Abstract
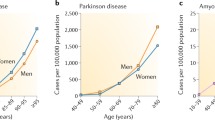
If aging is a physiological phenomenon—as maintained by the programmed aging paradigm—it must be caused by specific genetically determined and regulated mechanisms, which must be confirmed by evidence. Within the programmed aging paradigm, a complete proposal starts from the observation that cells, tissues, and organs show continuous turnover: As telomere shortening determines both limits to cell replication and a progressive impairment of cellular functions, a progressive decline in age-related fitness decline (i.e., aging) is a clear consequence. Against this hypothesis, a critic might argue that there are cells (most types of neurons) and organ parts (crystalline core and tooth enamel) that have no turnover and are subject to wear or manifest alterations similar to those of cells with turnover. In this review, it is shown how cell types without turnover appear to be strictly dependent on cells subjected to turnover. The loss or weakening of the functions fulfilled by these cells with turnover, due to telomere shortening and turnover slowing, compromises the vitality of the served cells without turnover. This determines well-known clinical manifestations, which in their early forms are described as distinct diseases (e.g., Alzheimer’s disease, Parkinson’s disease, age-related macular degeneration, etc.). Moreover, for the two organ parts (crystalline core and tooth enamel) without viable cells or any cell turnover, it is discussed how this is entirely compatible with the programmed aging paradigm.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Aarsland D, Londos E, Ballard C (2009) Parkinson’s disease dementia and dementia with Lewy bodies: different aspects of one entity. Int Psychogeriatr 21(2):216–219
Abbott A (2008) The plaque plan. Nature 456:161–164
Abbott RD, Ross GW, White LR, Nelson JS, Masaki KH, Tanner CM, Curb JD, Blanchette PL, Popper JS, Petrovitch H (2002) Midlife adiposity and the future risk of Parkinson’s disease. Neurology 59(7):1051–1057
Ablonczy Z, Gutierrez DB, Grey AC, Schey KL, Crouch RK (2012) Molecule-specific imaging and quantitation of A2E in the RPE. Adv Exp Med Biol 723. doi:10.1007/978-1-4614-0631-0_11
Ballard C, Hanney ML, Theodoulou M, Douglas S, McShane R, Kossakowski K, Gill R, Juszczak E, Yu LM, Jacoby R (2009) The dementia antipsychotic withdrawal trial (DART-AD): long-term follow-up of a randomised placebo-controlled trial. Lancet Neurol 8:151–157
Barnett-Cowan M, Dyde RT, Foxe SH, Moro E, Hutchison WD, Harris LR (2010) Multisensory determinants of orientation perception in Parkinson’s disease. Neuroscience 167(4):1138–1150
Barresi M, Ciurleo R, Giacoppo S, Foti Cuzzola V, Celi D, Bramanti P, Marino S (2012) Evaluation of olfactory dysfunction in neurodegenerative diseases. J Neurol Sci 323:16–24
Ben-Porath I, Weinberg R (2005) The signals and pathways activating cellular senescence. Int J Biochem Cell Biol 37:961–976
Berger JM, Fine SL, Maguire MG (1999) Age-related macular degeneration. Mosby, USA
Bermingham-McDonogh O, Reh TA (2011) Regulated reprogramming in the regeneration of sensory receptor cells. Neuron 71(3):389–405
Bertram L, Blacker D, Mullin K, Keeney D, Jones J, Basu S, Yhu S, McInnis MG, Go RC, Vekrellis K, Selkoe DJ, Saunders AJ, Tanzi RE (2000) Evidence for genetic linkage of Alzheimer’s disease to chromosome 10q. Science 290:2302–2303
