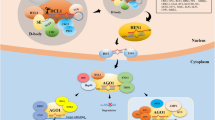
Abstract
MicroRNAs are small, ubiquitous, non-protein-coding essential endogenous task masters of RNA interference (RNAi). These are more or less 22 nucleotide-long RNAs that repress gene expression post transcriptionally by binding to the 3′ untranslated region of target mRNAs. MicroRNAs are self-regulating transcription units that balancing the physiological processes by maintaining the interaction between various factors. These conserved evolutionary units target the specific mRNAs to mediate post-transcriptional regulation by mean of translational repression changes. The paper highlights the involvement of miRNA biogenesis, mechanism and developmental aspects (such as regulating the flower development, root-shoot development) nutrient uptake, abiotic and biotic stress tolerance. With the introduction of molecular tools, the function of miRNAs will definitely have regarded as multidisciplinary role. Thus, an attempt is made to understand the role of miRNAs in coordinating the regulatory pathways of the plant life cycle.



Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- MIRNA:
-
Microrna
- RISC:
-
RNA induced silencing complex
- DCL1:
-
Dicer-like 1
- HEN1:
-
Hua enhancer 1
- SDN:
-
Small RNA degrading nuclease
- AGO:
-
Argonaute
- AP2:
-
Apetala 2
- SPL3:
-
Squamosa promoter binding protein-like 3
- CSD2:
-
Copper/zinc superoxide dismutase 2
- XRN4:
-
Exoribonuclease 4
- AMP1:
-
Altered meristemprogram1
- SGS3:
-
Suppressor of gene silencing 3
- RDR6:
-
RNA dependent RNA polymerase 6
- STM:
-
shoot meristemless
- WUS:
-
Wushel
- CLV:
-
Clavata
- LCR:
-
Leaf curling respoonsiveness
- HD ZIP III:
-
Class III homeodomain leucine zipper
- CUC:
-
Cup shaped cotyledons
- REV:
-
Revoluta
- PHB:
-
Phabolosa
- PHV:
-
Phavoluta
- RDL1:
-
Rolled leaf 1
- ARF3:
-
Auxin response factor 3
- AS1:
-
Asymmetrica leaves 1
- TCP:
-
Teosente branched 1 cycloidea and PCF
- GRFS:
-
Growth regulating factors
- AGL15:
-
Agamous-Like 15
- AG:
-
Agamous
- TOE 3:
-
Target of eat 3
- IDS1:
-
Indeterminate spikelet 1
- FIS:
-
Fistulata
- BL:
-
Blind
- CBF:
-
CCAAT box binding factor
- TIR:
-
Transport inhiobitor response 1
- AFB:
-
Auxin Signaling F-Box
- AUX/IAA:
-
Auxin/indole acetic acid
- SE:
-
Serrate
- SOD:
-
Superoxide dismutase
- COX:
-
Cytochrome c oxidase
- PC:
-
Plastocyanin
- CBFS:
-
C repeat binding factors
- DRE:
-
Dehydration responsive element
- PHO2:
-
Phosphate 2 gene
References
Abdel-Ghany SE, Pilon M (2008) MicroRNA-mediated systemic down-regulation of copper protein expression in response to low copper availability in Arabidopsis. J Biol Chem 283:15932–15945. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.M801406200
Achard P, Herr A, Baulcombe DC, Harberd NP (2004) Modulation of floral development by a gibberellin-regulated microRNA. Development 131:3357–3365. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.01206
Allen RS et al (2007) Genetic analysis reveals functional redundancy and the major target genes of the Arabidopsis miR159 family. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:16371–16376. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0707653104
Andrés F, Coupland G (2012) The genetic basis of flower-ing responses to seasonal cues. Nat Rev Genet 13:627–639. https://doi.org/10.1038/nrg3291
Aukerman MJ, Sakai H (2003) Regulation of flowering time and floral organ identity by a microRNA and its APETALA2- like target genes. Plant Cell 15:2730–2741. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.016238
Axtell MJ, Jan C, Rajagopalan R, Bartel DP (2006) A two-hit trigger for siRNA biogenesis in plants. Cell 127:565–577. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2006.09.032
Axtell MJ, Westholm JO, Lai EC (2011) Vive la diffe’rence: biogenesis and evolution of microRNAs in plants and animals. Genome Biol 12:221. https://doi.org/10.1186/gb-2011-12-4-221
Bari R, Datt Pant B, Stitt M, Scheible WR (2006) PHO2, microRNA399, and PHR1 define a phosphate-signaling pathway in plants. Plant Physiol 141:988–999. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.106.079707
Bazzini AA, Almasia NI, Manacorda CA, Mongelli VC, Conti G, Maroniche GA, Rodriguez MC, Distéfano AJ, Hopp HE, del Vas M, Asurmendi S (2009) Virus infection elevates transcriptional activity of miR164a promoter in plants. BMC Plant Biol 9:152. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2229-9-152
Bellini C, Pacurar DI, Perrone I (2014) Adventitious roots and lateral roots: similarities and differences. Annu Rev Plant Biol 65:639–666. https://doi.org/10.1146/annurev-arplant-050213-035645
Berger Y, Harpaz-Saad S, Brand A, Melnik H, Sirding N, Alvarez JP et al (2009) The NAC-domain transcription factor GOBLET specifies leaflet boundaries in compound tomato leaves. Development 136:823–832. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.031625
Bian H, Xie Y, Guo F, Han N, Ma S, Zeng Z, Wang J, Yang Y, Zhu M (2012) Distinctive expression patterns and roles of the miRNA393/TIR1 homolog module in regulating flag leaf inclination and primary and crown root growth in rice (Oryza sativa). New Phytol 196:149–161. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2012.04248.x
Blein T, Pulido A, Vialette-Guiraud A et al (2008) A conserved molecular framework for compound leaf development. Science 322:1835–1839. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1166168
