Abstract
Double-salary families are very common nowadays in the modern society. Parents may neglect to be there with their children as their children grow up. In 2014, the Child Welfare League Foundation conducted a survey and found that almost 64 % of parents believing the biggest problem was “no time after getting off work”. To avoid the lack of interaction and care in the long run, this study aimed to explore the influence of parenting time on children’s growth performances. There were two parts of this study: (1) literature review. This part discussed the lifestyles of families with children based on a survey regarding time use and the important features of accompanying activities for growth performances of children aged 0–12; and (2) questionnaire analyses, exploring the influence of time parents spent with their children aged 0–12 on these children’s performances. The questionnaires were issued in Oct, 2014. A total of 30 questionnaires were retrieved. The results are summarized below (ordered by after-work time):
-
1.
Spending time with children after getting off work, during 17:30–18:30 could lead to children positive and cheerful emotions as well as good performances in auditory comprehension.
-
2.
Spending time with children when they were reading during 20:0–21:30 helped them to pay attention to meaningful messages and information regarding the leading role of the story they were reading as well as improving their performances in language capability.
-
3.
Spending time with children during 22:30–24:00 helped to improve their social capability and performances in peer relations.
You have full access to this open access chapter, Download conference paper PDF
Similar content being viewed by others
Keywords
1 Introduction
According to Your life better index survey (2013) in Taiwan, about 14.76 % of employed people thought they have too much “work” time and too few “family interaction” time. Parent’s guidance has long term influence on the growth of children. Leibowitze (1974) have proven that parent’s parenting time has very significant correlation to the future development of the children. The main objective of this research is: To investigate the correlation between parenting time and the growth and performance of children aged 0–12.
2 Literature Review
2.1 The Life Form of Parenting Family
Parenting time spent by parents has great influence on the development of children (Apps and Rees 2002). In many researches, it was pointed out that parents of higher educational background, as compared to parents of lower educational background, will spend more time actively on taking care of their children (Guryan et al. 2008). Moreover, parents receiving higher education not only will invest more time in taking care of children, but also will change the distribution status of parenting time based on different development stage of children (Kalil et al. 2012).
2.2 The Relationship Between Parents-Child Interaction and Time
Landreth (2002) has proposed that through a daily companionship of 20–30 min with children for game playing, parents can build very close relationship with child, and such relationship will turn out to be very helpful to the feeling of safety, confidence and creativity of the child. According to a questionnaire survey, parents-child co-reading time is, on the average, about 11–20 min each day, then child’s reading habit developed will be helpful to the enhancement of child’s reading capability (Wu and Chang 2014).
2.3 Relationship Between Companionship and Child’s Growth Performance
This research will study if companionship activities can generate change on important features of children, and the literature surveys are as follows:
-
Sense of hearing: The interactive process is helpful to the child’s listening vocabulary comprehension, more importantly, in the story and game situation, child’s interactive skill and friendship with people can be built (Huang 2012).
-
Sense of sight: When the baby is accompanied for reading, the level of concentration of the baby will be higher, and baby’s eye will then concentrate on meaningful message and message regarding the leading role in the story (Jin 2010).
-
Language development: Companionship activity can provide the baby with more complicated chances of speaking, which in turn will affect both baby’s language development and reading capability (Zeng and Cheng 2011).
-
Personal identity: When the baby has more frequent interaction with parents, safety attachment relationship could be easily formed between parents and the baby, and baby will not feel sorrowful easily, which in turn will promote the generation of safety attachment relationship between the baby and his peers (Li et al. 2007).
-
Learning/identify: A child with good attachment relationship and parents-child interactive relationship tends to have less anxiety towards a stranger, such child tends to have better adaptive capability to the society, and better problem solving capability (Liu 2002).
3 Research Method
The research method adopted in this paper is questionnaire survey and statistical analysis. Investigating the relationship between the content of companionship and the child’s growth performance, therefore, parents with children aged under 12 years old are selected for the filling of survey questionnaire. Quantity of issuance: 30 copies and duration: October, 2014.
3.1 Experimental Variables
-
1.
Independent variable: According to American Time Use Survey, time is divided into half hour. In this research, parents’ off-duty companionship time for children is studied, therefore, the research is focused on the time period from 17:00–17:30 to 24:00, and each half hour is taken as one unit.
-
2.
Dependent variable: Child’ performance, and according to the above mentioned literature, dependent variables are listed and are numbered and labeled in the order of 1–12: Vocabulary comprehension capability, friendship relationship, interpersonal interactive skill, stare at meaningful message, language capability, not being sad, low feeling of dependency, peer relationship, emotion regulation capability, problem solving capability and social capability.
