Abstract
This review examines the hypothesis that the function of the α 6β 4 integrin is altered substantially as normal epithelia undergo malignant transformation and progress to invasive carcinoma and that the functions of this integrin contribute to the behavior of aggressive carcinoma cells. Specifically, α 6β 4 functions primarily as an adhesion receptor in normal epithelia, often as a component of hemidesmosomes and associated with intermediate filaments. Factors in the host-tumor microenvironment have the potential to mobilize α 6β 4 from hemidesmosomes and promote its association with F-actin in lamellae and filopodia, a process that is mediated by PKC-dependent phosphorylation of the β 4 cytoplasmic domain. Importantly, this altered localization of α 6β 4 appears to be coupled to an activation of its signaling potential, which may occur through its association with growth factor receptors or lipid rafts, possibilities that are not mutually exclusive. The primal signaling event triggered by α 6β 4 appears to be activation of PI3-K and this activation has profound consequences on the migration, invasion and survival of carcinoma cells. Arguably, the ability of α 6β 4 to stimulate the PI3-K-dependent translation of VEGF and possibly other growth factors may be the most significant contribution of this integrin to carcinoma because of the potential autocrine and paracrine effects of these factors.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mercurio A: Receptors for the laminins. Achieving specificity through cooperation. Trends Cell Biol 5: 419–423, 1995
Kikkawa Y, Sanzen N, Fujiwara H, Sonnenberg A, Sekiguchi K: Integrin binding specificity of laminin-10/11: laminin-10/11 are recognized by alpha 3 beta 1, alpha 6 beta 1 and alpha 6 beta 4 integrins. J Cell Sci 113: 869–876, 2000
Pouliot N, Connolly LM, Moritz RL, Simpson RJ, Burgess AW: Colon cancer cells adhesion and spreading on autocrine laminin-10 is mediated by multiple integrin receptors and modulated by EGF receptor stimulation. Exp Cell Res 261: 360–371, 2000
Borradori L, Sonnenberg A: Hemidesmosomes—Roles In Adhesion, Signaling and Human Diseases. Curr Opin Cell Biol 8: 647–656, 1996
De Melker AA, Sonnenberg A: Integrins: alternative splicing as a mechanism to regulate ligand binding and integrin signaling events. Bioessays 21: 499–509, 1999
Dowling J, Yu QC, Fuchs E: Beta-4 Integrin Is Required For Hemidesmosome Formation, Cell Adhesion and Cell Survival. J Cell Biol 134: 559–572, 1996
Vanderneut R, Krimpenfort P, Calafat J, Niessen CM, Sonnenberg A: Epithelial detachment due to absence of hemidesmosomes in integrin beta-4 null mice. Nature Genetics 13: 366–369, 1996
DiPersio CM, van der Neut R, Georges-Labouesse E, Kreidberg JA, Sonnenberg A, Hynes RO: alpha3beta1 and alpha6beta4 integrin receptors for laminin-5 are not essential for epidermal morphogenesis and homeostasis during skin development. J Cell Sci 113: 3051–3062, 2000
Vidal F, Aberdam D, Miquel C, Christiano AM, Pulkkinen L, Uitto J, Ortonne JP, Meneguzzi G: Integrin beta 4 mutations associated with junctional epidermolysis bullosa with pyloric atresia. Nature Genetics 10: 229–234, 1995
Borradori L, Sonnenberg A: Structure and function of hemidesmosomes: More than simple adhesion complexes. J Invest Dermatol 112: 411–418, 1999