Brodersen P, Sakvarelidze-Achard L, Bruun-Rasmussen M, Dunoyer P et al (2008) Widespread translational inhibition by plant miRNAs and siRNAs. Science 320:1185–1190. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1159151
Budak H, Akpinar BA (2015) Plant miRNAs: biogenesis, organization and origins. Funct Integr Genom 15:523–531. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-015-0451-2
Burkhead JL, Reynolds KA, Abdel-Ghany SE, Cohu CM, Pilon M (2009) Copper homeostasis. New Phytol 182:799- 816. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1469-8137.2009.02846.x
Çakır Ö, Arıkan B, Karpuz B, Turgut-Kara N (2021) Expression analysis of miRNAs and their targets related to salt stress in Solanum_lycopersicum H-2274. Biotechnol Biotechnol Equip 35:283–290. https://doi.org/10.1080/13102818.2020.1870871
Cartolano M, Castillo R, Efremova N, Kuckenberg M, Zethof J, Gerats T, Schwarz-Sommer Z, Vandenbussche M (2007) A conserved microRNA module exerts homeotic control over Petunia hybrida and Antirrhinum majus floral organ identity. Nat Genet 39:901–905. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng2056
Chauhan S, Yogindran S, Rajam MV (2017) Role of miRNAs in biotic stress reactions in plants. Indian J Plant Physiol 22:514–529. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40502-017-0347-3
Chen X (2004) A microRNA as a translational repressor of APETALA2 in Arabidopsis flower development. Science 303:2022–2025. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1088060
Chen HM, Chen LT, Patel K, Li YH, Baulcombe DC, Wu SH (2010) 22- nucleotide RNAs trigger secondary siRNA biogenesis in plants. Proc Natl Aca SciUSA 107:15269–15274. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1001738107
Chen H, Li Z, Xiong L (2012) A plant microRNA regulates the adaptation of roots to drought stress. FEBS Lett 586:1742–1747. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2012.05.013
Chen H, Zhang L, Yu K, Wang A (2015) Pathogenesis of soybean mosaic virus in soybean carrying Rsv1 gene is associated with miRNA and siRNA pathways, and breakdown of AGO1 homeostasis. Virology 476:395–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virol.2014.12.034
Chitwood DH, Nogueira FT, Howell MD, Montgomery TA, Carrington JC, Timmermans MC (2009) Pattern formation via small RNA mobility. Genes Dev 23:549–554. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1770009
Chuck G, Meeley R, Irish E, Sakai H, Hake S (2007) The maize tasselseed4 microRNA con-trols sex determination and meristem cell fate by targeting Tasselseed6/indeterminate spikelet1. Nat Genet 39:1517–1521. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng.2007.20
Chuck GS, Tobias C, Sun L, Kraemer F, Li C, Dibble D, Arora R, Bragg JN, Vogel JP, Singh S, Simmons BA, Pauly M, Hake S (2011) Overexpression of the maize corn-grass1 microRNA prevents flowering, improves digestibility, and increases starch content of switchgrass. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 108:17550–17555. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1113971108
Cuperus JT, Carbonell A, Fahlgren N, Garcia-Ruiz H et al (2010) Unique functionality of 22-nt miRNAs in triggering RDR6-dependent siRNA biogenesis from target transcripts in Arabidopsis. Nat Struc Mol Biol 17:997–1003. https://doi.org/10.1038/nsmb.1866
Curaba J, Singh MB, Bhalla PL (2014) MiRNAs in the crosstalk between phytohormone signalling pathways. J Exp Bot 65:1425–1438. https://doi.org/10.1093/jxb/eru002
Dharmasiri N, Dharmasiri S, Estelle M (2005) The F-box protein TIR1 is an auxin receptor. Nature 435:441–445. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature03543
Du P, Wu J, Zhang J, Zhao S, Zheng H, Gao G, Wei L, Li Y (2011) Viral infection induces expression of novel phased microRNAs from conserved cellular microRNA precursors. PLoS Pathog 7:e1002176. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.ppat.1002176
Fahlgren N, Montgomery TA, Howell MD, Allen E, Dvorak SK, Alexander AL, Carrington JC (2006) Regulation of AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR3 by TAS3 ta-siRNA affects developmental timing and patterning in Arabidopsis. Curr Biol 16:939–944. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2006.03.065
Fei Q, Xia R, Meyers BC (2013) Phased, secondary, small interfering RNAs in posttranscriptional regulatory networks. Plant Cell 25:2400–2415. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.113.114652
Fei Q, Yu Y, Liu L, Zhang Y et al (2018) Biogenesis of a 22-nt microRNA in Phaseoleae species by precursor-programmed uridylation. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 115:8037–8042. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1807403115
Ferdous J, Hussain SS, Shi BJ (2015) Role of microRNAs in plant drought tolerance. Plant Biotechnol J 13:293–305. https://doi.org/10.1111/pbi.12318
Gaillochet C, Lohmann JU (2015) The never-ending story: from pluripotency to plant developmental plasticity. Development 142:2237–2249. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.117614
Gandikota M, Birkenbihl RP, Hohmann S, Cardon GH, Saedler H, Huijser P (2007) The miRNA156/157 recognition element in the 30 UTRof the Arabidopsis SBP box gene SPL3 prevents early flowering by translational inhibition in seedlings. Plant J 49:683–693. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2006.02983.x
