Abstract
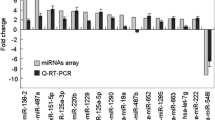
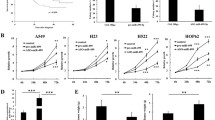
Our previous studies have showed that metastasis-associated protein 3 (MTA 3) is overexpressed in non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) tissue, and increased MTA3 mRNA levels is a risk factor of lymph node metastasis. Using bioinformatics analyses, we found that MTA3 was a potential target of miR-495. However, the pathophysiological role of miR-495 and its relevance to the growth and development of NSCLC have yet to be investigated. The purpose of this study was to elucidate the molecular mechanisms by which miR-495 acts as a tumor suppressor in NSCLC. qRT-PCR data showed significant downregulation of miR-495 in 56 NSCLC tissue samples and 5 lung cancer cell lines, compared with their adjacent normal tissue; furthermore, western blotting analysis revealed MTA3 protein was overexpressed in the tumor samples compared with the matched adjacent normal tissue. MiR-495 was shown to not only inhibit the proliferation of lung cancer cells (A549 and Calu-3) but also to inhibit cell migration in vitro. Using western blotting and luciferase assays, MTA3 was identified as a target of miR-495. These findings suggest the importance of miR-495 targeting of MTA3 in the regulation of lung cancer growth and migration.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Jemal A, Siegel R, Xu J, Ward E. Cancer statistics 2010. CA Cancer J Clin. 2010;60(5):277–300.
Herbst RS, Heymach JV, Lippman SM. Lung cancer. N Engl J Med. 2008;359(13):1367–80.
Brundage MD, Davies D, Mackillop WJ. Prognostic factors in non-small cell lung cancer: a decade of progress. Chest. 2002;122(3):1037–57.
Humphrey GW, Wang Y, Russanova VR, Hirai T, Qin J, Nakatani Y, et al. Stable histone deacetylase complexes distinguished by the presence of SANT domain proteins CoREST/kiaa0071 and Mta-L1. J Biol Chem. 2001;276(9):6817–24.
Fujita N, Jaye DL, Kajita M, Geigerman C, Moreno CS, Wade PA. MTA3, a Mi-2/NuRD complex subunit, regulates an invasive growth pathway in breast cancer. Cell. 2003;113(2):207–19.
Toh Y, Nicolson GL. The role of the MTA family and their encoded proteins in human cancers: molecular functions and clinical implications. Clin Exp Metastasis. 2009;26(3):215–27.
Bowen NJ, Fujita N, Kajita M, Wade PA. Mi-2/NuRD: multiple complexes for many purposes. Biochim Biophys Acta. 2004;1677(1–3):52–7.
Li H, Sun L, Xu Y, Li Z, Luo W, Tang Z, et al. Overexpression of MTA3 correlates with tumor progression in non-small cell lung cancer. Plos One. 2013;8(6):1–8.
Brüning A, Makovitzky J, Gingelmaier A, Friese K, Mylonas I. The metastasis-associated genes MTA1 and MTA3 are abundantly expressed in human placenta and chorionic carcinoma cells. Histochem Cell Biol. 2009;132(1):33–8.
Bruning A, Juckstock J, Blankenstein T, Makovitzky J, Kunze S, Mylonas I. The metastasis-associated gene MTA3 is downregulated in advanced endometrioid adenocarcinomas. Histol Histopathol. 2010;25(11):1447–56.
Zhang H, Stephens LC, Kumar R. Metastasis tumor antigen family proteins during breast cancer progression and metastasis in a reliable mouse model for human breast cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2006;12(5):1479–86.
Dannenmann C, Shabani N, Friese K, Jeschke U, Mylonas I, Bruning A. The metastasis-associated gene MTA1 is upregulated in advanced ovarian cancer, represses ERbeta, and enhances expression of oncogenic cytokine GRO. Cancer Biol Ther. 2008;7(9):1460–7.
Hofer MD, Kuefer R, Varambally S, Li H, Ma J, Shapiro GI, et al. The role of metastasis-associated protein 1 in prostate cancer progression. Cancer Res. 2004;64(3):825–9.
Iguchi H, Imura G, Toh Y, Ogata Y. Expression of MTA1, a metastasis-associated gene with histone deacetylase activity in pancreatic cancer. Int J Oncol. 2000;16(6):1211–4.
Jang KS, Paik SS, Chung H, Oh YH, Kong G. MTA1 overexpression correlates significantly with tumor grade and angiogenesis in human breast cancers. Cancer Sci. 2006;97(5):374–9.
Xia Y, Chen Q, Zhong Z, Caihua X, Chen W, Liu B, et al. Down-regulation of MiR-30c promotes the invasion of non-small cell lung cancer by targeting MTA1. CELL Physiol Biochem. 2013;32(2):476–85.
Zheng S, Du Y, Chu H, Chen X, Li P, Wang Y, et al. Analysis of MAT3 gene expression in NSCLC. Diagn Pathol. 2013;8:166
Hwang HW, Mendell JT. MicroRNAs in cell proliferation, cell death and tumorigenesis. Br J Cancer. 2006;94(6):776–80.