Green KJ, Jones JCR: Desmosomes and hemidesmosomes—structure and function of molecular components. FASEB J 10: 871–881, 1996
Hemler ME, Crouse C, Sonnenberg A: Association of the VLA alpha 6 subunit with a novel protein. A possible alternative to the common VLA beta 1 subunit on certain cell lines. J Biol Chem 264: 6529-6535, 1989
Tamura RN, Rozzo C, Starr L, Chambers J, Reichardt LF, Cooper HM, Quaranta V: Epithelial integrin alpha 6 beta 4: complete primary structure of alpha 6 and variant forms of beta 4. J Cell Biol 111: 1593–1604, 1990
Jones JC, Kurpakus MA, Cooper HM, Quaranta V: A function for the integrin alpha 6 beta 4 in the hemidesmosome. Cell Regul 2: 427–438, 1991
Sonnenberg A, Calafat J, Janssen H, Daams H, van der Raaij-Helmer LM, Falcioni R, Kennel SJ, Aplin JD, Baker J, Loizidou M and et al: Integrin alpha 6/beta 4 complex is located in hemidesmosomes, suggesting a major role in epidermal cell-basement membrane adhesion. J Cell Biol 113: 907-917, 1991
Mainiero F, Murgia C, Wary KK, Curatola AM, Pepe A, Blumemberg M, Westwick JK, Der CJ, Giancotti FG: The coupling of alpha6beta4 integrin to Ras-MAP kinase pathways mediated by Shc controls keratinocyte proliferation. Embo J 16: 2365–2375, 1997
Falcioni R, Kennel SJ, Giacomini P, Zupi G, Sacchi A, Expression of tumor antigen correlated with metastatic potential of Lewis lung carcinoma and B16 melanoma clones in mice. Cancer Res 46: 5772–5778, 1986
Kennel SJ, Foote LJ, Falcioni R, Sonnenberg A, Stringer CD, Crouse C, Hemler ME: Analysis of the tumor-associated antigen TSP-180. Identity with alpha 6-beta 4 in the integrin superfamily. J Biol Chem 264: 15515-15521, 1989
Rabinovitz I, Mercurio AM: The integrin alpha 6 beta 4 and the biology of carcinoma. Biochem Cell Biol 74: 811–821, 1996
Mercurio AM, Rabinovitz I: Towards a mechanistic understanding of tumor invasion-lessons from the alpha 6 beta 4integrin. Semin Cancer Biol 11: 129–141, 2001
Chao C, Lotz MM, Clarke AC, Mercurio AM: A function for the integrin alpha6beta4 in the invasive properties of colorectal carcinoma cells. Cancer Res 56: 4811–4819, 1996
Shaw LM, Rabinovitz I, Wang HH, Toker A, Mercurio AM: Activation of phosphoinositide 3-OH kinase by the alpha6beta4 integrin promotes carcinoma invasion. Cell 91: 949–960, 1997
O'Connor KL, Shaw LM, Mercurio AM: Release of cAMP gating by the alpha6beta4 integrin stimulates lamellae formation and the chemotactic migration of invasive carcinoma cells. J Cell Biol 143: 1749–1760, 1998
Rabinovitz I, Mercurio AM: The integrin alpha6beta4 functions in carcinoma cell migration on laminin-1 by mediating the formation and stabilization of actin- containing motility structures. J Cell Biol 139: 1873–1884, 1997
Bachelder RE, Ribick MJ, Marchetti A, Falcioni R, Soddu S, Davis KR, Mercurio AM: p53 inhibits alpha 6 beta 4 integrin survival signaling by promoting the caspase 3-dependent cleavage of AKT/PKB. J Cell Biol 147: 1063–1072, 1999
Rabinovitz I, Toker A, Mercurio AM: Protein kinase C-dependent mobilization of the alpha6beta4 integrin from hemidesmosomes and its association with actin-rich cell protrusions drive the chemotactic migration of carcinoma cells. J Cell Biol 146: 1147–1160, 1999