Bodnar AG, Ouellette M, Frolkis M, Holt SE, Chiu CP, Morin GB, Harley CB, Shay JW, Lichtsteiner S, Wright WE (1998) Extension of life-span by introduction of telomerase into normal human cells. Science 279(5349):349–352
Brück D, Wenning GK, Stefanova N, Fellner L (2016) Glia and alpha-synuclein in neurodegeneration: A complex interaction. Neurobiol Dis 85:262–274
Buchtova M, Stembirek J, Glocova K, Matalova E, Tucker AS (2012) Early regression of the dental lamina underlies the development of diphyodont dentitions. J Dent Res 91(5):491–498
Caballol N, Martí MJ, Tolosa E (2007) Cognitive dysfunction and dementia in Parkinson disease. Mov Disord 22(S17):S358–S366
Caggiano M, Kauer JS, Hunter DD (1994) Globose basal cells are neuronal progenitors in the olfactory epithelium: a lineage analysis using a replication-incompetent retrovirus. Neuron 13:339–352
Candia OA (2004) Electrolyte and fluid transport across corneal, conjunctival and lens epithelia. Exp Eye Res 78(3):527–535
Chen X, Fang H, Schwob JE (2004) Multipotency of purified, transplanted globose basal cells in olfactory epithelium. J Comp Neurol 469:457–474
Chong EW, Wong TY, Kreis AJ, Simpson JA, Guymer RH (2007) Dietary antioxidants and primary prevention of age related macular degeneration: systematic review and meta-analysis. BMJ 335(7623):755
Counter CM, Hahn WC, Wei W, Caddle SD, Beijersbergen RL, Lansdorp PM, Sedivy JM, Weinberg RA (1998) Dissociation among in vitro telomerase activity, telomere maintenance, and cellular immortalization. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 95(25):14723–14728
D’Emic MD, Whitlock JA, Smith KM, Fisher DC, Wilson JA, Evans AR (2013) Evolution of High Tooth Replacement Rates in Sauropod Dinosaurs. PLoS ONE 8(7):e69235
Davie CA (2008) A review of Parkinson’s disease. Br Med Bull 86(1):109–127
de Lau LM, Breteler MM (2006) Epidemiology of Parkinson’s disease. Lancet Neurol 5(6):525–535
Delcourt C, Cristol JP, Tessier F, Léger CL, Michel F, Papoz L (2000) Risk factors for cortical, nuclear, and posterior subcapsular cataracts: the POLA study. Pathologies Oculaires Liées à l’Age. Am J Epidemiol 151:497–504
Dickson DV (2007) Neuropathology of movement disorders. In: Tolosa E. Jankovic JJ. Parkinson’s disease and movement disorders. Lippincott Williams and Wilkins, Hagerstown (MD), pp. 271–283
Doty RL (2012) Olfactory dysfunction in Parkinson disease. Nat Rev Neurol 8:329–339
Doty RL, Shaman P, Applebaum SL, Giberson R, Siksorski L, Rosenberg L (1984) Smell identification ability: changes with age. Science 226:1441–1443
Duff K, McCaffrey RJ, Solomon GS (2002) The Pocket Smell Test: successfully discriminating probable Alzheimer’s dementia from vascular dementia and major depression. J Neuropsychiatry Clin Neurosci 14:197–201
Duffy VB, Backstrand JR, Ferris AM (1995) Olfactory dysfunction and related nutritional risk in free-living, elderly women. J Am Diet Assoc 95:879–884
Ellul J, Archer N, Foy CM, Poppe M, Boothby H, Nicholas H, Brown RG, Lovestone S (2007) The effects of commonly prescribed drugs in patients with Alzheimer’s disease on the rate of deterioration. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 78:233–239
Factor SA, Weiner WJ (eds) (2008) Parkinson’s Disease: Diagnosis and Clinical Management, 2nd edn. Demos Medical Publishing, New York, pp. 72–73
