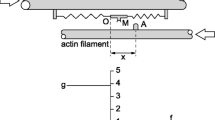
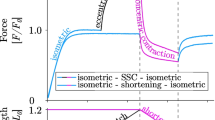
This study talks about gastrocnemius muscle identification. During biological activation, every contractile structure is unsynchronized. Likewise, contraction and relaxation phases depend on all contractile elements, the activation type and the state of health. Moreover, gastrocnemius muscle is composed of three fibre types: fast (IIB), resistant (IIA), and slow (I) fibres.
Access this chapter
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Preview
Unable to display preview. Download preview PDF.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arsos GA, Dimitriu PP (2004) A fractal characterization of the type II fibre distribution in the extensor digitorum longus and soleus muscles of the adult rat, Muscle and Nerve, 18:961-968.
Cross SS (1997) Fractals in pathology, J. Pathol. 182:1-8.
Delvolvé I, Bem T, Cabelguen J-M (1997) Epaxial and limb muscle activy during swimming and terrestrial stepping in the adult newt, Pleurodeles waltl, J. Neurophysiol., 78:638-650.
Delvolvé I, Branchereau P, Dubuc R, Cabelguen J-M (1999) Fictive patterns of rhythmic motor activity induced by NMDA in an in vitro brainstem-spinal cord preparation from an adult urodele amphibian, J. Neurophysiol., 82:1074-1078.
Goldberger AL, Amaral LAN, Hausdorff JM, Ivanov PCh, Peng C-K, Stanley HE (February 2002) Fractal dynamics in physiology: alterations with disease and aging, PNAS, 99(Suppl. 1):2466-2472.
Grünwald AK (1867) Ueber begrenzte Derivationen und deren Anwendung, Z. Angew. Math. Phys., 12:441-480.
Liouville J (1832) Mémoire sur le calcul des différentielles à indices quelconques, Ecole Polytechnique, 13(21):71-162.
Lowen SB, Cash SS, Poo M-M, Teich MC (August 1997) Quantal neurotransmitter secretion rate exhibits fractal behavior, J. Neurosci., 17 (15):5666-5677.
Malti R, Aoun M, Battaglia J-L, Oustaloup A, Madami K (August 1989) Fractional multimodels - Application to heat transfert modelling, 13th IFAC Symposium on System Identification, Rotterdam, The Netherlands.
Miller KS, Ross B (1993) An Introduction to the Fractional Calculus and Fractional Differential Equation. Wiley, New York.
Oustaloup A (1995) La Derivation Non Entière, Hermes, Paris.
Ravier P, Buttelli O, Couratier P (2005) An EMG fractal indicator having different sensitivities to changes in force and muscle fatigue during voluntary static muscle contractions, J. Electromyogr. Kinesiol., 15 (2):210-221.
Rossignol S (1996) Neural control of stereotypic limb movements, International Handbook of Physiology (Rowell LB, Sheperd JT ed.). American Physiological Society, pp. 173-216.
Samko AG, Kilbas AA, Marichev OI (1987) Fractional Integrals and Derivatives. Gordon and Breach Science, Minsk.
Shepherd GM (1994) Neurobiology. Oxford, New york.
Sommacal L, Melchior P, Cabelguen J-M, Oustaloup A, et Ijspeert A (2005) Fractional model of a gastrocnemius muscle for tetanus pattern, Fifth ASME International Conference on Multibody Systems, Nonlinear Dynamics and Control, Long Beach, California, USA.
Subrahmanyam MB (August 1989) An extension of the simplex method to constrained nonlinear optimization, Int. J. Optim. Theory Appl., 62 (2):311-319.
Woods DJ (May 1985) An interactive approach for solving multi-objective optimization problems, Technical Report 85-5, Rice University, Houston.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Editor information
Editors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
Copyright information
© 2007 Springer
About this chapter
Cite this chapter
Sommacal, L., Melchior, P., Cabelguen, JM., Oustaloup, A., Ijspeert, A. (2007). Fractional Multimodels of the Gastrocnemius Muscle for Tetanus Pattern. In: Sabatier, J., Agrawal, O.P., Machado, J.A.T. (eds) Advances in Fractional Calculus. Springer, Dordrecht. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-6042-7_19
Download citation
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-6042-7_19
Publisher Name: Springer, Dordrecht
Print ISBN: 978-1-4020-6041-0
Online ISBN: 978-1-4020-6042-7
eBook Packages: EngineeringEngineering (R0)