Gasciolli V, Mallory AC, Bartel DP, Vaucheret H (2005) Partially redundant functions of Arabidopsis DICER-like enzymes and a role for DCL4 in producing trans-acting siRNAs. Curr Biol 15:1494–1500. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2005.07.024
Gautam V, Singh A, Verma S, Kumar A, Kumar P, Singh S, Mishra V, Sarkar AK (2017) Role of miRNAs in root development of model plant Arabidopsis thaliana. Indian J Plant Physiol 22:382–392. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40502-017-0334-8
German MA, Pillay M, Jeong DH, Hetawal A, Luo S, Janardhanan P et al (2008) Global identification of microRNA–target RNA pairs by parallel analysis of RNA ends. Nature Biotech 26:941–946. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1417
Gevaert A, Witvrouwen I, Vrints C et al (2018) MicroRNA profiling in plasma samples using qPCR arrays: recommendations for correct analysis and interpretation. PLoS One 13:e0193173. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0193173
Giehl RF, Meda AR, von Wiren N (2009) Moving up, down, and everywhere: signaling of micronutrients in plants. Curr Opin Plant Biol 12:320–327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbi.2009.04.006
Gifford ML, Dean A, Gutierrez RA, Coruzzi GM, Birnbaum KD (2008) Cell-specific nitrogen responses mediate developmental plasticity. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 105:803–808. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0709559105
Gray WM, Kepinski S, Rouse D, Leyser O, Estelle M (2001) Auxin regulates SCFTIR1- dependent degradation of AUX/IAA proteins. Nature 414:271–276. https://doi.org/10.1038/35104500
Grigg SP, Canales C, Hay A, Tsiantis M (2005) SERRATE coordinates shoot meristem function and leaf axial patterning in Arabidopsis. Nature 437:1022–1026. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature04052
Grigg SP, Galinha C, Kornet N, Canales C, Scheres B, Tsiantis M (2009) Repression of apical homeobox genes is required for embryonic root development in Arabidopsis. Curr Biol 19:1485–1490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2009.06.070
Großhans H, Filipowicz W (2008) The expanding world of small RNAs. Nature 451:414–416. https://doi.org/10.1038/451414a
Guan Q, Lu X, Zeng H, Zhang Y, Zhu J (2013) Heat stress induction of miR398 triggers a regulatory loop that is critical for thermotolerance in Arabidopsis. The Plant J 74:840–851. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12169
Guddeti S, Zhang de C, Li AL, Leseberg CH, Kang H, et al. 2005. Molecular evolution of the rice miR395 gene family. Cell Res 15:631–638. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.cr.7290333
Gupta M, Das Nath U (2015) Divergence in patterns of leaf growth polarity is associated with the expression divergence of miR396. Plant Cell 27:2785–2799. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.15.00196
Gutierrez L, Bussell JD, Pacurar DI, Schwambach J, Pacurar M, Bellini C (2009) Phenotypic plasticity of adventitious rooting in Arabidopsis is controlled by complex regulation of auxin response factor transcripts and microRNA abundance. Plant Cell 21:3119–3132. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.108.064758
Gutierrez L, Mongelard G, Flokova K, Pacurar DI, Novák O, Staswick P, Kowalczyk M, Pacurar M, Demailly H, Geiss G, Bellini C (2012) Auxin controls Arabidopsis adventitious root initiation by regulating jasmonic acid homeostasis. Plant Cell 24:2515–2527. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.112.099119
Hibara K, Karim MR, Takada S, Taoka K, Furutani M, Aida M, Tasaka M (2006) Arabidopsis cupshaped cotyledon3 regulates postembryonic shoot meristem and organ boundary formation. Plant Cell 18:2946–2957. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.106.045716
Hong R, Hamaguchi L, Busch MA, Weigel D (2003) Regulatory elements of the floral home-otic gene AGAMOUS identified by phylogenetic footprinting and shadowing. Plant Cell 15:1296–1309. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.009548
Horiguchi G, Kim GT, Tsukaya H (2005) The transcription factor AtGRF5 and the transcription coactivator AN3 regulate cell proliferation in leaf primordia of Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 43:68–78. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2005.02429.x
Hou G, Du C, Gao H, Liu S, Sun W, Lu H, Kang J, Xie Y, Ma D, Wang C (2020) Identification of microRNAs in developing wheat grain that are potentially involved in regulating grain characteristics and the response to nitrogen levels. BMC Plant Biol 20:1–21. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-020-2296-7
Howell MD, Fahlgren N, Chapman EJ, Cumbie JS, Sullivan CM, Givan SA, Kasschau KD, Carrington JC (2007) Genome-wide analysis of the RNA-DEPENDENT RNA POLYMERASE6/DICER-LIKE4 pathway in Arabidopsis reveals dependency on miRNA- and tasiRNA-directed targeting. Plant Cell 19:926–942. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.107.050062
Hsieh LC, Lin SI, Shih AC, Chen JW, Lin WY, Tseng CY, Li WH, Chiou TJ (2009) Uncovering small RNA-mediated responses to phosphate deficiency in Arabidopsis by deep sequencing. Plant Physiol 151:2120–2132. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.109.147280
