Summary
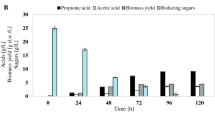
Apple pomace was used as a fsubstrate for citric acid production by five strains of Aspergillus niger. A. niger NRRL 567 produced the greatest amount of citric acid from apple pomace in the presence of 4% methanol. The yield was 88% based on the amount of sugar consumed.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Dubois, M., Gilles, K. A., Hamilton, J. K., Roberts, D. A. and Smith, F. 1956. Anal. Chem. 28, 350–356.
Jewell, W. J. and Cummings, R. J. 1984. J. Food Sci. 49, 407–410.
Kapoor, K. K., Chandharg, K., and Tauro, P. 1982. Citric Acid. In: Prescott and Dunn's Industrial Microbiology. 4th ed. G. Reed (ed.). pp. 709–747 Connecticut: AVI
Taussky, H. H. 1949. J. Biol. Chem. 181, 195–198.
Walter, R. H. and Sherman, R. M. 1976. J. Agr. Food Chem. 24, 1244–1245.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hang, Y.D., Woodams, E.E. Apple pomace: A potential substrate for citric acid production by Aspergillus niger . Biotechnol Lett 6, 763–764 (1984). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00133071
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00133071