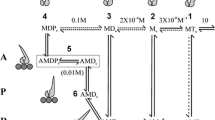
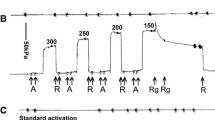
Summary
2,3-butanedione 2-monoxime (BDM) inhibits muscle contraction and actomyosin ATPase both in fibres and in solution. It is potentially useful as a tool for exploring weak interactions between actin and myosin. We have examined the effect of BDM on several key steps of the myosin subfragment-1 and actomyosin subfragment-1 ATPase in solution. These studies show that BDM shifts the equilibrium between two actomyosin states towards a more weakly bound form when the acto.myosin complex has ADP alone or ADP and phosphate bound. We also confirm the findings of Herrmann and colleagues (1993, Biochemistry, 31, 12227–32) that the main effect of BDM on the myosin subfragment-1 ATPase is to slow the release of phosphate following ATP hydrolysis. Skinned fibre studies show that the effects of BDM and phosphate on the steady isometric tension of the fibres are additive. This is consistent with the interpretation that BDM is reducing fibre tension either by increasing phosphate binding or by a direct effect on the crossbridge. Tension transients induced by rapid pressure release were examined in single muscle fibres; they showed that BDM reduces the rate of tension generation following pressure release. This result suggest that BDM directly affects the force generating event in the crossbridge.
Since we submitted this paper, Y. Zhao and M. Kawai have published evidence that BDM reduces the equilibrium constant of the power stroke step in rabbit psoas muscle fibres (Am. J. Physiol. 266, C437-47 (1994)). This is consistent with the main findings in our work.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
BAGSHAW, C. R. & TRENTHAM, D. R. (1974) The characterisation of myosin-product complexes and of product release steps during the magnesium ion-dependent adenosine triphosphatase reaction. Biochem. J. 141, 331–49.
BAGNI, M. A., CECCHI, G., COLOMO, F. & GARZELLA, P. (1992) The effects of 2,3-butanedione monoxime on the crossbridge kinetics in frog single muscle fibres. J. Mus. Res. Cell Motil. 13, 516–22.
Belknap, B., White, H. D., Pate, E. & Cooke, R. (1993) BDM has similar effects on the nucleoside triphosphate hydrolysis in solution and on the mechanical properties of muscle fibres. Biophys, J. 64, A24.
BRANDT, P. W., COX, R. N., KAWAI, M. & ROBINSON, T. (1982) Regulation of tension in skinned muscle fibres. Effects of cross-bridge kinetics on apparent Ca2+ sensitivity. J. Gen. Physiol. 79, 996–1016.
COATES, J. H., CRIDDLE, A. H. & GEEVES, M. A. (1985) Pressure relaxations of actomyosin S1. Biochem. J. 232, 351–6.
COOKE, R. & PATE, E. (1985). The effects of ADP and phosphate on the contraction of muscle fibres. Biophys. J. 48, 789–98.
CRIDDLE, A. H., GEEVES, M. A. & JEFFRIES, T. (1985) The use of actin labelled with N-(1-pyrenyl)iodoacetamide to study the interaction of actin with myosin subfragments and troponin/tropomyosin. Biochem. J. 232, 343–9.
DANTZIG, J. A., GOLDMAN, Y. E., MILLAR, N. C., LACTIS, J. & HOMSHER, E. (1992) Reversal of the crossbridge force-generating transition by photogeneration of phosphate in rabbit psoas muscle fibres. J. Physiol. 451, 247–78.
EDSALL, J. T. & GUTFREUND, H. (1983) Biothermodynamics New York: J. Wiley and Sons.
FORTUNE, N. S., GEEVES, M. A. & RANATUNGA, K. W. (1989) Pressure sensitivity of active tension in glycerinated rabbit psoas muscle fibres: effects of ADP and phosphate. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 10, 113–23.
FORTUNE, N. S., GEEVES, M. A. & RANATUNGA, K. W. (1991). Tension responses to rapid pressure release in glycerinated rabbit muscle fibres. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 88, 7323–7.
FRYER, M. W., GAGE, P. W., NEERING, I. R., DULHUNTY, A. F. & LAMB, G. D. (1988) Paralysis of skeletal muscle by butanedione monoxime, a chemical phosphatase. Pflügers Arch. 411, 76–9.
