Abstract
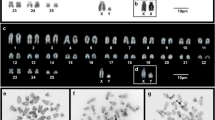
The high-quality karyotype of a specimen of Nycticebus coucang is described and illustrated. The X chromosome is found to be indistinguishable from that of the greater galagos, and may represent a synapomorphic trait. The Y chromosome is a medium to small submetacentric (3.2% TCL) and constitutes one of the larger Y chromosomes known in primates. N. coucang is found to have multiple NOR-bearing chromosomes in contrast to the single pair found in galagine and catarrhine monkeys. Since a single NOR-bearing pair is often considered ancestral for primates, this new finding may have important implications for the evolution of these cistrons. One of the chromosomal polymorphisms in this specimen is a pericentric inversion, involving a NOR-bearing autosomal pair (no. 6), that alters the position of the active site. Further, homologues 2p differ by aparacentric inversion. These results confirm that lorisiforms are characterized by considerable chromosomal polymorphism.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ardito, G., Lamberti, L., Bigatti, P. & Stanyon, R., 1986. NOR distribution and satellite associations in Callithrix jacchus. Caryologia (in press).
BenderM. A. & MettlerL. E., 1958. Chromosome studies in primates. Science 128: 186–190.
ChuE. H. Y. & BenderM. A., 1962. Cytogenetics and evolution of primates. Ann. N. Y. Acad. Sci 102: 253–266.
DeBoerL. E. M., 1971. Observations on associations between the marked chromosomes of catarrhine monkeys (Primates). Genen Phaenen 2: 24–30.
DeBoerL. E. M., 1973a. Studies on the cytogenetics of Prosimians. J. hum. Evol. 2: 271–278.
DeBoerL. E. M., 1973b. Cytotaxonomy of the Lorisoidea (Primates: Prosimii). I. Chromosome studies and karyological relationships in the Galagidae. Genetica 44: 155–193.
DeBoerL. E. M., 1973c. Cytotaxonomy of the Lorisoidea (Primates: Prosimii). II. Chromosome studies in the Lorisidae and karyological relationships within the superfamily. Genetica 44: 330–367.
DutrillauxB., CouturierJ., LombardM. & ChauvierG., 1979. Cytogénétique de deux Lorisidae (Nycticebus coucang et Perodicticus potto). Comparaison avec les lémuriens et les simiens. Ann. Génét. 22: 93–98.
DutrillauxB., CouturierJ., WarterS. & RumplerY., 1982. Chromosomal evolution in ‘Lemurs’. VI. Chromosomal banding studies of Galago senegalensis, Galago alleni, Galago demidovii and Euoticus elegantulus. Folia primatol. 37: 280–296.
EgozcueJ. & Vilarasau de EgozcueM., 1966a. The chromosomes of the slow loris (Nycticebus coucang). Mamm. Chrom. Newsl. 20: 50.
EgozcueJ. & Vilarasau de EgozcueM., 1966b. The chromosome complement of the slow loris (Nycticebus coucang Boddaert, 1785). Primates 7: 423–432.
FordC. E., PollockD. L. & GustavssonI., 1980. Proceedings of the First International Conference for the standardisation of banded karyotypes of domestic animals. Hereditas 92: 145–162.
GarciaM., MiroR. & EgozcueJ., 1978. Banding patterns of the chromosomes of Nycticebus coucang (Boddaert, 1785). Folia primat. 29: 103–106.
HayataI., SontaS., ItohM. & KondoN., 1971. Notes on the karyotypes of some prosimians, Lemur mongoz Lemur catta, Nycticebus coucang and Galago crassicaudatus. Jap. J. Genet. 46: 61–64.
HendersonA. S., WarburtonD. & AtwoodK. C., 1972. Location of ribosomal DNA in the human chromosome complement. Proc. natn. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 69: 3394–3398.
HendersonA. S., WarburtonD. & AtwoodK. C., 1974. Localization of rDNA in the chromosome complement of the rhesus (Macaca mulatta). Chromosoma 44: 367–370.
KlingerH. P., 1963. The somatic chromosomes of some primates (Tupaia glis, Nycticebus coucang, Tarsius bancanus, Cercocebus aterrimus, Symphalangus syndactylus). Cytogenetics 2: 140–151.
LedbetterD. H., 1981. NOR bearing Y chromosome in a primate, Hylobates (Symphalangus) syndactylus. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 29: 250–252.
MastersJ. C., StanyonR. & RomagnoD., 1987. Standardized karyotypes for the greater galagos, Galago crassicaudatus (E. Geoffroy, 1912) and G. garnettii (Ogilby, 1838). Genetica 75: 123–129.
PasztorL. M. & VanHornR. N., 1977. Intraspecific chromosomal variation within Galago crassicaudatus (Galaginae). J. hum. Evol. 6: 569–573.
PoormanP. A., 1982. Banded chromosomes of Galago crassicaudatus monteiri, C. c. garnettii, and a subspecific hybrid. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 34: 296–304.
QuirkS. & HendersonA. S., 1985. Equivalence of nucleolar organizer activity among primate species. Cytogenet. Cell Genet. 39: 134–135.
YingK. L. & ButlerH., 1971. Chromosomal polymorphism in the lesser bush babies (Galago senegalensis). Can. J. Genet. Cytol. 13: 793–800.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Stanyon, R., Masters, J.C. & Romagno, D. The chromosomes of Nycticebus coucang (Boddaert, 1785) (Primates: Prosimii). Genetica 75, 145–152 (1987). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00055258
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00055258