Summary
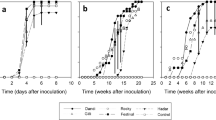
Six inoculation techniques were compared for the artificial promotion of downy mildew (Peronosclerospora sorghi) in sorghum. These were (1) sprouted seeds incubated between sporulating infected leaves, (2) sprouted seeds depped in conidial suspension, (3) sprouted seeds sprayed with conidial suspension, (4) seedlings at plumule stage inoculated with drops of a conidial suspension, (5) seedlings at plumule stage sprayed with a conidial suspension, and (6) seedling showered with conidia falling from infected leaves. Seedlings at the one-leaf stage sprayed with a conidial suspension (6 × 105 ml-1) showed the highest systemic infection (100%) in the susceptible lines IS 643 and IS 18433. This technique is effective, repeatable, and allows the deposition of a conidial suspension as a fine mist on the entire seedling surface. In the greenhouse, the technique was used to test the downy mildew reaction of genotypes previously reported as resistant (< 5% incidence) in 3–4 years of field screenings. Of the 61 genotypes tested, 21 were free from downy mildew, 14 had less than 5% incidence, and the rest showed variable susceptible reactions. Therefore, the technique can be reliably and effectively used in the greenhouse to detect disease escapes and to indentify resistance.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anahosur, K.H. & R.K. Hegde, 1979. Assessment of the techniques used in screening genotypes to downy mildew. Mysore J. Agric. Sci. 13: 449–451.
Craig, J., 1976. An inoculation technique for identifying resistance to downy mildew. Plant Dis. Rept. 60: 350–352.
Frederiksen, R.A., 1980. Sorghum downy mildew in the United States: Overview and outlook. Plant Dis. 64: 903–908.
Frederiksen, R.A. & B.L. Renfro, 1977. Global status of maize downy mildew. Ann. Rev. Phytopath. 15: 249–275.
Jones, B.L., 1970. A simple technique of inoculating sorghum with Sclerospora sorghi using conidia as inoculum. Plant Dis. Rept. 54: 603–604.
Reddy, B.V.S., L.K. Mughogho, Y.D. Narayana, K.D. Nicodemus & J.W. Stenhouse, 1992. Inheritance pattem of downy mildew resistance in advanced generation of sorghum. Ann. Appl. Biol. 121: 249–255.
Safeeulla, K.M., 1976. Biology and control of downy mildews of pearl millet, sorghum and finger millet. Wesley Press, 304 pp.
Schmitt, C.G. & R.E. Freytag, 1974. Quantitative technique for inoculating corn and sorghum with conidia of Sclerospora sorghi. Plant Dis. Rept. 58: 825–829.
Singh, S.D. & R. Gopinath, 1985. A seedling inoculation technique for detecting downy mildew resistance in pearl millet. Plant Dis. 68: 582–584.
Williams, R.J., 1984. Downy mildew of tropical cereals. Adv. in Plant Path. 2: 1–103.
Williams, R.J., S.R.S. Dange, L.K. Mughogho & K.N. Rao, 1982. Identification of QL-3 sorghum, a source of resistance to Peronosclerospora sorghi. Plant Dis. 66: 807–809.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Narayana, Y.D., Mughogho, L.K. & Bandyopadhyay, R. Evaluation of greenhouse inoculation techniques to screen sorghum for resistance to downy mildew. Euphytica 86, 49–53 (1995). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00035938
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00035938