Abstract
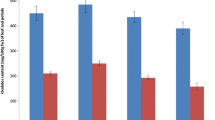
The objective of this study was to determine if plant roots have to take up nitrate at their maximum rate for achieving maximum yield. This was investigated in a flowing-solution system which kept nutrient concentrations at constant levels. Nitrate concentrations were maintained in the range 20 to 1000 μM. Maximum uptake rate for both species was obtained at 100 μM.
Concentrations below 100 μM resulted in decreases in uptake rate per cm root (inflow) for both spinach and kohlrabi by 1/3 and 2/3, respectively. However, only with kohlrabi this caused a reduction in N uptake and yield. Thus indicating that this crop has to take up nitrate at the maximum inflow. Spinach, however, compensated for lower inflows by enhancing its root absorbing surface with more and longer roots hairs. Both species increased their root length by 1/3 at low nitrate concentrations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barber S A 1984 Soil Nutrient Bioavailability — A Mechanistic Approach. Academic Press, New York.
Bergmann W 1988 Ernährungsstörungen bei Kulturpflanzen. VEB Fischer Verlag, Jena, Germany.
Brouwer R 1983 Functional equilibrium: Sense or nonsense. Neth. J. Agric. Sci. 31, 335–348.
Burns I G 1980 Influence of the spatial distribution of nitrate on the uptake of N by plants: A review and a model for rooting depth. J. Soil Sci. 31, 155–173.
Claassen N and Barber S A 1974 A method for characterizing the relation between nutrient concentration and flux into roots of intact plants. Plant Physiol. 54, 564–568.
Clement C R, Hopper M J and Jones L H P 1978 The uptake of nitrate by Lolium perenne from flowing nutrient solution 1. Effect of nitrate concentration. J. Exp. Bot. 29, 453–464.
Doddema H 1978 Uptake of Nitrate by Chlorate-resistant Mutants of Arabidopsis thaliana (L). Heynh. Dissertation Groningen, The Netherlands.
Edwards D G and Asher C J 1974 The significance of solution flow rate in flowing culture experiments. Plant and Soil 41, 161–175.
Edwards J H and Barber S A 1976 Nitrogen uptake characteristics of corn roots at low N concentration as influenced by plant age. Agron. J. 68, 17–19.
Foehse D, Claassen N and Jungk A 1988 Phosphorus efficiency of plants. 1. External and internal P requirement and P uptake efficiency of different plant species. Plant and Soil 110, 101–109.
Foehse D and Jungk A 1983 Influence of phosphate and nitrate supply on root hair formation of rape, spinach and tomato plants. Plant and Soil 74, 359–368.
Heins B and Schenk M K 1986 Nitrate-uptake characteristics of roots as affected by nitrate supply. In Fundamental, Ecological and Agricultural Aspects of Nitrogen Metabolism in Higher Plants. Eds. HLambers, J JNeeteson and IStulen. pp 41–45. Martinus Nijhoff Publishers, Dordrecht, The Netherlands.
Heins B and Schenk M K 1987 Root growth and nitrate uptake of vegetable crops. J. Plant Nutr. 10, 1743–1751.
Newman E I 1966 A method of estimating the total length of root in a sample. J. Appl. Ecol. 3, 139–145.
Olsen C 1950 The significance of concentration for the rate of ion absorption by higher plants in water culture. Physiol. Plant. 3, 152–164.
Williams R F 1948 The effect of phosphorus supply on the rates of intake of phosphorus and nitrogen upon certain aspects of phosphorus metabolism in gramineous plants. Aust. J. Sci. Res. 1, 333–361.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Steingrobe, B., Schenk, M.K. Influence of nitrate concentration at the root surface on yield and nitrate uptake of kohlrabi (Brassica oleracea gongyloides L.) and spinach (Spinacia oleracea L.). Plant Soil 135, 205–211 (1991). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00010908
Received:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00010908