Rabinovitz I, Gipson IK, Mercurio AM: Traction Forces Mediated by alpha6beta4 Integrin: Implications for Basement Membrane Organization and Tumor Invasion. Mol Biol Cell 12: 4030–4043, 2001
Chung J, Bachelder RE, Lipscomb EA, Shaw LM, Mercurio AM: Integrin (alpha 6 beta 4) regulation of eIF-4E activity and VEGF translation: a survival mechanism for carcinoma cells. J Cell Biol 158: 165–174, 2002
Goldfinger LE, Hopkinson SB, deHart GW, Collawn S, Couchman JR, Jones JC: The alpha3 laminin subunit, alpha6beta4 and alpha3beta1 integrin coordinately regulate wound healing in cultured epithelial cells and in the skin. J Cell Sci 112: 2615–2629, 1999
Gambaletta D, Marchetti A, Benedetti L, Mercurio AM, Sacchi A, Falcioni R: Cooperative signaling between alpha(6)beta(4) integrin and ErbB-2 receptor is required to promote phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase-dependent invasion. J Biol Chem 275: 10604–10610, 2000
Hintermann E, Bilban M, Sharabi A, Quaranta V: Inhibitory Role of alpha6beta4-associated erbB-2 and Phosphoinositide 3- Kinase in Keratinocyte Haptotactic Migration Dependent on alpha3beta1 Integrin. J Cell Biol 153: 465–478, 2001
Owens DM, Romero MR, Gardner C, Watt FM: Suprabasal alpha6beta4 integrin expression in epidermis results in enhanced tumourigenesis and disruption of TGFbeta signaling. J Cell Sci 116: 3783–3791, 2003
Nguyen BP, Gil SG, Carter WG: Deposition of laminin 5 by keratinocytes regulates integrin adhesion and signaling. J Biol Chem 275: 31896–31907, 2000
Geuijen CA, Sonnenberg A: Dynamics of the alpha6beta4 integrin in keratinocytes. Mol Biol Cell 13: 3845–3858, 2002
Spinardi L, Rietdorf J, Nitsch L, Bono M, Tacchetti C, Way M, Marchisio PC: A dynamic podosome-like structure of epithelial cells. Exp Cell Res 295: 360–374, 2004
Weaver VM, Lelievre S, Lakins JN, Chrenek MA, Jones JC, Giancotti F, Werb Z, Bissell MJ: Beta4 integrin-dependent formation of polarized three-dimensional architecture confers resistance to apoptosis in normal and malignant mammary epithelium. Cancer Cell 2: 205–216, 2002
Zahir N, Lakins JN, Russell A, Ming W, Chatterjee C, Rozenberg GI, Marinkovich MP, Weaver VM: Autocrine laminin-5 ligates alpha6beta4 integrin and activates RAC and NFkappaB to mediate anchorage-independent survival of mammary tumors. J Cell Biol 163: 1397–1407, 2003
Russell AJ, Fincher EF, Millman L, Smith R, Vela V, Waterman EA, Dey CN, Guide S, Weaver VM, Marinkovich MP: Alpha 6 beta 4 integrin regulates keratinocyte chemotaxis through differential GTPase activation and antagonism of alpha 3 beta 1 integrin. J Cell Sci 116: 3543–3556, 2003
Santoro MM, Gaudino G, Marchisio PC: The MSP receptor regulates alpha6beta4 and alpha3beta1 integrins via 14-3-3 proteins in keratinocyte migration. Dev Cell 5: 257–271, 2003
Trusolino L, Bertotti A, Comoglio PM: A signaling adapter function for alpha6beta4 integrin in the control of HGF-dependent invasive growth. Cell 107: 643–654, 2001
Gagnoux-Palacios L, Dans M, van't Hof W, Mariotti A, Pepe A, Meneguzzi G, Resh MD, Giancotti FG: Compartmentalization of integrin alpha6beta4 signaling in lipid rafts. J Cell Biol 162: 1189–1196, 2003
Dajee M, Lazarov M, Zhang JY, Cai T, Green CL, Russell AJ, Marinkovich MP, Tao S, Lin Q, Kubo Y, Khavari PA: NF-kappaB blockade and oncogenic Ras trigger invasive human epidermal neoplasia. Nature 421: 639–643, 2003
