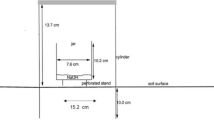
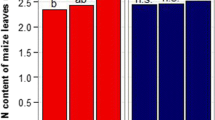
Abstract
In the northern Guinea Savanna of Ghana (1984–1987) a field experiment was conducted to study the reasons for beneficial effects of rotating maize (Zea mays) and cowpea (Vigna unguiculata) on yield and N and P use of maize. The treatments included two cropping systems, maize monocropping and maize/cowpea rotation, two levels of nitrogen (0 and 80 kg N ha-1 as urea) and two levels of phosphorus application (0 and 60 kg ha-1 P as Volta phosphate rock). Yields and nutrient accumulation of maize were larger in rotation than in monocropping, independent of the N and P level. Fertilizer application (N and P) increased yields of maize in both cropping systems to the same extent. Nitrate contents of the soil after cowpea and after maize monoculture were comparable at the beginning of the cropping period. Also, potential nitrogen mineralization was only slightly larger after cowpea in the unfertilized plots. However, soil nitrate of fertilized plots was similar or even higher under monocropping than under crop rotation, especially in deeper soil layers and at the end of the cropping period. This indicates that in addition to the availability of mineral N, its use by the plants was limiting for the productivity of maize. Root length densities of maize were significant lower in monocropped maize than in maize grown in rotation. Soil physical parameters (infiltration, bulk density, aggregate stability and water capacity) showed a significant deterioration compared to a bush fallow plot, but differed only slightly between the cropping systems. Also in a pot experiment maize growth was much better in the soil from the crop rotation than from the monocropping plots, provided P was eliminated as the main growth-limiting factor. Since this effect persisted in spite of N application and optimization of soil physical properties by mixing the soil with polystyrol it is concluded that the results indicate that yield decline in maize monocropping might be due to allelopathic effects.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Barber S A 1984 Soil Nutrient Bioavailability. John Wiley, New York.
Barraclough P B 1989 Root growth, macro-nutrient uptake dynamics and soil fertility requirements of a high-yielding winter oil-seed rape crop. Plant and Soil 119, 59–70.
Böhm W 1979 Methods of studying Root Systems. Springer Verlag, Berlin.
Bowen W T, Quintana J O, Pereira J, Bouldin D R, Reid W S and Lathwell D J 1988 Screening legume green manures as nitrogen sources to succeeding non-legume crops. Plant and Soil 111, 75–80.
Breakwell D P and Turco R F 1989 Nutrient and phytotoxic contributions of residue to soil in no-till continuous-corn ecosystems. Biol. Fertil. Soils 8, 328–334.
Bruulsema T W and Christie B R 1987 Nitrogen contribution to succeeding corn from alfalfa and red clover. Agron. J. 79, 96–100.
Burns J G 1980 Influence of the spatial distribution on the uptake of N by plants. A review and a model for rooting depth. J. Soil Sci. 31, 155–173.
De Boodt M and De Leenkheer L 1967 Aggregate stability determination in the field. In West European methods for soil structure determination. Ed. West European working group on soil structure of the Intern. Soil Sci. Soc. Ed. Com. State. pp 60–61.
De Willigen P and Van Noordwijk M 1987 Roots. Plant Production and Nutrient Use Efficiency. PhD Thesis, Agric. Univ. Wageningen.
Evans J, Fettel N A, Coventry D R, O'Connor G E, Walsgott D N, Mahoney J and Armstrong E L 1991 Wheat response after temperate crop legumes in south-eastern. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 42, 31–43.
Frede H G and Meyer B 1983 Bestimmung der Dichte von Bodenaggregaten durch Messung des Auftriebs. Z. Pflan-zenernaehr. Bodenkd. 146, 365–368.
Guenzi W D, McCalla T M and Norstadt F A 1967 Presence and persistence of phytotoxic substances in wheat, oat, corn and sorghum residues. Agron. J. 59, 163–165.
Härdter R 1989 Utilization of nitrogen and phosphorus by intercropping and sole cropping systems of maize (Zea mays L.) and cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L.) on an alfisol in northern Ghana Nyankpala Agric Res Rep 5. Verlag J Margraf D-6992 Wekersheim
Härdter R and Horst W J 1991 Nitrogen and phosphorus use in maize sole cropping and maize/cowpea mixed cropping systems on an Alfisol in the Northern Guinea Savanna of Ghana. Biol. Fert. Soils 10, 267–275.
Härdter R, Horst W J, Schmidt G and Frey E 1991 Yields and land use efficiency of maize/cowpea crop rotation in comparison to mixed and monocropping on an Alfisol in Northern Ghana. J. Agron. Crop Sci. 166, 326–337.
Horst W J, Wiesler F, Härdter, R and Isokeit U 1990 Rooting patterns of maize and winter wheat cultivars in relation to subsoil nitrogen utilization. In First Congress of the European Society of Agronomy, Paris, 5–7 Dec. 1990. Ed. A Scaife. P001 ISBN 2–9505124–0–2, 3.