Huang S, Zhou J, Gao L, Tang Y (2020) Plant miR397 and its functions. Funct Plant Biol. https://doi.org/10.1071/FP20342
Ibrahim F, Rohr J, Jeong WJ, Hesson J, Cerutti H (2006) Untemplated oligoadenylation promotes degradation of RISC-cleaved transcripts. Science 314:1893. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1135268
Irish VF, Sussex IM (1990) Function of the APETALA-1 gene during Arabidopsis floral development. P Cell 2:741–753. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.2.8.741
Itoh J, Hibara K, Sato Y, Nagato Y (2008) Developmental role and auxin responsiveness of class III homeodomain leucine zipper gene family members in rice. Plant Physiol 147:1960–1975. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.108.118679
Iwakawa H, Iwasaki M, Kojima S, Ueno Y, Soma T, Tanaka H, Semiarti E, Machida Y, Machida C et al (2007) Expression of the ASYMMETRIC LEAVES2 gene in the adaxial domain of Arabidopsis leaves represses cell proliferation in this domain and is critical for the development of properly expanded leaves. Plant J 51:173–184. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03132.x
Jack T (2001) Relearning our ABCs: new twists on an old model. Trends Plant Sci 6:310–316. https://doi.org/10.1016/S1360-1385(01)01987-2
Jerome Jeyakumar JM, Ali A, Wang WM, Thiruvengadam M (2020) Characterizing the role of the miR156-SPL network in plant development and stress response. Plants 9:1206. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9091206
Ji L, Liu X, Yan J, Wang W, Yumul RE, Kim YJ et al (2011) ARGONAUTE10 and ARGONAUTE1 regulate the termination of floral stem cells through two microRNAs in Arabidopsis. PLoS Genet 7:e1001358. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pgen.1001358
Jin H (2008) Endogenous small RNAs and antibacterial immunity in plants. FEBS Lett 582:2679–2684. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.febslet.2008.06.053
Jin D, Wang Y, Zhao Y, Chen M (2013) MicroRNAs and their cross-talks in plant development. J Genet Genomics 40:161–170. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jgg.2013.02.003
Jones-Rhoades MW, Bartel DP (2004) Computational identification of plant micro- RNAs and their targets, including a stress-induced miRNA. Mol Cell 14:787–799. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2004.05.027
Juarez MT, Kui JS, Thomas J, Heller BA, Timmermans MC (2004) MicroRNA-mediated repression of rolled leaf 1 specifies maize leaf polarity. Nature 428:84–88. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02363
Jung JH, Seo YH, Seo PJ, Reyes JL, Yun J, Chua NH, Park CM (2007) The GIGANTEA-regulated microRNA172 mediates photoperiodic flowering independent of CONSTANS in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 19:2736–2748. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.107.054528
Jung JH, Lee S, Yun J, Lee M, Park CM (2014) The miR172 target TOE3 represses AGAMOUS expression during Arabidopsis floral patterning. Plant Sci 215:29–38. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.plantsci.2013.10.010
Kantar M, Unver T, Budak H (2010) Regulation of barley miRNAs upon dehydration stress correlated with target gene expression. Funct Integr Genomics 10:493–507. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10142-010-0181-4
Kepinski S, Leyser O (2005) The Arabidopsis F-box protein TIR1 is an auxin receptor. Nature 435:446–445. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature03542
Kidner CA and Martienssen RA (2004) Spatially restricted microRNA directs leaf polarity through ARGONAUTE1. Nature 428: 81–84. https://doi.org https://doi.org/10.1038/nature02366
Kim JH, Choi D, Kende H (2003) The AtGRF family of putative transcription factors is involved in leaf and cotyledon growth in Arabidopsis. Plant J 36:94–104. https://doi.org/10.1046/j.1365313X.2003.01862.x
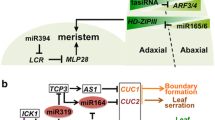
Knauer S, Holt AL, Rubio-Somoza I, Tucker EJ et al (2013) A protodermal miR394 signal defines a region of stem cell competence in the Arabidopsis shoot meri-stem. Dev Cell 24:125–132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2012.12.009
Koyama T, Mitsuda N, Seki M, Shinozaki K et al (2010) TCP transcription factors regulate the activities of ASYMMETRIC LEAVES1 and miR164, as well as the auxin response, during differentiation of leaves in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 22:3574–3588. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.110.075598
Laufs P, Peaucelle A, Morin H, Traas J (2004) MicroRNA regulation of the CUC genes is required for boundary size control in Arabidopsis meristems. Development 131:4311–4322. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.01320
Li L, Lodish HF (2004) Bartel DP. MicroRNAs modulate hematopoietic lineage differentiation Science 303:83–86. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1091903
Li WX, Oono Y, Zhu J, He XJ (2008) The Arabidopsis NFYA5 transcription factor is regulated transcriptionally and post transcriptionally to promote drought resistance. Plant Cell 20:2238–2251. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.108.059444
Li X, Wang X, Zhang S, Liu D, Duan Y, Dong W (2012) Identification of soybean microRNAs involved in soybean cyst nematode infection by deep sequencing. PLoS One 7:e39650. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0039650