Wan HY, Guo LM, Liu T, Liu M, Li X, Tang H. Regulation of the transcription factor NF-kappaB1 by microRNA-9 in human gastric adenocarcinoma. Mol Cancer. 2010;9(16):1–10.
Zamore PD, Haley B. Ribo-gnome: the big world of small RNAs. Science. 2005;309(5740):1519–24.
Mattick JS, Makunin IV. Non-coding RNA. Hum Mol Genet.2006;15(Spec No 1):R17–29
Norbury C, Nurse P. Animal cell cycles and their control. Annu Rev Biochem. 1992;61:441–70.
Manchado E, Guillamot M, Malumbres M. Killing cells by targeting mitosis. Cell Death Differ. 2012;19(3):369–77.
Ouyang W, Ma Q, Li J, Zhang D, Liu ZG, Rustgi AK, et al. Cyclin D1 induction through IkappaB kinase beta/nuclear factor-kappaB pathway is responsible for arsenite-induced increased cell cycle G1-S phase transition in human keratinocytes. Cancer Res. 2005;65(20):9287–93.
Ouyang W, Li J, Ma Q, Huang C. Essential roles of PI-3K/Akt/IKKbeta/ NFkappaB pathway in cyclinD1 induction by arsenite in JB6 Cl41 cells. Carcinogenesis. 2006;27(4):864–73.
Zhang H, Singh RR, Talukder AH, Kumar R. Metastatic tumor antigen 3 is a direct corepressor of the Wnt4 pathway. Genes Dev. 2006;20(21):2943–8.
Mishra SK, Talukder AH, Gururaj AE, Yang Z, Singh RR, Mahoney MG, et al. Upstream determinants of estrogen receptor-alpha regulation of metastatic tumor antigen 3 pathway. J Biol Chem. 2004;279(31):32709–15.
Fujita N, Kajita M, Taysavang P, Wade PA. Hormonal regulation of metastasis-associated protein 3 transcription in breast cancer cells. Mol Endocrinol. 2004;18(12):2937–49.
Chen Y, Miyazaki J, Nishizawa H, Kurahashi H, Leach R, Wang K. MTA3 regulates CGB5 and Snail genes in trophoblast. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 2013;433(4):379–84.
Bagheri-Yarmand R, Talukder AH, Wang RA, Vadlamudi RK, Kumar R. Metastasis-associated protein 1 deregulation causes inappropriate mammary gland development and tumorigenesis. Development. 2004;131(14):3469–79.
Manavathi B, Singh K, Kumar R. MTA family of coregulators in nuclear receptor biology and pathology. Nucl Recept Signal. 2007;5:e010.
Wang TC, Cardiff RD, Zukerberg L, Lees E, Arnold A, Schmidt EV. Mammary hyperplasia and carcinoma in MMTV-cyclin D1 transgenic mice. Nature. 1994;369(6482):669–71.
Resnitzky D, Reed SI. Different roles for cyclins D1 and E in regulation of the G1-to-S transition. Mol Cell Biol. 1995;15(7):3463–9.
Spruck CH, Won KA, Reed SI. Deregulated cyclin E induces chromosome instability. Nature. 1999;401(6750):297–300.
Hubalek MM, Widschwendter A, Erdel M, Gschwendtner A, Fiegl HM, Muller HM, et al. Cyclin E dysregulation and chromosomal instability in endometrial cancer. Oncogene. 2004;23(23):4187–92.
Noren Hooten N, Abdelmohsen K, Gorospe M, Ejiogu N, Zonderman AB, Evans MK. microRNA expression patterns reveal differential expression of target genes with age. PloS One. 2010;5(5):e10724
Takahashi Y, Forrest AR, Maeno E, Hashimoto T, Daub CO, Yasuda J. MiR-107 and MiR-185 can induce cell cycle arrest in human non small cell lung cancer cell lines. PloS One. 2009;4(8):e6677.
Qin W, Ren Q, Liu T, Huang Y, Wang J. MicroRNA-155 is a novel suppressor of ovarian cancer-initiating cells that targets CLDN1. FEBS Lett. 2013;587(9):1434–9.
Miao LJ, Huang SF, Sun ZT, Gao ZY, Zhang RX, Liu Y, et al. Mir-449 targets c-myc and inhibits NSCLC cell progression. FEBS Lett. 2013;587(9):1359–65.
Li J, Wang Y, Luo J, Fu Z, Ying J, Yu Y, et al. Mir-134 inhibits epithelial to mesenchymal transition by targeting FOXM1 in non-small cell lung cancer cells. FEBS Lett. 2012;586(20):3761–5.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by Science and Technology Commission of Henan Province of China (no. 122102310552).
Conflicts of interest
None
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Chu, H., Chen, X., Wang, H. et al. MiR-495 regulates proliferation and migration in NSCLC by targeting MTA3. Tumor Biol. 35, 3487–3494 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-013-1460-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13277-013-1460-1