lignin-biodegradation. FEBS Lett 267:99–102
Brink RH, Onbach JP, Lynch DL (1960) Measurement of carbohydrates in soil hydrolysates with anthrone. Soil Sci 89:157–166
Chang SC, Steinkraus KH (1982) Lignocellulolytic enzymes produced by Volvariella volvacae the edible straw mushroom. Appl Environ Microbiol 43:440–446
Danai O, Levanon D, Silanikove N (1989) Cotton straw silage as a substrate for Pleurotus sp. cultivation. Mushroom Sci 12:81–90
Freer SN, Detroy RW (1982) Biological delignification of 14C-labeled lignocellulose by basidiomycetes: degradation and solubilization of the lignin and cellulose components. Mycologia 74:943–951
Glenn JK, Gold MH (1983) Decolourization of seveal polymeric dyes by the lignin degrading basidiomycete Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Appl Environ Microbiol 45:1741–1747
Hiroi T, Eriksson KE (1976) Microbial degradation of lignin. 1. The influence of cellulose on the degradation of lignins by the white rot fungus Pleurotus ostreatus. Sven Papperstidn 5:157–161
Kimura Y, Asuda Y, Kuwahra M (1990) Screening of basidiomycetes for lignin peroxidase genes using DNA probe. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 32:435
Kirk TK (1988) Biochemistry of lignin degradation by Phanerochaete chrysosporium. In: Aubert JP, Beguin P, Millet J (eds) Biochemistry and genetics of cellulose degradation. Academic Press, London, pp 315–348
Kirk TK, Schultz WJ, Connors LF, Lorenz A, Zeikus JG (1978) Influence of culture parameters on lignin metabolism by Phanerochaete chrysosporium. Arch Microbiol 117:277–285
Levanon D, Danai O, Masaphy S (1988) Chemical and physical parameters in recycling organic wastes for mushroom production. Biol Wastes 26:341–348
Ljungdahl LG, Erikson KE (1985) Ecology of microbial cellulose degradation. Adv Microb Ecol 8:237–299
Madan M, Bisaria R (1983) Cellulolytic enzyme from an edible mushroom Pleurotus sajo-cajo. Biotechnol Lett 5:601–604
Platt M (1984) The degradation of lignocellulose by the edible mushroom Pleurotus. Ph. D. thesis, Hebrew University of Jerusalem, 96 pp
Platt M, Hadar Y, Chet I (1984) Fungal activities involved in lignocellulolytic degradation by Pleurotus. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 20:150–154
Sannia G, Limong P, Cocca E, Buonocore F, Nitti G, Giardina P (1991) Purification and characterization of veratryl alcohol oxidase enzyme from the lignin degrading basidiomycete Pleurotus ostreatus. Biochim Biophys Acta 1073:114–119
Tien M, Kirk TK (1983) Lignin degrading enzyme from the hymenomycete Phanerochaete chrysosporium Burds. Science 221:661–663
Turner EM (1974) Polyphenol oxidase activity in relation to substrate and development stage in Agaricus bisporus. Trans Br Mycol Soc 63:541–547
Varadi J (1972) The effect of aromatic compounds on cellulose and xylanase production of the fungi Schizophyllum and commune Chaetomium globosum. In: Walters AM, Hulchran EH (eds) Biodeterioration of materials. Applied Science, London, pp 129–135
Vetter J (1985) Exocellular phenoloxidase of Pleurotus species. Bot Kozl 72:267–276
Vetter J (1986) Extracellular cellulase and xylanase production of Pleurotus species. Acta Bot Hung 32:285–293
Waldner R, Leisola MSA, Fletcher A (1988) Comparison of lignolytic activities of selected white rot fungi. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 29:400–407
Weatherman MW (1967) Phenol hypochlorite reaction for determination of ammonia. Anal Chem 39:971–974
Wood DA, Claydon N, Dudley KJ, Stephens SK, Allen M (1988) Cellulase production in the life cycle of the cultivated mushroom Agaricus bisporus. In: Auberet JP, Begum P, Miller J (eds) Biochemistry and genetics of cellulose degradation. Academic Press, London, pp 53–70
Wood TM, Bhat KM (1988) Methods for measuring cellulose activities. Methods Enzymol 160:87–115
Zadrazil F (1978) Cultivation of Pleurotus. In: Chang ST, Hayes WA (eds) The biology and cultivation of edible mushrooms. Academic Press, New York, pp 521–554
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Offprint requests to: D. Levanon
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Masaphy, S., Levanon, D. The effect of lignocellulose on lignocellulolytic activity of Pleurotus pulmonarius in submerged culture. Appl Microbiol Biotechnol 36, 828–832 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00172203
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00172203