Abstract
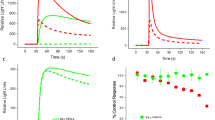
Stable cell lines are potentially excellent tools for large-scale screening of new compounds. Two carboxyterminal-deleted constructs of the two splice variants a and b of the calcium channel class C αl subunit were expressed stably in HEK 293 cells. Each cell line produced regular L-type calcium currents. The opening and closing of the calcium channel elicited by potassium depolarization was followed by Fura-2 transients. These transients were blocked by the calcium channel blocker mibefradil with a concentration for 50% inhibition of 1.7 μM. The cell lines expressing the truncated cardiac α1C−a or smooth muscle α1C−b calcium channel were both blocked by nisoldipine under patch clamp conditions. Nisoldipme interacted with higher affinity with the α1C−b channel than with the α1C−a channel. These results indicate that the two cell lines retain the differential dihydropyridine sensitivity of smooth muscle and cardiac calcium channels and may be potential tools for the screening of L-type calcium channel blockers.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Biel M, Ruth P, Bosse E, Hullin R, Stühmer W, Flockerzi V, Hofmann F (1990) Primary structure and functional expression of high voltage activated calcium channel from rabbit lung. FEBS Lett 269:409–412
Bosse E, Bottlender R, Kleppisch T, Hescheler J, Welling A, Hofmann F, Flockerzi V (1992) Stable and functional expression of the calcium channel α1 subunit from smooth muscle in somatic cell lines. EMBO J 11:2033–2038
Grynkiewicz G, Poenie M, Tsien RY (1985) A new generation of Ca2+ indicators with greatly improved fluorescence properties. J Biol Chem 260:3440–3450
Haase H, Karczewski P, Beckert R, Krause EG (1993) Phosphorylation of the L-type calcium channel β subunit is involved in β-adrenergic signal transduction in canine myocardium. FEBS Lett 335:217–222
Hamill OP, Marty E, Neher E, Sakmann B, Sigworth FJ (1981) Improved patch-clamp techniques for high-resolution current recording from cells and cell-free membrane patches. Pflügers Arch 391:85–100
Hofmann F, Biel M, Flockerzi V (1994) Molecular basis for Ca2+ channel diversity. Annu Rev Neurosci 17:399–418
Kalász H, Watanabe T, Yabana H, Itagaki K, Naito K, Nakayama H, Schwartz A, Vaghy PL (1993) Indentification of 1,4-dihydropyridine binding domains within the primary structure of the α1 subunit of the skeletal muscle L-type calcium channel. FEBS Lett 331:177–181
Koch WJ, Ellinor PT, Schwartz A (1990) cDNA cloning of a dihydropyridine-sensitive calcium channel from rat aorta. J Biol Chem 265:17786–17791
Lacinová L, Welling A, Bosse E, Ruth P, Flockerzi V, Hofmann F (1995) Interaction of Ro 40–5967 with the stable expressed α1 subunit of the cardiac L-type calcium channel. J Pharmacol Exp Ther 274:54–63
Mikami A, Imoto K, Tanabe T, Niidome T, Mori Y, Takeshima H, Narumiya S, Numa S (1989) Primary structure and functional expression of the cardiac dihydropyridine-sensitive calcium channel. Nature 340:230–233
Neely A, Wei X, Olcese R, Birnbaumer L, Stefani E (1993) Potentiation by the β subunit of the ratio of the ionic current to the charge movement in the cardiac calcium channel. Science 262:575–578
Olcese R, Qin N, Schneider T, Neely A, Wei X, Stefani E, Birnbaumer L (1994) The amino terminus of a calcium channel β subunit sets rates of channel inactivation independently of the subunit's effect on activation. Neuron 13:1433–1438
Perez-Reyes E, Yuan W, Wei X, Bers DM (1994) Regulation of the cloned L-type cardiac calcium channel by cyclic-AMP-dependent protein kinase. FEBS Lett 342:119–123
Regulla S, Schneider T, Nastainczyk W, Meyer HE, Hofmann F (1991) Identification of the site of interaction of the dihydropyridine channel blockers nitrendipine and azidopine with the calcium channel αl subunit. EMBO J 10:45–49
Ruth P, Wang G-X, Boekhoff I, May B, Pfeifer A, Penner R, Korth M, Breer H, Hofmann F (1993) Transfected cGMP dependent protein kinase suppresses calcium transients by inhibition of inositol 1,4,5 triphosphate production. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 90:2623–2627
Sanguinetti MC, Kass RS (1984) Voltage-dependent block of calcium channel current in calf cardiac Purkinje fiber by dihydropyridine calcium channel antagonists. Circ Res 55:336–348
Singer D, Biel M, Lotan I, Flockerzi V, Hofmann F, Dascal N (1991) Roles of the subunits of calcium channel in its expression and function. Science 253:1553–1557
Soldatov NM, Bouron A, Reuter H (1995) Different voltage-dependent inhibition by dihydropyridines of human Ca2+ channel splice variants. J Biol Chem 270:10540–10543
Striessnig J, Murphy BJ, Catterall WA (1991) Dihydropyridine receptor of L-type Ca2+ channels: identification of binding domains for [3H]( + )-PN200–110 and [3H]azidopine within the α1 subunit. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 88:10769–10773
Wei X, Neely A, Lacerda AE, Olcese R, Stefani E, Perez-Reyes E, Birnbaumer L (1994) Modificaton of Ca2+ channel activity by deletions at the carboxyl terminus of the cardiac αl subunit. J Biol Chem 269:1635–1640
Welling A, Bosse E, Cavalié A, Bottlender R, Ludwig A, Nastainczyk W, Flockerzi V, Hofmann F (1993a) Stable coexpression of calcium channel αl, β and α2/δ subunits in a somatic cell line. J Physiol 471:749–765
Welling A, Kwan YW, Bosse E, Flockerzi V, Hofmann F, Kass RS (1993b) Subunit-dependent modulation of recombinant L-type calcium channels: molecular basis for dihydropyridine tissue selectivity. Cite Res 73:974–980
Welling A, Lacinovä L, Donatin K, Ludwig A, Bosse E, Flockerzi V, Hofmann F (1995) Expression of the L-type calcium channel with two different β subunits and its modulation by Ro 40–5967. Pflügers Arch 429:400–411
Yoshida A, Takahashi M, Nishimura S, Takeshima H, Kokubun S (1992) Cyclic AMP-dependent phosphorylation and regulation of the cardiac dihydropyridine-sensitive Ca channel. FEBS Lett 309:343–349
Zong X, Schreieck J, Mehrke G, Welling A, Schuster A, Bosse E, Flockerzi V, Hofmann F (1995) On the regulation of the expressed L-type calcium channel by cAMP-dependent protein kinase. Pflügers Arch 430:340–347
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seisenberger, C., Welling, A., Schuster, A. et al. Two stable cell lines for screening of calcium channel blockers. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg's Arch Pharmacol 352, 662–669 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00171326
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00171326