GEEVES, M. A. (1989) Dynamic interaction between actin and myosin subfragment-1 in the presence of ADP. Biochemistry, 28, 5864–71.
GEEVES, M. A. (1991) The dynamics of actin and myosin association and the crossbridge model of muscle contraction. Biochem. J. 274, 1–14.
GEEVES, M. A. & JEFFERIES, T. E. (1988) The effect of nucleotide upon a specific isomerization of acto.S1. Biochem. J. 256, 41–6.
HERRMANN, C., WRAY, J., TRAVERS, F. & BARMAN, T. (1993) The effect of 2,3,butanedione monoxime on myosin and myofibrillar ATPases. An example of an uncompetitive inhibitor. Biochemistry 31, 12227–32.
HIGUCHI, H. & TAKEMORI, S. (1988) Butanedione monoxime suppresses contraction and ATPase activity of rabbit skeletal muscle. J. Biochem 105, 638–43.
HORIUTI, K., HIGUCHI, H., UMAZUME, Y., KONISHI, M., OKAZAKI, O. & KURIHARA, S. (1988). Mechanism of action of BDM on contraction of frog skeletal muscle. J. Mus. Res. Cell Motil. 9, 156–64.
JOHNSON, K. A. & TAYLOR, E. W. (1978) Intermediate states of subfragment-1 and actosubfragment-1 ATPase: Reevaluation of the mechanism. Biochemstry 17, 3432–42.
LEHRER, S. S. & KERWAR, G. (1972) Intrinsic fluorescence of actin Biochemistry 11, 1211–17.
MCKILLOP, D. F. A. & GEEVES, M. A. (1990) The effect of phosphate and sulphate on the interaction of actin and myosin subfragment-1. Biochem. Soc. Trans. 18, 585–6.
MCKILLOP, D. F. A. & GEEVES, M. A. (1993) Regulation of the interaction between actin and myosin subfragment 1. Evidence for three states of the thin filament. Biophys. J. 65, 693–701.
MILLAR, N. C. & GEEVES, M. A. (1988) Protein fluorescence changes associated with ATP and adenosine 5′-[γ-thio]triphosphate binding to skeletal muscle myosin subfragment-1 and actomyosin subfragment-1. Biochem. J. 249, 735–43.
MILLAR, N. C. & HOMSHER, E. (1990) The effect of phosphate and calcium on force generation in glycerinated rabbit skeletal muscle fibres. J. Biol. Chem. 265, 20234–40.
MILLAR, N. C. & HOMSHER, E. (1992) Kinetics of force generation and phosphate release in skinned rabbit skeletal muscle fibres. Am. J. Physiol. 262, C1239–45.
Mulieri, L. A. & Alpert, N. R. (1984) Differential effects of BDM on activation and contraction. Biophys. J. 45, 47a.
PATE, E. & COOKE, R. (1989) A model of cross-bridge action: the effects of ATP, ADP and Pi. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 10, 181–96.
SIEMANKOWSKI, R. F. & WHITE, H. D. (1984) Kinetics of the interaction between actin, ADP, and cardiac myosin-S1. J. Biol. Chem. 259, 5045–53.
Silva, J. K., Forgaca, R. T. H. & Godt, R. E. (1993) Effects of inorganic phosphate, orthovanadate and BDM on contraction of triton skinned fibres from rabbit and lobster muscle. Biophys. J. 64, A363.
SLEEP, J. A. & HUTTON, R. L. (1980) Exchange between inorganic phosphate and adenosine 5′-triphosphate in the medium by actomyosin subfragment-1. Biochemistry 19, 1276–83.
SLEEP, J. A. & TAYLOR, E. W. (1976) Intermediate states of actomyosin adensine triphosphatase. Biochemistry 15, 5813–17.
WEEDS, A. G. & TAYLOR, R. S. (1974) Separation of subfragment-1 isoenzymes from rabbit skeletal muscle myosin. Nature 257, 54–7.
Zhao, Y. & Kawai, M. (1993) BDM affects nucleotide binding steps of the crossbridge cycle in rabbit psoas fibres. Biophys. J. 64, A118.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Mckillop, D.F.A., Fortune, N.S., Ranatunga, K.W. et al. The influence of 2,3-butanedione 2-monoxime (BDM) on the interaction between actin and myosin in solution and in skinned muscle fibres. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 15, 309–318 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00123483
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00123483