Fine SL, Berger JW, Maguire MG, Ho AC (2000) Age-related macular degeneration. N Engl J Med 342:483–492
Flanary B (2009) Telomeres: function, shortening, and lengthening. In: Telomeres: Function. Shortening and Lengthening. Nova Science Publ. Inc., New York, pp. 379–386
Forrester J, Dick A, McMenamin P, Lee W (1996) The Eye: Basic Sciences in Practice. W. B. Saunders Company Ltd., London, London
Fossel MB (1996) Reversing human aging. William Morrow and Company, New York
Fossel MB (2004) Cells, aging and human disease. Oxford University Press, New York
Friedman B, Lahad A, Dresner Y, Vinker S (2013) Long-term statin use and the risk of Parkinson’s disease. Am J Manag Care 19(8):626–632
Fuenzalida M, Lemus S, Illanes J, Montiel E, Acuña O, Lemus D (2000) Histochemical detection of sugar residues in lizard teeth (Liolaemus gravenhorsti): a lectin-binding study. Biol Res 33(3–4):215–226
Gaete M, Tucker AS (2013) Organized emergence of multiple-generations of teeth in snakes is dysregulated by activation of Wnt/beta-catenin signalling. PLoS One 8(9):e74484
Galpern WR, Lang AE (2006) Interface between tauopathies and synucleinopathies: a tale of two proteins. Ann Neurol 59(3):449–458
Gao X, Simon KC, Schwarzschild MA, Ascherio A (2012) Prospective study of statin use and risk of Parkinson disease. Arch Neurol 69(3):380–384
Gorelick PB (2004) Risk factors for vascular dementia and Alzheimer disease. Stroke 35:2620–2622
Hill K, Hurtado AM (1996) Ache life history. Aldine De Gruyter, New York
Hill JM, Zalos G, Halcox JPJ, Schenke WH, Waclawiw MA, Quyyumi AA, Finkel T (2003) Circulating endothelial progenitor cells, vascular function, and cardiovascular risk. N Engl J Med 348:593–600
Holmes DJ, Austad SN (1995) Birds as animal models for the comparative biology of aging: a prospectus. J Gerontol A Biol Sci 50:B59–B66
Horner PJ, Gage FH (2000) Regenerating the damaged central nervous system. Nature 407:963–970
Hu G, Jousilahti P, Nissinen A, Antikainen R, Kivipelto M, Tuomilehto J (2006) Body mass index and the risk of Parkinson disease. Neurology 67(11):1955–1959
Hu G, Jousilahti P, Bidel S, Antikainen R, Tuomilehto J (2007) Type 2 diabetes and the risk of Parkinson’s disease. Diabetes Care 30(4):842–847
Huard JM, Youngentob SL, Goldstein BJ, Luskin MB, Schwob JE (1998) Adult olfactory epithelium contains multipotent progenitors that give rise to neurons and non-neural cells. J Comp Neurol 400:469–486
Iwai N, Zhou Z, Roop DR, Behringer RR (2008) Horizontal basal cells are multipotent progenitors in normal and injured adult olfactory epithelium. Stem Cells 26(5):1298–1306
Jager RD, Mieler WF, Miller JW (2008) Age-related macular degeneration. N Engl J Med 358(24):2606–2617
Jankovic J (2008) Parkinson’s disease: clinical features and diagnosis. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatr 79(4):368–376
Kirkwood TB, Melov S (2011) On the programmed/non-programmed nature of ageing within the life history. Curr Biol 21(18):R701–R707
Klein BE, Klein R, Lee KE, Grady LM (2006) Statin use and incident nuclear cataract. JAMA 295:2752–2758
Klein R, Deng Y, Klein BE, Hyman L, Seddon J, Frank RN, Wallace RB, Hendrix SL, Kuppermann BD, Langer RD, Kuller L, Brunner R, Johnson KC, Thomas AM, Haan M (2007) Cardiovascular disease, its risk factors and treatment, and age-related macular degeneration: Women’s Health Initiative Sight Exam ancillary study. Am J Ophthalmol 143:473–483
