Abstract
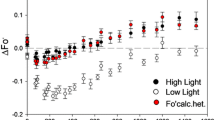
Characteristics of thermoluminescence (TL) glow curves were studied in thylakoids (isolated from pea leaves) or in intact pea leaves after an exposure to very high light for 2 min in the TL device. The inhibition of photosynthesis was detected as decreases of oxygen evolution rates and/or of variable fluorescence.
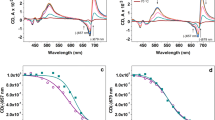
In thylakoids exposed to high light, then dark adapted for 5 min, a flash regime induced TL glow curves which can be interpreted as corresponding to special B bands since: 1) they can be fitted by a single B band (leaving a residual band at −5°C) with a lower activation energy and a shift of the peak maximum by −5 to −6°C and, 2) the pattern of oscillation of their amplitudes was normal with a period of 4 and maxima on flashes 2 and 6. During a 1 h dark adaptation, no recovery of PS II activity occurred but the shift of the peak maximum was decreased to −1 to −2°C, while the activation energy of B bands increased. It is supposed that centers which remained active after the photoinhibitory treatment were subjected to reversible and probably conformational changes.
Conversely, in intact leaves exposed to high light and kept only some minutes in the dark, TL bands induced by a flash regime were composite and could be deconvoluted into a special B band peaking near 30°C and a complex band with maximum at 2–5°C. In the case of charging bands by one flash, this low temperature band was largely decreased in size after a 10 min dark adaptation period; parallely, an increase of the B band type component appeared. Whatever was the flash number, bands at 2–5°C were suppressed by a short far red illumination given during the dark adaptation period and only remained a main band a 20°C; therefore, the origin of the low temperature band was tentatively ascribed to recombinations in centers blocked in state S2QA −QB 2−. In vivo, the recovery of a moderately reduced state in the PQ pool, after an illumination, would be slow and under the dependence of a poising mechanism, probably involving an electron transfer between cytosol and chloroplasts or the so-called ‘chlororespiration’ process.
Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- Ea-:
-
activation energy
- FR-:
-
far-red
- MV-:
-
methylviologen
- pBQ-:
-
p-benzoquinone
- PQ-:
-
plastoquinone
- PS II-:
-
Photosystem II
- QA-:
-
primary quinone electron acceptor of PS II
- QB-:
-
secondary quinone electron acceptor of PS II
- TL-:
-
thermoluminescence
References
Bennoun P (1982) Evidence for a respiratory chain in chloroplasts. Proc Natl Sci USA 79: 4352–4356
Briantais JM, Ducruet JM, Hodges M and Krause GH (1992) Effects of high light at chilling temperature on Photosystem II in spinach leaves. Photosynth Res 31: 1–10
Cerovic Z and Plesnicar M (1984) An important procedure for the isolation of intact chloroplasts of high photosynthetic capacity. Biochem J 223: 543–545
Demeter S and Govindjee (1989) Thermoluminescence in plants. Physiol Plant 75: 121–130
Demming B and Bjorkman O (1987) Comparison of the effect of excessive light on chlorophyll fluorescence (77 K) and photon yield of O2 evolution in leaves of higher plants. Planta 171: 171–184
Ducruet JM and Miranda T (1992) Graphical and numerical analysis of thermoluminescence and fluorescence F0 emission in photosynthetic material. Photosynth Res 33: 15–27
Ducruet JM, Gaillardon P and Vienot J (1984) Use of chlorophyll fluorescence kinetics to study translocation and detoxification of DCMU type herbicides in plant leaves. Z Naturforsch 39c: 354–358
Farineau J (1990) Photochemical alterations of Photosystem II induced by two different inhibitory treatments in isolated chloroplasts of Pea. A thermoluminescence study. Biochim Biophys Acta 1016: 357–363
Farineau J and Laval-Martin D (1992) Oxygen-evolving system and secondary quinonic acceptors are highly reduced in dark-adapted Euglena cells: A thermoluminescence study. Photosynth Res 32: 167–180
Garab GY, Lajko F, Mustardy L and Marton L (1989) Respiratory control over photosynthetic electron transport in chloroplasts of higher-plants cells: Evidence for chlorespiration. Planta 179: 349–358
Ogren E (1988) Photoinhibition of photosynthesis in willow leaves under field conditions. Planta 175: 229–236
Ohad I, Koike H, Schochat S and Inoue Y (1988) Changes in the properties of reaction centers II during the initial stages of photoinhibition as revealed by thermoluminescence measurements. Biochim Biophys Acta 933: 288–298
Ohad R, Adir N, Koike H, Kyle DJ and Inoue Y (1990) Mechanism of photoinhibition in vivo. A reversible light-induced conformational change of reaction center is related to an irreversible modification of the D1 protein. J Biol Chem 265: 1972–1979
Oquist G, Greer DH and Ogren E (1987) Light stress at low temperature. In: Kyle DJ, Osmond CB and Arntzen CJ (eds) Photoinhibition, pp 67–88. Elsevier Science Publishers, Amsterdam, New York, Oxford
Powles S (1984) Photoinhibition of photosynthesis induced by visible light. Annu Rev Plant Physiol 35: 15–44
Rebeillé F and Gans P (1988) Interaction between chloroplasts and mitochondria in microalgae. Role of glycolysis. Plant Physiol 88: 973–975
Rutherford AW, Crofts AR and Inoue Y (1982) Thermoluminescence as a probe of Photosystem II photochemistry. The origin of the flash-induced glow peaks. Biochim Biophys Acta 682: 457–465
Rutherford AW, Renger G, Koike H and Inoue Y (1984a) Thermoluminescence as a probe of Photosystem II. The redox and protonation states of the secondary acceptor quinone and the O2-evolving enzyme. Biochim Biophys Acta 767: 548–556
Rutherford AW, Govindjee and Inoue Y (1984b) Charge accumulation and photochemistry in leaves studied by thermoluminescence and delayed light emission. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 81: 1107–1111
Sane PV and Rutherford AW (1986) Thermoluminescence from photosynthetic membranes. In: Govindjee, Amesz J and Fork DC(eds) Light Emission by Plants and Bacteria, pp 329–360. Academic Press, New York
Styring S, Virgin H, Ehrenberg A and Andersson B (1990) Strong light photoinhibition of electron transport in Photosystem II. Impairment of the function of the first quinone acceptor, QA. Biochim Biophys Acta 1015: 269–278
Vass I and Inoue Y (1991) Thermoluminescence in the study of Photosystem II. In: Barber J(ed) The Photosystems: Structure, Function and Molecular Biology. Topics in Photosynthesis, Vol 11, pp 259–294. Elsevier Science Publishers, Amsterdam, London, New York, Tokyo
Vass I, Horvath G, Herczeg T and Demeter S (1981) Photosynthetic energy conservation investigated by thermoluminescence. Activation energies and half-lives of thermoluminescence bands of chloroplasts determined by mathematical resolution of glow curves. Biochim Biophys Acta 634: 140–152
Vass I, Mohanty N and Demeter S (1988) Photoinhibition of electron transport activity of Photosystem II in isolated thylakoids studied by thermoluminescence and delayed luminescence. Z Naturforsch 43c: 871–876
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Farineau, J. Compared thermoluminescence characteristics of pea thylakoids studied in vitro and in situ (in leaves). The effect of photoinhibitory treatments. Photosynth Res 36, 25–34 (1993). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00018072
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00018072