Jarrel W M and Beverly R B 1981 The dilution effect in plant nutrition studies. Adv. Agron. 34, 197–224.
Jungk A and Claassen N 1989 Availability in soil and acquisition by plants as the basis for phosphorus and potassium supply to plants. Z. Pflanzenernaehr. Bodenkd. 152, 151–157.
Keating J D, Chapnanian N and Saxena M C 1988 Effect of improved management of legumes in a legume-cereal rotation on field estimates of crop nitrogen uptake and symbiotic nitrogen fixation in northen Syria. J. Agric. Sci. 110, 651–659.
Kimber R W L 1967 Phytotoxicity from plant residues: I. The influence of rotted wheat straw on seedling growth. Aust. J. Agric. Res. 18, 361–374.
Krogmeier M J and Bremner J M 1989 Effects of phenolic acids on seed germination and seedling growth in soil. Biol. Fertil. Soils 8, 116–122.
Kuchenbuch R O and Barber S A 1987 Yearly variation of root distribution with depth in relation to nutrient uptake and corn yield. Commun. Soil Sci. Plant Anal. 18, 255–263.
Latif M A, Mehuys G R, Mackenzie A F, Alli I and Faris M A 1992 Effects of legumes on soil physical quality in a maize crop. Plant and Soil 140, 15–23.
Martin V L, McCoy E L and Dick W A 1990 Allelopathy of crop residues influences corn seed germination and early growth. Agron. J. 82, 555–560.
McCown R L, Cogle A L, Ockwell A P and Reeves T G 1988 Nitrogen supply to cereals in legume ley system under pressure. In Advances in Nitrogen Cycling in Agricultural Ecosystems. Ed. J R Wilson. pp 292–314 CAB International, Wallingford.
McVay K A, Radcliffe D E and Hargrove W C 1989 Winter legume effects on soil properties and nitrogen fertilizer requirements. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 53, 1856–1862.
Navone R 1964 Proposed method for nitrate in potable waters. AWWA 56, 781–183.
Ofori F and Stern W R 1987 Cereal-legume intercropping systems. Adv. Agron. 41, 41–90.
Patra D D, Sachdev M S and Subbiah B V 1987 Forms of nitrogen residues in soil after intercropping of maize. Biol. Fert. Soil 4, 155–161.
Raimbault T and Vyn B A 1991 Crop rotation and tillage effects on corn growth and soil structural stability. Agron. J. 83, 979–985.
Reid J B and Goss M J 1982 Interactions between soil drying due to plant water use and decreases in aggregate stability caused by maize roots. J. Soil Sci. 33, 47–53.
Reuter D J and Robinson J B 1986 Plant analysis. An interpretation manual. Inkata Press, Melbourne, Sydney.
Robinson D, Linehan D J and Caul S 1991 What limits nitrate uptake from soil? Plant, Cell Environ. 14, 77–85.
Rowland I C, Mason M G and Hamblin J 1988 Effects of lupins and wheat on the yield of subsequent wheat crops grown at several rates of applied nitrogen. Aust. J. Exp. Agric. 28, 91–97.
Schippers B, Bakker A W and Bakker P A H M 1987 Interaction of deleterious and beneficial rhizosphere microorganisms and the effect of cropping practices. Ann. Rev. Phytopathol. 25, 339–358.
Schmidt G and Frey E 1988 Crop rotation effects in savannah soil. Nyankpala Agric Res Rep 4. Verlag J Margraf D-6992 Wekersheim.
Senaratne R and Hardarson G 1988 Estimation of residual N effect of faba bean and pea on two succeeding cereals using a 15N methodology. Plant and Soil 110, 81–89.
Suwanarit A, Suwannarat C and Chotechaungmanirat S 1986. Quantities of fixed N and effects of grain legumes on following maize, and N and P status of soil as indicated by isotopes. Plant and Soil 93, 249–258.
Tennant D 1975 A test of a modified line intersect method of estimating root length. J. Ecol. 63, 995–1001.
Thomas R L, Sheard R W and Moyer J R 1967 Comparison of conventional and automated procedures for nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium analysis of plant material using a single digestion. Agron. J. 59, 240–243.
Troll C 1964 Karte der Jahreszeitenklimata der Erde mit einer farbigen Karte von C Troll und K Pfaffen. Erdkunde 18, 5–28.
Trouse A C 1979 Soil physical characteristics and root growth. In Soil Physical Properties and Crop Production in the Tropics. Eds. RLal and D JGreenland. Wiley Chichester.
Wiesler F and Horst W J 1991 Wurzelwachstum und Nutzung des Nitratangebots bei Maissorten. Mitteil. Dt. Bodenkdl. Gesellsch. 66, II, 753–756.
Yakle G A and Cruse R M 1984 Effects of fresh and decomposing plant residues extracts on corn seedling development. Soil Sci. Soc. Am. J. 48, 1143–1146.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Horst, W.J., Härdter, R. Rotation of maize with cowpea improves yield and nutrient use of maize compared to maize monocropping in an alfisol in the northern Guinea Savanna of Ghana. Plant Soil 160, 171–183 (1994). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00010143
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00010143