Kruman II, Culmsee C, Chan SL, Kruman Y, Guo Z, Penix L, Mattson MP (2000) Homocysteine elicits a DNA damage response in neurons that promotes apoptosis and hypersensitivity to excitotoxicity. J Neurosci 20(18):6920–6926
Kuhn TS (1962) The structure of scientific revolutions. The University of Chicago Press, Chicago
Lai SW, Liao KF, Lin CL, Lin CC, Sung FC (2014) Hearing loss may be a non-motor feature of Parkinson’s disease in older people in Taiwan. Eur J Neurol 21(5):752–757
Leung CT, Coulombe PA, Reed RR (2007) Contribution of olfactory neural stem cells to tissue maintenance and regeneration. Nat Neurosci 10:720–726
Libertini G (1988) An adaptive theory of the increasing mortality with increasing chronological age in populations in the wild. J Theor Biol 132:145–162
Libertini G (2009a) The role of telomere-telomerase system in age-related fitness decline, a tameable process. In: Telomeres: Function, Shortening and Lengthening. Nova Science Publ. Inc., New York, pp. 77–132
Libertini G (2009b) Prospects of a longer life span beyond the beneficial effects of a healthy lifestyle. In: handbook on longevity: genetics, Diet & Disease. Nova Science Publ. Inc., New York, pp. 35–95
Libertini G (2012) Classification of phenoptotic phenomena. Biochem (Mosc) 77(7):707–715
Libertini G (2014) The programmed aging paradigm: how we get old. Biochem (Mosc) 79(10):1004–1016
Libertini G (2015a) Non-programmed versus programmed aging paradigm. Curr Aging Sci 8(1):56–68
Libertini G (2015b) Phylogeny of aging and related phenoptotic phenomena. Biochem (Mosc) 80(12):1781–1801
Lin FR, Metter EJ, O’Brien RJ, Resnick SM, Zonderman AB, Ferrucci L (2011) Hearing loss and incident dementia. Arch Neurol 68(2):214–220
Lopez-Real A, Rey P, Soto-Otero R, Mendez-Alvarez E, Labandeira-Garcia JL (2005) Angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibition reduces oxidative stress and protects dopaminergic neurons in a 6-hydroxydopamine rat model of Parkinsonism. J Neurosci Res 81(6):865–873
Maier EC, Saxena A, Alsina B, Bronner ME, Whitfielda TT (2014) Sensational placodes: Neurogenesis in the otic and olfactory systems. Dev Biol 389(1):50–67
Mares JA, Voland R, Sondel SA, Millen AE, Larowe T, Moeller SM, Klein ML, Blodi BA, Chappell RJ, Tinker L, Ritenbaugh C, Gehrs KM, Sarto GE, Johnson E, Snodderly DM, Wallace RB (2011) Healthy lifestyles related to subsequent prevalence of age-related macular degeneration. Arch Ophthalmol 129(4):470–480
Martin GM, Oshima J (2000) Lessons from human progeroid syndromes. Nature 408:263–266
Mercer LD, Kelly BL, Horne MK, Beart PM (2005) Dietary polyphenols protect dopamine neurons from oxidative insults and apoptosis: investigations in primary rat mesencephalic cultures. Biochem Pharmacol 69(2):339–345
Miners JS, Baig S, Palmer J, Palmer LE, Kehoe PG, Love S (2008) Abeta-degrading enzymes in Alzheimer’s disease. Brain Pathol 18(2):240–252
Morales I, Sanchez A, Rodriguez-Sabate C, Rodriguez M (2015) The degeneration of dopaminergic synapses in Parkinson’s disease: a selective animal model. Behav Brain Res 289:19–28
Murphy C, Schubert CR, Cruickshanks KJ, Klein BE, Klein R, Nondahl DM (2002) Prevalence of olfactory impairment in older adults. JAMA 288:2307–2312
Nussey DH, Froy H, Lemaitre JF, Gaillard JM, Austad SN (2013) Senescence in natural populations of animals: widespread evidence and its implications for bio-gerontology. Ageing Res Rev 12:214–225
