Abstract
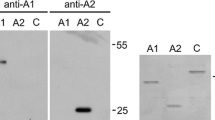
Cardiac ankyrin repeat protein (CARP) and its two close homologs ankrd2 (Arpp) and DARP correspond to a conserved gene family of muscle ankyrin repeat proteins (MARPs). All three genes respond to a variety of stress/strain injury signals with their cytokine-like induction and can associate with the elastic region of titin/connectin. Recently, both CARP and ankrd2 were observed to be elevated in cardiac diseases as well as muscular dystrophies, implicating their joined signaling in muscle diseases. Here we show that CARP in the yeast two-hybrid system (YTH) interacts with itself and desmin. To further verify the YTH data and to investigate possible CARP subunit structure(s), we expressed CARP in E. coli. Expressed CARP has an apparent mobility of about 70 kDa on gel filtration, corresponding to a dimeric species. Yeast two-hybrid experiments using amino- and carboxyterminal deletion clones suggest that CARP, ankrd2, and DARP contain potential coiled-coil dimerization motifs within their unique aminoterminal domains that mediate the formation of homo-dimers. In contrast, we could not detect the formation of hetero-dimers between CARP, ankrd2, and DARP. Therefore, when CARP, ankrd2 and DARP are upregulated in disease/stress states, they are likely to be sorted into distinct structural protein complexes since CARP within the MARP family contains a unique aminoterminal dimerization motif.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Arber S, Hunter JJ, Ross J Jr, Hongo M, Sansig G, Borg J, Perriard JC, Chien KR, Caroni P, (1997) MLP-deficient mice exhibit a disruption of cardiac cytoarchitectural organization, dilated cardiomyopathy, and heart failure Cell 88:393–403
Bakay M, Zhao P, Chen J, Hoffman EP, (2002) A web-accessible complete transcriptome of normal human and DMD muscle Neuromuscul Disord 12:S125–141
Bang ML, Mudry RE, McElhinny AS, Trombitas K, Geach AJ, Yamasaki R, Sorimachi H, Granzier H, Gregorio CC, Labeit S, (2001) Myopalladin, a novel 145-kilodalton sarcomeric protein with multiple roles in Z-disc and I-band protein assemblies J Cell Biol 153:413–427
Barash IA, Mathew L, Ryan AF, Chen J, Lieber RL, (2004) Rapid muscle-specific gene expression changes after a single bout of eccentric contractions in the mouse Am J Physiol Cell Physiol 286:C355–C364
Baumeister A, Arber S, Caroni P, (1997) Accumulation of muscle ankyrin repeat protein transcript reveals local activation of primary myotube endcompartments during muscle morphogenesis J Cell Biol 139:1231–1242
Centner T, Yano J, Kimura E, McElhinny AS, Pelin K, Witt CC, Bang ML, Trombitas K, Granzier H, Gregorio CC, Sorimachi H, Labeit S, (2001) Identification of muscle specific ring finger proteins as potential regulators of the titin kinase domain J Mol Biol 306:717–726
Clark KA, McElhinny AS, Beckerle MC, Gregorio CC, (2002). Striated muscle cytoarchitecture: an intricate web of form and function Annu Rev Cell Dev Biol 18:637–706
Dubendorff JW, Studier FW, (1991) Creation of a T7 autogene. Cloning and expression of the gene for bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase under control of its cognate promoter J Mol Biol 219:61–68
Granzier H, Labeit S, (2004) The giant protein titin: a major player in myocardial mechanics, signaling, and disease Circ Res 94:284–295
Gregorio CC, Trombitas K, Centner T, Kolmerer B, Stier G, Kunke K, Suzuki K, Obermayer F, Herrmann B, Granzier H, Sorimachi H, Labeit S, (1998) The NH2 terminus of titin spans the Z-disc; Its interaction with a novel 19 kD ligand (T-cap) is required for sarcomeric integrity J Cell Biol 143:1013–1027
Ishiguro N, Baba T, Ishida T, Takeuchi K, Osaki M, Araki N, Okada E, Takahashi S, Saito M, Watanabe M, Nakada C, Tsukamoto Y, Sato K, Ito K, Fukayama M, Mori S, Ito H, Moriyama M. (2002) Carp, a cardiac ankyrin-repeated protein, and its new homologue, Arpp, are differentially expressed in heart, skeletal muscle, and rhabdomyosarcomas Am J Pathol 160:1767–1778
Ikeda K, Emoto N, Matsuo M, Yokoyama M, (2003) Molecular identification and characterization of a novel nuclear protein whose expression is up-regulated in insulin-resistant animals J Biol Chem 278:3514–3520
Jeyaseelan R, Poizat C, Baker RK, Abdishoo S, Isterabadi LB, Lyons GE, Kedes LA, (1997) A novel cardiac-restricted target for doxorubicin. CARP, a nuclear modulator of gene expression in cardiac progenitor cells and cardiomyocytes J Biol Chem 272:22800–22808
Kemp TJ, Sadusky TJ, Saltisi F, Carey N, Moss J, Yang SY, Sassoon DA, Goldspink G, Coulton GR, (2000) Identification of Ankrd2, a novel skeletal muscle gene coding for a stretch-responsive ankyrin-repeat protein Genomics 66:229–241
Knöll R, Hoshijima M, Hoffman HM, Person V, Lorenzen-Schmidt I, Bang ML, Hayashi T, Shiga N, Yasukawa H, Schaper W, McKenna W, Yokoyama M, Schork NJ, Omens JH, McCulloch AD, Kimura A, Gregorio CC, Poller W, Schaper J, Schultheiss HP, Chien KR, (2002) The cardiac mechanical stretch sensor machinery involves a Z disc complex that is defective in a subset of human dilated cardiomyopathy Cell 111:943–955