Li S, Liu L, Zhuang X, Yu Y, Liu X et al (2013) MicroRNAs inhibit the translation of target mRNAs on the endoplasmic reticulum in Arabidopsis. Cell 153:562–574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2013.04.005
Liu PP, Montgomery TA, Fahlgren N, Kasschau KD, Nonogaki H (2007) Repression of AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR10 by MicroRNA160 is critical for seed germination and post germination stages. Plant J 52:133–146. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03218.x
Liu Q, Yao X, Pi L, Wang H, Cui X, Huang H (2009) The ARGONAUTE10 gene modulates shoot apical meristem maintenance and establishment of leaf polarity by repressing miR165/166 in Arabidopsis. Plant J 58:27–40. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2008.03757.x
Lobbes D, Rallapalli G, Schmidt DD, Martin C, Clarke J (2006) SERRATE: a new player on the plant microRNA scene. EMBO Rep 7:1052–1058. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.embor.7400806
Lu S, Sun YA, Amerson H, Chiang VL (2007) MicroRNAs in loblolly pine (Pinus taeda L) and their association with fusiform rust gall development. Plant J 51:1077–1098. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03208.x
Machida C, Nakagawa A, Kojima S, Takahashi H, Machida Y (2015) The complex of ASYMMETRIC LEAVES (AS) proteins plays a central role in antagonistic inter-actions of genes for leaf polarity specification in Arabidopsis. Wiley Interdiscip Rev Dev Biol 4:655–671. https://doi.org/10.1002/wdev.196
Mallory AC, Reinhart BJ, Jones-Rhoades MW, Tang G (2004) MicroRNA control of PHABULOSA in leaf development: importance of pairing to the microRNA 50 region. EMBO J 23:3356–3364. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.emboj.7600340
Mallory AC, Bartel DP, Bartel B (2005) MicroRNA-directed regulation of Arabidopsis AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR17 is essential for proper development and modulates expression of early auxin response genes. Plant Cell 17:1360–1375. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.105.031716
Marin E, Jouannet V, Herz A, Lokerse AS, Weijers D, Vaucheret H, Nussaume L, Crespi MD, Maizel A (2010a) MiR390, Arabidopsis TAS3 tasiRNAs, and their AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR targets define an autoregulatory network quantitatively regulating lateral root growth. Plant Cell 22:1104–1117. https://doi.org https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.109.072553
Marin E, Jouannet V, Herz A, Annemarie S et al (2010b) miR390, Arabidopsis TAS3 tasiRNAs, and their AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR targets define an autoregu-latory network quantitatively regulating lateral root growth. Plant Cell 22:1104–1117. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.109.072553
Mathieu J, Yant LJ, Mürdter F, Küttner F, Schmid M (2009) Repression of flowering by the miR172 target SMZ. PLoS Biol 7:e1000148. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.1000148
Millar AA (2020) The function of miRNAs in plants. Plants 9: 198. https://doi.org/10.3390/plants9020198
Miyashima S, Koi S, Hashimoto T, Nakajima K (2011) Non-cell-autonomous microRNA165 acts in a dose-dependent manner to regulate multiple differentia- tion status in the Arabidopsis root. Development 138:2303–2313. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.060491
Miyashima S, HondaM HK, Tatematsu K, Hashimoto T, Sato-Nara K, Okada K, Nakajima K (2013) A comprehensive expression analysis of the Arabidopsis MICRORNA165/6 gene family during embryogenesis reveals a conserved role in meristem specification and a non-cell-autonomous function. Plant Cell Physiol 54:375–384. https://doi.org/10.1093/pcp/pcs188
Montgomery TA, Howell MD, Cuperus JT, Li D, Hansen JE, Alexander AL, Chapman EJ, Fahlgren N, Allen E, Carrington JC (2008) Specificity of ARGONAUTE7-miR390 interaction and dual functionality in TAS3 trans-acting siRNA formation. Cell 133:128–141. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2008.02.033
Nag A, King S, Jack T (2009) miR319a targeting of TCP4 is critical for petal growth and development in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 106:22534–22539. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0908718106
Navarro L, Dunoyer P, Jay F, Arnold B, Dharmasiri N, Estelle M, Voinnet O, Jones JD (2006) A plant miRNA contributes to antibacterial resistance by repressing Auxin signaling. Science 312:436–439. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1126088
Nikovics K, Blein T, Peaucelle A, Ishida T et al (2006) The balance between the MIR164A and CUC2 genes controls leaf margin serration in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 18:2929–2945. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.106.045617
Nogueira FT, Timmermans MC (2007) An interplay between small regulatory RNAs patterns leaves. Plant Signal Behav 2:519–521. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1528607
Ori N, Cohen AR, Etzioni A, Brand A, Yanai O, Shleizer S, Menda N, Amsellem Z, Efroni I, Pekker I, Alvarez JP, Blum E, Zamir D, Eshed Y (2007) Regulation of LANCEOLATE by miR319 is required for compound-leaf development in tomato. Nat Genet 39:787–791. https://doi.org/10.1038/ng2036