3.2 Research Tool
Subjective feeling scale. Likert’s five-point scale is used as measurement standard, “Very agree, agree, not sure, disagree, very disagree” are used as selection items. Based on his past companionship experience with child and observation of child’s growth performance.
3.3 Statistical Analysis
-
1.
Descriptive statistics: Basic statistics of the data.
-
2.
Descriptive statistics and ANOVA: Whether parenting time would influence child’s performance.
4 Experimental Result
4.1 Descriptive Statistics
After sorting, the average educational background is from university or college, or from university of science and technology. Ages of persons under test fall in the range of 29–49 years old, with average age of 37.9 (years old); age of child is 5.04 (years old), and the youngest age is of 0.8 month, and the eldest age is of 12 years old.
4.2 ANOVA Results
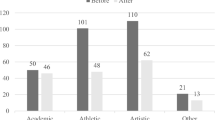
According to the results from the test of homogeneity (P > 0.05) and ANOVA, the significant items (P < 0.05) are listed in Table 2.
5 Conclusions and Discussions
5.1 Late Marriage Phenomenon
Presently, when the ages of persons under test are investigated regardless of gender, as shown in Table 1, the average age falls on 37.9, which shows that late marriage phenomenon dominates in Taiwan, meanwhile, the average educational background is above university, therefore, it is concluded that time for receiving education affects the age of marriage.
5.2 Parenting Time Will Affect Child’s Performance
The result of Table 2 shows the companionship time with a child for reading, playing game and dining is on the average of about 30 min, which turns out to be helpful to a child’s development.
-
1.
In the time period of 17:30–18:30, it usually brings positive and happy mood to a child, therefore, in the sense of hearing aspect, the child tends to have better vocabulary comprehension capability.
-
2.
In the time period of 20:30–21:30, the effectiveness of interaction with a child is most significant, at this moment, the child will notice meaningful message and the message from the leading role of a story, and the child tends to have better performance in logic of language; meanwhile, independent thinking capability of the child is trained too so that the child will not have too strong dependence on family members.
-
3.
In later time period of 22:30–24:00, child and parents usually have difficulty to concentrate, therefore, it is recommended that the parents only chat with child or just stay quietly with the child, with this period of companionship with child, child can get along with others easily, therefore, and the child tends to have good relationship with his friends.
References
Apps, P., Rees, R.: Household production, full consumption and the costs of children. Labour Econ. 8, 621–648 (2002)
Guryan, J., Hurst, E., Kearney, M.: Parental education and parental time with children. J. Econ. Perspect. 22(3), 23–46 (2008)
Huang, C.Y.:. Action research on using picture books to promote interaction between children with hearing impairment. National Taipei University of Education, Taipei (2012, unpublished)
Jin, H.H.: Research eyes movement for effect of companionship on 2-3 years-old child’s reading. Early Childhood Educ. 465–466, 27–30 (2010)
Kalil, A., Ryan, R., Corey, M.: Diverging destinies: maternal education and the developmental gradient in time with children. Demography 49, 1361–1383 (2012)
Landreth, G.L.: Play Therapy: the Art of the Relationship, 2nd edn. Brunner-Routledge, New York (2002)
Leibowitze, A.: Home investments in children. J. Polit. Econ. 82(2), 111–131 (1974)
Li, M.Z, Dong, X.B., et al.: The self-other boundary of independent vs. interdependent self reflected in parent-child sleep arrangement. Ministry of Science and Technology, Research Project: NSC 94-2413-004-020 (2007, unpublished)
Liu, S.C.: Investigating of a secure attachment relationship and child social development. Educ. Mon. 418, 42–45 (2002)
Zeng, S.S., Cheng, S.F.: A case study of the toy library in Chenxi Tribe. J. Taipei Municipal Univ. Educ. 2, 35–36 (2011)
Wu, T.L., Chang, R.H.: Children’s demand for environment and furniture. In: Parent-Child Reading, Conference of Ergonomics Society of Taiwan. Taichung. 28 March 2014
Your better life Index. Directorate-General of Budget, Accounting and Statistics (30 Aug 2013). Accessed 6 June 2014. http://www.dgbas.gov.tw/ct.asp?xItem=34777&ctNode=5624
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2015 Springer International Publishing Switzerland
About this paper
Cite this paper
Chang, JH., Yeh, TL. (2015). The Influence of Parenting Time on Children’s Growth and Development. In: Stephanidis, C. (eds) HCI International 2015 - Posters’ Extended Abstracts. HCI 2015. Communications in Computer and Information Science, vol 528. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-21380-4_61
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-21380-4_61
Publisher Name: Springer, Cham
Print ISBN: 978-3-319-21379-8
Online ISBN: 978-3-319-21380-4
eBook Packages: Computer ScienceComputer Science (R0)