Synopsis
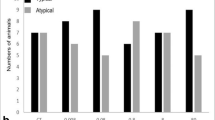
The development of rapid, yet sensitive toxicity testing methods is needed for the establishment of water quality standards to protect aquatic life. A technique using changes in the behavior of bluegill (Lepomis macrochirus) was utilized to evaluate the impact of five sublethal levels of a cadmium (Cd) and zinc (Zn) mixture. The technique proved very sensitive and various changes in behavior occurred at the lowest metal levels used; 21 ug Cd per liter and 99 ug Zn per liter. Coughs, yawns, partial jerks and jerk swimming were especially sensitive indicators of elevated metal levels. The frequency, but not the form, of eight of the nine behaviors quantified changed significantly with increasing metal levels.
Similar content being viewed by others
References cited
American Public Health Association, American Water Works Association & Water Pollution Control Federation. 1971. Standard methods for the examination of water and wastewater, 13th ed., American Public Health Assoc. Washington, D.C. 874 pp.
Avila, V. A. 1976. A field study of nesting behavior of male bluegill sunfish (Lepomis macrochirus, Rafinesque). Am. Midland Nat. 96: 195–206.
Benoit, D. A., E. M. Leonard, G. M. Christensen & J. T. Fiandt, 1976. Toxic effects of cadmium on three generations of brook trout (Salvelinus fontinalis). Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 105: 550–560.
Brungs, W. A. 1969. Chronic toxicity of zinc to the fathead minnow, Pimephales promelas Rafinesque. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 98: 272–279.
Eaton, J. G. 1973. Chronic toxicity of a copper, cadmium and zinc mixture to the fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas Rafinesque). Water Res. 7: 1723–1736.
Eaton, J. G. 1974. Chronic cadmium toxicity to the bluegill. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 103: 729–735.
Friberg, L., M. Piscator & G. Nordberg. 1971. Cadmium in the environment. CRC Press, Cleveland, Ohio. 166 pp.
Gerking, S. D. 1959. The restricted movements of fish populations. Biol. Rev. (Cambridge) 34: 221–242.
Greenberg, M. 1947. Some relations between territory, social hierarchy and leadership in the green sunfish. Physiol. Zool. 20: 269–299.
McDonald, A. L. & N. W. Heimstra. 1965. Agonistic behavior in several species of fish. Psychol. Rep. 16: 845–850.
McDonald, A. L. & L. A. Kessel. 1967. Relationship between social hierarchy and coloration in green sunfish (Lepomis cyanellus). Psychol. Rep. 20: 748–750.
Miller, H. C. 1963. The behavior of the pumpkinseed sunfish, Lepomis gibbosus (Linneaus), with notes on the behavior of other species of Lepomis and the pigmy sunfish, Elassoma evergladei. Behavior 22: 88–151.
Pickering, Q. H. & M. H. Gast. 1972. Acute and chronic toxicity of cadmium to the fathead minnow (Pimephales promelas). J. Fish. Res. Board Can. 29: 1099–1106.
Poulsen, H. R. & D. Chiszer. 1975. Interaction of predation and intraspecific aggression in bluegill sunfish, Lepomis macrochirus. Behaviour 55: 268–286.
Reed, R. J. 1971. Underwater observations of the population density and behavior of pumpkinseed, Lepomis gibbosus (Linnaeus) in Cranberry Pond Massachusetts. Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 100: 350–352.
Scott, W. B. & E. J. Crossman. Freshwater fishes of Canada. Fish. Res. Board Can. Bull. 184: 1–966.
Snedecor, G. W. & W. G. Cochran. 1967. Statistical methods. Iowa State Univ. Press, Ames, Iowa. 593 pp.
Spehar, R. L. 1976. Cadmium and zinc toxicity to flagfish, Jordanella floridae. J. Fish. Res. Board Can. 33: 1939–1945.
Spehar, R. L., E. N. Leonard & D. L. Defoe. 1978. Chronic effects of cadmium and zinc mixtures on flagfish (Jordanella floridae). Trans. Am. Fish. Soc. 107: 354–360.
Sprague, J. B. 1976. Current status of sublethal tests of pollutants on aquatic organisms. J. Fish Res. Board Can. 33: 1988–1992.
Stacey, P. & D. Chiszar. 1975. Changes in the darkness of four body features of bluegill sunfish (Lepomis macrochirus, Rafinesque) during aggressive encounters. Behav. Biol. 14: 41–49.
Sullivan, J. F., B. R. Murphy, G. J. Atchison & A. W. McIntosh. 1978. Time dependent cadmium uptake by fathead minnows (Pimephales promelas) during field and laboratory exposure. Hydrobiologia 57: 65–68.
United States Environmental Protection Agency. 1975. Methods for acute toxicity tests with fish, macroinvertebrates, and amphibians. Ecological Research Series EPA-660/3-75009: 1–61.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Henry, M.G., Atchison, G.J. Behavioral changes in bluegill (Lepomis macrochirus) as indicators of sublethal effects of metals. Environ Biol Fish 4, 37–42 (1979). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00005926
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00005926