Abstract
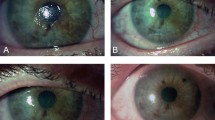
We report three patients with persistent epithelial defects in the context of neurotrophic keratopathy that healed while on treatment with topically applied, mouse-derived epidermal growth factor (m-EGF). The clinical course of these patients was striking and suggests that EGF may have a potential role in the treatment of persistent epithelial defects in subjects suffering from neurotrophic keratitis.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Cohen S (1983) The epidermal growth factor. Cancer 51:1787–1791
Cohen S, Elliot GA (1963) The stimulation of epidermal keratinization by a protein isolated from the submaxillary gland of the mouse. J Invest Dermatol 40:1–9
Daniele S, Delogu A (1990) Il fattore di crescita epidermale (EGF) in Oculistica. Boll d'Ocul 5:1035–1045
Daniele S, Frati L, Fiore C, Santoni G (1979) The effect of the epidermal growth factor (EGF) on the corneal epithelium in humans. Graefe's Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 210:159–165
Frati L, Daniele S, Delogu A, Covelli I (1972) Selective binding of the epidermal growth factor and its specific effects on the epithelial cells of the cornea. Exp Eye Res 14:135–141
Gilbard JP, Rossi SR (1990) Tear film and ocular surface changes in a rabbit model of neurotrophic keratitis. Ophthalmology 97:308–312
Gospodarowicz D, Mescher AL, Brown KD, Birdwell CR (1977) The role of fibroblast growth factor and epidermal growth factor in the proliferative response of the corneal and lens epithelium. Exp Eye Res 25:631–634
Leibowitz HM, Morello S, Stern M, Kupferman A (1990) Effect of topically administered epidermal growth factor on corneal wound strength. Arch Ophthalmol 108:734–737
Magendie F (1824) De l'influence de la cinquieme paire de nerfs sur la nutrision et les functions de l'oéil. J Phyl (Paris) 4:176–181
Ohashi Y, Motakura M, Kinoshita Y (1989) Presence of epidermal growth factor in human tears. Invest Ophthalmol 30:1879–1882
Savage CR, Cohen S (1973) Proliferation of corneal epithelium induced by epidermal growth factor. Exp Eye Res 15:361–366
Sigelman S, Friedenwald JS (1954) Mitotic and wound-healing activities of the corneal epithelium. Arch Ophthalmol 52:46–47
Tripathi RC, Raja SC, Tripathi B (1990) Prospect for epidermal growth factor in the management of corneal disorders. Surv Ophthalmol 34:457–462
Van Setten GB, Viinikka L, Tervo T, Pesonen Tarkkanen A (1989) Epidermal growth factor is a constant component of normal human tear fluid. Graefe's Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 227:184–187
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Correspondence to: S. Daniele
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Daniele, S., Gilbard, J.P. & Schepens, C.L. Treatment of persistent epithelial defects in neurotrophic keratitis with epidermal growth factor: a preliminary open study. Graefe's Arch Clin Exp Ophthalmol 230, 314–317 (1992). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00165937
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00165937