Orman-Ligeza B, Parizot B, Gantet PP, Beeckman T, Bennett MJ, Draye X (2013) Postembryonic root organogenesis in cereals: branching out from model plants. Trends Plant Sci 18:459–467. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2013.04.010
Pacheco R, García-Marcos A, Barajas D, Martiáñez J, Tenllado F (2012) PVX–potyvirus synergistic infections differentially alter microRNA accumulation in Nicotiana benthamiana. Virus Rres 165:231–235. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virusres.2012.02.012
Palatnik JF, Allen E, Wu X, Schommer C et al (2003) Control of leaf morphogenesis by microRNAs. Nature 425:257–263. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature01958
Palatnik JF, Wollmann H, Schommer C, Schwab R et al (2007) Sequence and expression differences underlie Funtional specialization of Arabidopsis MicroRNAs miR159 and miR319. Dev Cell 13:115–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.devcel.2007.04.012
Papp I, Mette MF, Aufsatz W, Daxinger L, Schauer SE et al (2003) Evidence for nuclear processing of plant micro RNA and short interfering RNA precursors. Plant Physiol 132:1382–1390. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.103.021980
Parry G, Calderon-Villalobos LI, Prigge M, Peret B, Dharmasiri S, Itoh H, Lechner E, Gray WM, Bennett M, Estelle M (2009) Complex regulation of the TIR1/AFB family of auxinreceptors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 106:22540–22545. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0911967106
Paul S, Datta SK, Datta K (2015) MiRNA regulation of nutrient homeostasis in plants. Front Plant Sci 6:232. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2015.00232
Pradhan B, Naqvi AR, Saraf S, Mukherjee SK, Dey N (2015) Prediction and characterization of tomato leaf curl New Delhi virus (ToLCNDV) responsive novel microRNAs in Solanum lycopersicum. Virus Res 195:183–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.virusres.2014.09.001
Pratt AJ, MacRae IJ (2009) The RNA-induced silencing complex: a versatile gene-silencing machine. J Biol Chem 284:17897–17901. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.R900012200
Prigge MJ, Clark SE (2006) Evolution of the class IIIHD-zip gene family in land plants. Evol Dev 8:350–361. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1525-142X.2006.00107.x
Qu J, Ye J, Fang R (2007) Artificial microRNA-mediated virus resistance in plants. J Virol 81:6690–6699. https://doi.org/10.1128/JVI.02457-06
Rajam MV (2020) RNA silencing technology: a boon for crop improvement. J Biosci 45:1–5. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12038-020-00082-x
Ramachandran V, Chen X (2008) Degradation of microRNAs by a family of exoribonucleases in Arabidopsis. Science 321:1490–1492. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1163728
Raman S, Greb T, Peaucelle A, Blein T, Laufs P, Theres K (2008) Interplay of miR164, CUP-SHAPED COTYLEDON genes and LATERAL SUPPRESSOR controls axillary meristem formation in Arabidopsis thaliana. Plant J 55:65–76. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2008.03483.x
Reinhart BJ, Weinstein EG, Rhoades MW, Bartel B, Bartel DP (2002) MicroRNAs in plants. Genes Dev 16:1616–1626. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1004402
Ren G, Xie M, Zhang S, Vinovskis C, Chen X, Yu B (2014) Methylation protects microRNAs from an AGO1-associated activity that uridylates 50 RNA fragments generated by AGO1 cleavage. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 111:6365–6370. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1405083111
Reyes JL, Chua NH (2007) ABA induction of miR159 controls transcript levels of two MYB factors during Arabidopsis seed germination. Plant J 49:592–606. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2006.02980.x
Rhoades MW, Reinhart BJ, Lim LP, Burge CB, Bartel B, Bartel DP (2002) Prediction of plant microRNA targets. Cell 110:513–520. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0092-8674(02)00863-2
Rodriguez RE, Mecchia MA, Debernardi JM, Schommer C, Weigel D, Palatnik JF (2010) Control of cell proliferation in Arabidopsis thaliana by microRNA miR396. Development 137:103–112. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.043067
Rogers K, Chen X (2013) Biogenesis, turnover, and mode of action of plant microRNAs. Plant Cell 25:2383–2399. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.113.113159
Rubio-Somoza I, Zhou CM, Confraria A, Martinho C et al (2014) Temporal control of leaf com-plexity by miRNA-regulated licensing of protein complexes. Curr Biol 24:2714–2719. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cub.2014.09.058
Rubio-Somoza I, Weigel D, Qu L-J (2013) Coordination of Flower Maturation by a Regulatory Circuit of Three MicroRNAs. PLoS Genetics 9 (3):e1003374
Schmid M, Uhlenhaut NH, Godard F et al (2003) Dissection of floral induction pathways using global expression analysis. Development 130:6001–6012. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.00842
Schommer C, Palatnik JF, Aggarwal P, Chetelat A, Cubas P, Farmer EE, Nath U, Weigel D (2008) Control of jasmonate biosynthesis and senescence by miR319 targets. PLoS Biol 6:e230. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.0060230
Serivichyaswat P, Ryu HS, Kim W, Kim S, Chung KS, Kim JJ, Ahn JH (2015) Expression of the floral repressor miRNA156 is positively regulated by the AGAMOUS-like pro-teins AGL15 and AGL18. Mol Cells 38:259–266. https://doi.org/10.14348/molcells.2015.2311