Maruyama K, (1997) Connectin/titin, giant elastic protein of muscle FASEB J 11:341–345
Miller MK, Bang ML, Witt CC, Labeit D, Trombitas K, Watanabe K, Granzier H, Gregorio CC, Labeit S, (2003) The muscle ankyrin repeat proteins: CARP, ankrd2/Arpp and DARP as a family of titin filament based stress response molecules J Mol Biol 333:951–964
Miller MK, Granzier H, Ehler E, Gregorio CC, (2004) The sensitive giant: the role of titin-based stretch sensing complexes in the heart Trends Cell Biol 14:119–126
Mues A, van der Ven PFM, Young P, Fürst DO, Gautel M, (1998) Two immunoglobulin-like domains of the Z-disc portion of titin interact in a conformation-dependent way with telethonin FEBS Lett 428:111–114
Nagueh SF, Shah G, Wu Y, Torre-Amione G, King NM, Lahmers S, Witt CC, Becker K, Labeit S, Granzier HL, (2004) Altered titin expression, myocardial stiffness, and left ventricular function in patients with dilated cardiomyopathy Circulation 110:155–162
Nakada C, Tsukamoto Y, Oka A, Nonaka I, Takeda S, Sato K, Mori S, Ito H, Moriyama M, (2003) Cardiac-restricted ankyrin-repeat protein is differentially induced in duchenne and congenital muscular dystrophy Lab Invest 83:711–719
Peters D, Barash IA, Burdi M, Yuan PS, Mathew L, Friden J, Lieber RL, (2003) Asynchronous functional, cellular and transcriptional changes after a bout of eccentric exercise in the rat J Physiol 553:947–957
Porter JD, Khanna S, Kaminski HJ, Rao JS, Merriam AP, Richmonds CR, Leahy P, Li J, Guo W, Andrade FH, (2002) A chronic inflammatory response dominates the skeletal muscle molecular signature in dystrophin-deficient mdx mice Hum Mol Genet 11:263–72
Ravulapalli R, Garcia Diaz B, Campbell RL and Davies PL (2005) Homodimerization of calpain 3 penta-EF-hand domain. Biochem J 388:585–591
Sepulveda JL, Vlahopoulos S, Iyer D, Belaguli N, Schwartz RJ, (2002) Combinatorial expression of GATA4, Nkx2-5, and serum response factor directs early cardiac gene activity J Biol Chem 277:25775–25782
Sorimachi H, Kinbara K, Kimura S, Takahashi M, Ishiura S, Sasagawa N, Sorimachi N, Shimada H, Tagawa K, Maruyama K, Suzuki K, (1995) Muscle-specific calpain, p94, responsible for limb girdle muscular dystrophy type 2A, associates with connectin through IS2, a p94-specific sequence J Biol Chem 270:31158–31162
Squire JM, (1997) Architecture and function in the muscle sarcomere Curr Opin Struct Biol 7:247–257
Tskhovrebova L, Trinick J, (2003) Titin: properties and family relationships Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol 4:679–689
Toko H, Zhu W, Takimoto E, Shiojima I, Hiroi Y, Zou Y, Oka T, Akazawa H, Mizukami M, Sakamoto M, Terasaki F, Kitaura Y, Takano H, Nagai T, Nagai R, Komuro I, (2002) Csx/Nkx2-5 is required for homeostasis and survival of cardiac myocytes in the adult heart J Biol Chem 277:24735–24743
Vicart P, Dupret JM, Hazan J, Li Z, Gyapay G, Krishnamoorthy R, Weissenbach J, Fardeau M, Paulin D, (1996) Human desmin gene: cDNA sequence, regional localization and exclusion of the locus in a familial desmin-related myopathy Hum Genet 98:422–429
Wanker EE, Rovira C, Scherzinger E, Hasenbank R, Walter S, Tait D, Colicelli J, Lehrach H, (1997) HIP-I: a huntingtin interacting protein isolated by the yeast two-hybrid system Hum Mol Genet 6:487–495
Watanabe K, Nair P, Labeit D, Kellermayer MS, Greaser M, Labeit S, Granzier H, (2002b) Molecular mechanics of cardiac titin’s PEVK and N2B spring elements J Biol Chem 277:11549–11558
Way M, Gooch J, Pope B, Weeds AG, (1989) Expression of human plasma gelsolin in Escherichia coli and dissection of actin binding sites by segmental deletion mutagenesis J Cell Biol 109:593–605
Witt CC, Ono Y, Puschmann E, McNabb M, Wu Y, Gotthardt M, Witt SH, Haak M, Labeit D, Gregorio CC, Sorimachi H, Granzier H, Labeit S. (2004) Induction and myofibrillar targeting of CARP, and suppression of the Nkx2.5 pathway in the MDM mouse with impaired titin-based signaling J Mol Biol 336:145–154
Wu Y, Bell SP, Trombitas K, Witt CC, Labeit S, LeWinter MM, Granzier H, (2002). Changes in titin isoform expression in pacing-induced cardiac failure give rise to increased passive muscle stiffness Circulation 106:1384–1389
Zou Y, Evans S, Chen J, Kuo HC, Harvey RP, Chien KR, (1997). CARP, a cardiac ankyrin repeat protein, is downstream in the Nkx2-5 homeobox gene pathway Development 124:793–800
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to thank Richard Carmouche from the EMBL gene core for expert technical assistance. This work was supported by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (LA668/7-2 to SL and LA1969/1-1 to DL).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Witt, S.H., Labeit, D., Granzier, H. et al. Dimerization of the cardiac ankyrin protein CARP: Implications for MARP titin-based signaling. J Muscle Res Cell Motil 26, 401–408 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10974-005-9022-9
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10974-005-9022-9