Nuytemans K, Theuns J, Cruts M, Van Broeckhoven C (2010) Genetic etiology of Parkinson disease associated with mutations in the SNCA, PARK2, PINK1, PARK7, and LRRK2 genes: a mutation update. Hum Mutat 31(7):763–780
Obeso JA, Rodríguez-Oroz MC, Benitez-Temino B, Blesa FJ, Guridi J, Marin C, Rodriguez M (2008) Functional organization of the basal ganglia: therapeutic implications for Parkinson’s disease. Mov Disord 23(Suppl 3):S548–S559
Obeso JA, Rodriguez-Oroz MC, Goetz CG, Marin C, Kordower JH, Rodriguez M, Hirsch EC, Farrer M, Schapira AH, Halliday G (2010) Missing pieces in the Parkinson’s disease puzzle. Nat Med 16(6):653–661
Price WA (1939) Nutrition and Physical Degeneration. Paul B. Hoeber, New York–London
Qiu WQ, Walsh DM, Ye Z, Vekrellis K, Zhang J, Podlisny MB, Rosner MR, Safavi A, Hersh LB, Selkoe DJ (1998) Insulin-degrading enzyme regulates extracellular levels of amyloid beta-protein by degradation. J Biol Chem 273:32730–32738
Rosendorff C, Beeri MS, Silverman JM (2007) Cardiovascular risk factors for Alzheimer’s disease. Am J Geriatr Cardiol 16(3):143–149
Samii A, Nutt JG, Ransom BR (2004) Parkinson’s disease. Lancet 363(9423):1783–1793
Schubert CR, Cruickshanks KJ, Fischer ME, Huang GH, Klein BE, Klein R, Pankow JS, Nondahl DM (2012) Olfactory impairment in an adult population: the Beaver Dam Offspring Study. Chem Senses 37:325–334
Schulz-Schaeffer WJ (2010) The synaptic pathology of alpha-synuclein aggregation in dementia with Lewy bodies, Parkinson’s disease and Parkinson’s disease dementia. Acta Neuropathol 120(2):131–143
Sergeyenko Y, Lall K, Liberman MC, Kujawa SG (2013) Age-related cochlear synaptopathy: an early-onset contributor to auditory functional decline. J Neurosci 33:13686–13694
Shoshani J (2000) Elephants: majestic creatures of the wild. Checkmark Books, New York
Single G, Dickman CR, MacDonald DW (2001) Rodents. In: MacDonald DW. Oxford University Press, Oxford, The Encyclopedia of Mammals, pp. 578–587
Skulachev VP (1997) Aging is a specific biological function rather than the result of a disorder in complex living systems: biochemical evidence in support of Weismann’s hypothesis. Biochem (Moscow) 62:1191–1195
Skulachev VP (1999) Phenoptosis: programmed death of an organism. Biochem (Moscow) 64:1418–1426
Sonsalla PK, Coleman C, Wong LY, Harris SL, Richardson JR, Gadad BS, Li W, German DC (2013) The angiotensin converting enzyme inhibitor captopril protects nigrostriatal dopamine neurons in animal models of parkinsonism. Exp Neurol 250:376–383
Sparrow JR (2003) Therapy for macular degeneration: Insights from acne. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 100:4353–4354
Sturm E, Stefanova N (2014) Multiple system atrophy: genetic or epigenetic? Exp Neurobiol 23(4):277–291
Tassin J, Malaise E, Courtois Y (1979) Human lens cells have an in vitro proliferative capacity inversely proportional to the donor age. Exp Cell Res 123:388–392
Tomlinson DR, Gardiner NJ (2008) Glucose neurotoxicity. Nat Rev Neurosci 9(1):36–45
Undela K, Gudala K, Malla S, Bansal D (2013) Statin use and risk of Parkinson’s disease: a meta-analysis of observational studies. J Neurol 260(1):158–165
Vaziri H (1998) Extension of life span in normal human cells by telomerase activation: a revolution in cultural senescence. J Anti-Aging Med 1:125–130