Smith ZR, Long JA (2010) Control of Arabidopsis apical–basal embryo polarity by antagonistic transcription factors. Nature 464:423–426. https://doi.org/10.1038/nature08843
Souret FF, Kastenmayer JP, Green PJ (2004) AtXRN4 degrades mRNAin Arabidopsis and its substrates include selected miRNA targets. Mol Cell 15:173–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molcel.2004.06.006
Sunkar R, Li Y-F, Jagadeeswaran G (2012) Functions ofmicroRNAs in plant stress responses. Trends in Plant Science 17:196–203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tplants.2012.01.010
Swiezewski S, Crevillen P, Liu F, Ecker JR, Jerzmanowski A, Dean C (2007) Small RNA-mediated chromatin silencing directed to the 30 region of the Arabidopsis gene encoding the developmental regulator, FLC. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 104:3633–3638. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.0611459104
Tousi N, Eini O, Ahmadvand R, Carra A, Miozzi L, Noris E et al (2017) In silico prediction of miRNAs targeting ToLCV and their regulation in susceptible and resistant tomato plants. Australasian Plant Pathol 46:379–386. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13313-017-0500-5
Trindade I, Capitao C, Dalmay T, Fevereiro MP, Santos DM (2010) miR398 and miR408 are upregulated in response to water deficit in Medicago truncatula. Planta 231:705–716. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00425-009-1078-0
Várallyay E, Válóczi A, Ágyi A, Burgyán J, Havelda Z (2017) Plant virus-mediated induction of miR168 is associated with repression of ARGONAUTE1 accumulation. The EMBO J 36:1641–1642. https://doi.org/10.15252/embj.201797083
Waheed S, Zeng L (2020) The critical role of miRNAs in regulation of flowering time and flower development. Genes 11:319. https://doi.org/10.3390/genes11030319
Wang JJ, Guo HS (2015) Cleavage of INDOLE-3-ACETIC ACID INDUCIBLE28 mRNA by microRNA847 upregulates auxin signaling to modulate cell proliferation and lateral organ growth in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 27:574–590. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.15.00101
Wang JW, Wang LJ, Mao YB, Cai WJ, Xue HW, Chen XY (2005) Control of root cap formation by microRNA-targeted auxin response factors in Arabidopsis. Plant Cell 17:2204–2216. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.105.033076
Wei L, Zhang D, Xiang F, Zhang Z (2009) Differentially expressed miRNAs potentially involved in the regulation of defense mechanism to drought stress in maize seedlings. Int J Plant Sci 170:979–989. https://doi.org/10.1086/605122
Willmann MR, Mehalick AJ, Packer RL, Jenik PD (2011) MicroRNAs regulate the timing of embryo maturation in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 155:1871–1884. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.110.171355
Wollmann H, Mica E, Todesco M, Long JA, Weigel D (2010) On reconciling the interactions between APETALA2, miR172 and AGAMOUS with the ABC model of flower development. Development 137:3633–3642. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.036673
Wu G, Poethig RS (2006) Temporal regulation of shoot development in Arabidopsis thaliana by miR156 and its target SPL3. Development 133:3539–3547. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.02521
Wu MF, Tian Q, Reed JW (2006) Arabidopsis microRNA167 controls pat-terns of ARF6 and ARF8 expression, and regulates both female and male reproduction. Development 133:4211–4218. https://doi.org/10.1242/dev.02602
Wu G, Park MY, Conway SR, Wang JW, Weigel D, Poethig RS (2009) The sequential action of miR156 and miR172 regulates developmental timing in Arabidopsis. Cell 138: 750–759. https://doi.org https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2009.06.031
Wu F, Shu J, Jin W (2014) Identification and validation of miRNAs associated with the resistance of maize (Zea mays L) to Exserohilum turcicum. PLoS One 9(1):e87251. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0087251
Xia R, Xu J, Meyers BC (2017) The emergence, evolution, and diversification of the miR390–TAS3 ARF pathway in land plants. Plant Cell 29:1232–1247. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.17.00185
Xie Z, Allen E, Fahlgren N, Calamar A, Givan SA, Carrington JC (2005) Expression of Arabidopsis MIRNA genes. Plant Physiol 138:2145–2154. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.105.062943
Xie K, Wu C, Xiong L (2006) Genomic organization, differential expres-Sion, and interaction of SQUAMOSA promoter-binding-like Tran-scription factors and microRNA156 in rice. Plant Physiol 142:280–293. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.106.084475
Xing L, Zhu M, Zhang M, Li W, Jiang H, Zou J, Wang L, Xu M (2017) High-Throughput sequencing of small RNA transcriptomes in maize kernel identifies miRNAs involved in embryo and endosperm development. Genes 8:385
Xu Z, Zhong S, Li X, Li W, Rothstein SJ, Zhang S, Bi Y, Xie C (2011) Genome-wide identification of microRNAs in response to low nitrate availability in maize leaves and roots. PLoS One 6:e28009. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0028009
Xu X, Chen X, Chen Y, Zhang Q, Su L, Chen X, Chen Y, Zhang Z, Lin Y, Lai Z (2020) Genome-wide identification of miRNAs and their targets during early somatic embryogenesis in Dimocarpus longan Lour. Sci Rep 10:1–15. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-60946-y
