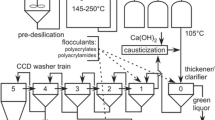
Abstract
In alumina production or alumina refining, bauxite is converted to alumina (aluminium oxide) using the Bayer Process. Throughout the entire history of alumina production there has been a desire to utilize the bauxite residue created in the Bayer process with either by recovering additional products from it or using it. The red mud applications falls into several categories such as rare earths recovery, manufactured construction materials (cement, bricks, tiles, aggregate blocks and wood substitute) and bulk impermeable material for covering landfill. Considerable effort has been expended in finding applications for bauxite residue but a number of key factors affect the feasibility and economics of its adoption. The use of the carbonation can be an advantageous solution for overcoming problems associated with red mud storage and the emissions of several thousand tons of CO2 from aluminium manufacturers each year. The key utilization of bauxite residue or red mud is to prepare “Calcium Sulfoaluminate (CSA) (Green cement)”.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
World Aluminium, (2013) Global life cycle inventory data for the primary aluminium industry 2010 data, published pp.1–53.
International Aluminium Institute, (2012) “Results of the 2012 Anode Effect Survey”. pp.124.
Sustainable development report, (2012) Rio Tinto Alcan Yarwun, pp.1–66.
Kozeky Laszlo., (2012) Utilization of the red mud, pp.1–14.
Y. Pontikes, G.N., (2013) Angelopoulos, Bauxite residue in cement and cementitious applications: Current status and a possible way forward, Resources, Conservation and Recycling, 73, pp.53–63.
G. Stavrinides, (2010) Alternative cements in concrete construction. University College London: Assessment, Prospects & Commercialisation Strategies [MSc.]; 2010
Schneider, M., Romer, M., Tschudin, M., Bolio, H., (2011) Sustainable cement production present and future, Cement and Concrete Research, 41, pp. 642–50.
Shi, C., Jiménez, A.F., Palomo, A., (2011) New cements for the 21st century: the pursuit of an alternative to Portland cement, Cement and Concrete Research, 41, pp.750 – 63.
Juenger, M.C.G., Winnefeld, F., Provis, J.L., Ideker, J.H., (2011) Advances in alternative cementitious binders, Cement and Concrete Research, 41, pp.1232–1243.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 TMS (The Minerals, Metals & Materials Society)
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Ahn, J.W., Thriveni, T., Nam, S.Y. (2015). Sustainable Recycling Technologies for Bauxite Residue (Red Mud) Utilization. In: Jha, A., et al. Energy Technology 2015. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-48220-0_19
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-48220-0_19
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-48602-4
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-48220-0
eBook Packages: Chemistry and Materials ScienceChemistry and Material Science (R0)