Vaziri H, Benchimol S (1998) Reconstitution of telomerase activity in normal cells leads to elongation of telomeres and extended replicative life span. Curr Biol 8:279–282
Vekrellis K, Ye Z, Qiu WQ, Walsh D, Hartley D, Chesneau V, Rosner MR, Selkoe DJ (2000) Neurons regulate extracellular levels of amyloid beta-protein via proteolysis by insulin-degrading enzyme. J Neurosci 20:1657–1665
Vitale C, Marcelli V, Allocca R, Santangelo G, Riccardi P, Erro R, Amboni M, Pellecchia MT, Cozzolino A, Longo K, Picillo M, Moccia M, Agosti V, Sorrentino G, Cavaliere M, Marciano E, Barone P (2012) Hearing impairment in Parkinson’s disease: expanding the nonmotor phenotype. Mov Disord 27(12):1530–1535
Vogel T, Benetos A, Verreault R, Kaltenbach G, Kiesmann M, Berthel M (2006) Risk factors for Alzheimer: towards prevention?] [Article in French. Presse Med 35:1309–1316
von Zglinicki T, Serra V, Lorenz M, Saretzki G, Lenzen-Grossimlighaus R, Gessner R, Risch A, Steinhagen-Thiessen E (2000) Short telomeres in patients with vascular dementia: an indicator of low antioxidative capacity and a possible risk factor? Lab Investig 80:1739–1747
Watt FM, Lo Celso C, Silva-Vargas V (2006) Epidermal stem cells: an update. Curr Opin Genet Dev 16:518–524
Whitmer RA, Gunderson EP, Barrett-Connor E, Quesenberry CP Jr., Yaffe K (2005) Obesity in middle age and future risk of dementia: a 27 year longitudinal population based study. BMJ 330(7504):1360–1362
Williams RW, Herrup K (1988) The control of neuron number. Annu Rev Neurosc 11(1):423–453
Wong AC, Ryan AF (2015) Mechanisms of sensorineural cell damage, death and survival in the cochlea. Front Aging Neurosci 7:58
Woo KS, Chook P, Lolin YI, Cheung AS, Chan LT, Sun YY, Sanderson JE, Metreweli C, Celermajer DS (1997) Hyperhomocyst(e)inemia is a risk factor for arterial endothelial dysfunction in humans. Circulation 96:2542–2544
Wu P, Wu X, Jiang T-X, Elsey RM, Temple BL, Divers SJ, Glenn TC, Yuan K, Chen M-H, Widelitz RB, Chuon C-M (2013) Specialized stem cell niche enables repetitive renewal of alligator teeth. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110(22):E2009–E2018
Yan D, Zhu Y, Walsh T, Xie D, Yuan H, Sirmaci A, Fujikawa T, Wong AC, Loh TL, Du L, Grati M, Vlajkovic SM, Blanton S, Ryan AF, Chen ZY, Thorne PR, Kachar B, Tekin M, Zhao HB, Housley GD, King MC, Liu XZ (2013) Mutation of the ATP-gated P2X2 receptor leads to progressive hearing loss and increased susceptibility to noise. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 110:2228–2233
Yao SC, Hart AD, Terzella MJ (2013) An evidence-based osteopathic approach to Parkinson disease. Osteopath Fam Physician 5(3):96–101
Zhan W, Cruickshanks KJ, Klein BE, Klein R, Huang GH, Pankow JS, Gangnon RE, Tweed TS (2010) Generational differences in the prevalence of hearing impairment in older adults. Am J Epidemiol 171:260–266
Zhang P, Tian B (2014) Metabolic syndrome: an important risk factor for Parkinson’s disease. Oxidative Med Cell Longev 2014:729194
Zhao C, Deng W, Gage FH (2008) Mechanisms and functional implications of adult neurogenesis. Cell 132(4):645–660
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
About this article
Cite this article
Libertini, G., Ferrara, N. Aging of perennial cells and organ parts according to the programmed aging paradigm. AGE 38, 35 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-016-9895-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s11357-016-9895-0