Yang L, Liu Z, Lu F, Dong A, Huang H (2006) SERRATE is a novel nuclear regulator in primary microRNA processing in Arabidopsis. Plant J 47:841–850. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2006.02835.x
Yang L, Wu G, Poethig RS (2012) Mutations in the GW-repeat protein SU Oreveal a developmental function for microRNA-mediated translational repression in Arabidopsis. Proc Natl Acad Sci SA 109:315–320. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1114673109
Yang J, Tian L, Sun MX, Huang XY, Zhu J, Guan YF, Jia QS, Yang ZN (2013a) AUXIN RESPONSE FACTOR17 is essential for pollen wall pattern formation in Arabidopsis. Plant Physiol 162:720–731. https://doi.org/10.1104/pp.113.214940
Yang L, Jue D, Li W, Zhang R, Chen M, Yang Q (2013b) Identification of miRNA from eggplant (Solanum melongena L) by small RNA deep sequencing and their response to Verticillium dahlia infection. PLoS One 8(8):e72840. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0072840
Yant L, Mathieu J, Dinh TT, Ott F, Lanz C, Wollmann H, Chen X, Schmid M (2010) Orchestration of the floral transition and floral development in Arabidopsis by the bifunctional transcrip-tion factor APETALA2. Plant Cell 22:2156–2170. https://doi.org/10.1105/tpc.110.075606
Yoshikawa M, Peragine A, Park MY, Poethig RS (2005) A pathway for the biogenesis of trans-acting siRNAs in Arabidopsis. Genes Dev 19:2164–2175. https://doi.org/10.1101/gad.1352605
Yoshikawa M, Iki T, Tsutsui Y, Miyashita K et al (2013) 3′ fragment of miR173-programmed RISC cleaved RNA is protected from degradation in a complex with RISC and SGS3. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:4117–4122. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1217050110
Yu B, Yang Z, Li J, Minakhina S, Yang M, Padgett RW, Steward R, Chen X (2005) Methylation as a crucial step in plant microRNA biogenesis. Science. 307:932–935. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1107130
Yu N, Niu QW, Ng KH, Chua NH (2015) The role of miR156/SPLs modules in Arabi-dopsis lateral root development. Plant J 83:673–685. https://doi.org/10.1111/tpj.12919
Yu J, Su D, Yang D, Dong T, Tang Z, Li H, Han Y, Li Z, Zhang B (2020) Chilling and heat stress-induced physiological changes and MicroRNA-related mechanism in Sweetpotato (Ipomoea batatas L.). Front Plant Sci 11:687. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpls.2020.00687
Zeng H, Wang G, Hu X, Wang H, Du L, Zhu Y (2014) Role of microRNAs in plant responses to nutrient stress. Plant Soil 374:1005–1021. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3040.2007.01643.x
Zhang J, Xu Y, Huan Q, Chong K (2009) Deep sequencing of Brachypodium small RNAs at the global genome level identifies microRNAs involved in cold stress response. BMC Genomics 10:449. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2164-10-449
Zhao B, Liang R, Ge L, Li W, Xiao H, Lin H, Ruan K, Jin Y (2007a) Identification of drought induced microRNAs in rice. Biochem Biophys Res Commun 354:585–590. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bbrc.2007.01.022
Zhao L, Kim Y, Dinh TT, Chen X (2007b) miR172 regulates stem cell fate and defines the inner boundary of APETALA3 and PISTILLATA expression domain in Arabidopsis floral meristems. Plant J 51:840–849. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-313X.2007.03181.x
Zhao BT, Ge LF, Liang RQ, Li W, Ruan KC, Lin HX, Jin YX (2009) Members of miR169 family are induced by high salinity and transiently inhibit the NF-YA transcription factor. BMC Mol Biol 10:29. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2199-10-29
Zhou XF, Wang GD, Zhang WX (2007) UV-B responsive MicroRNA genes in Arabidopsis thaliana. Mol Sys Biol 3:103. https://doi.org/10.1038/msb4100143
Zhou CM, Zhang TQ, Wang X, Yu S, Lian H, Tang H, Feng ZY, Zozomova-Lihová J, Wang JW (2013) Molecular basis of age-dependent vernalization in Cardamine flexuosa. Science 340:1097–1100. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1234340
Zhou Y, Honda M, Zhu H, Zhang Z, Guo X, Li T, Li Z, Peng X, Nakajima K, Duan L, Zhang X (2015) Spatiotemporal sequestration of miR165/166 by Arabidopsis Argonaute10 promotes shoot apical meristem maintenance. Cell Rep 10:1819–1827. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2015.02.047
Zhou R, Yu X, Ottosen CO, Zhang T, Wu Z, Zhao T (2020) Unique miRNAs and their targets in tomato leaf responding to combined drought and heat stress. BMC Plant Biol 20:1–10. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12870-020-2313-x
Zhu H, Hu F, Wang R, Zhou X, Sze SH et al (2011) Arabidopsis Argonaute10 specifically sequesters miR166/165 to regulate shoot apical meristem development. Cell 145:242–256. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cell.2011.03.024
Zuo J, Wang Y, Liu H, Ma Y, Ju Z, Zhai B, Fu D, Zhu Y, Luo Y, Zhu B (2011) MicroRNAs in tomato plants. Science China Life Sciences 54:599–605
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher’s note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Choudhary, A., Kumar, A., Kaur, H. et al. MiRNA: the taskmaster of plant world. Biologia 76, 1551–1567 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-021-00720-1
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11756-021-00720-1