Mercurio AM, Rabinovitz I, Shaw LM: The alpha 6 beta 4 integrin and epithelial cell migration. Curr Opin Cell Biol 13: 541–545, 2001
Giannelli G, Astigiano S, Antonaci S, Morini M, Barbieri O, Noonan DM, Albini A: Role of the alpha3beta1 and alpha6beta4 integrins in tumor invasion. Clin Exp Mets 19: 217–223, 2002
Shaw LM: Identification of insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS-1) and IRS-2 as signaling intermediates in the alpha6beta4 integrin-dependent activation of phosphoinositide 3-OH kinase and promotion of invasion. Mol Cell Biol 21: 5082–5093, 2001
Lipscomb EA, Dugan AS, Rabinovitz I, Mercurio AM: Use of RNA interference to inhibit integrin (alpha6beta4)-mediated invasion and migration of breast carcinoma cells. Clin Exp Mets 20: 569–576, 2003
Ridley AJ, Schwartz MA, Burridge K, Firtel RA, Ginsberg MH, Borisy G, Parsons JT, Horwitz AR: Cell migration: Integrating signals from front to back. Science 302: 1704–1709, 2003
Stetler-Stevenson WG, Aznavoorian S, Liotta LA: Tumor cell interactions with the extracellular matrix during invasion and metastasis. Annu Rev Cell Biol 9: 541–573, 1993
Wiche G: Role of plectin in cytoskeleton organization and dynamics. J Cell Sci 111: 2477–2486, 1998
Geerts D, Fontao L, Nievers MG, Schaapveld RQ, Purkis PE, Wheeler GN, Lane EB, Leigh IM, Sonnenberg A: Binding of integrin alpha6beta4 to plectin prevents plectin association with F-actin but does not interfere with intermediate filament binding. J Cell Biol 147: 417–434, 1999
Bachelder RE, Wendt MA, Fujita N, Tsuruo T, Mercurio AM: The cleavage of Akt/protein kinase B by death receptor signaling is an important event in detachment-induced apoptosis. J Biol Chem 276: 34702–34707, 2001
Bachelder RE, Crago A, Chung J, Wendt MA, Shaw LM, Robinson G, Mercurio AM: Vascular endothelial growth factor is an autocrine survival factor for neuropilin-expressing breast carcinoma cells. Cancer Res 61: 5736–5740, 2001
Rossen K, Dahlstrom KK, Mercurio AM, Wewer UM: Expression of the alpha 6 beta 4 integrin by squamous cell carcinomas and basal cell carcinomas: possible relation to invasive potential? Acta Derm Venereol 74: 101–105, 1994
Mainiero F, Pepe A, Yeon M, Ren Y, Giancotti FG: The intracellular functions of alpha6beta4 integrin are regulated by EGF. J Cell Biol 134: 241–253, 1996
Alt A, Ohba M, Li L, Gartsbein M, Belanger A, Denning MF, Kuroki T, Yuspa SH, Tennenbaum T: Protein kinase Cdelta-mediated phosphorylation of alpha6beta4 is associated with reduced integrin localization to the hemidesmosome and decreased keratinocyte attachment. Cancer Res 61: 4591–4598, 2001
Rabinovitz I, Tsomo L, Mercurio AM: Protein kinase C-alpha phosphorylation of specific serines in the connecting segment of the beta 4 integrin regulates the dynamics of type II hemidesmosomes. Mol Cell Biol 24: 4351–4360, 2004
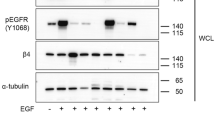
Mariotti A, Kedeshian PA, Dans M, Curatola AM, Gagnoux-Palacios L, Giancotti FG: EGF-R signaling through Fyn kinase disrupts the function of integrin alpha6beta4 at hemidesmosomes: role in epithelial cell migration and carcinoma invasion. J Cell Biol 155: 447–458, 2001
Falcioni R, Antonini A, Nistico P, Di Stefano S, Crescenzi M, Natali PG, Sacchi A: Alpha6beta4 and alpha6beta1 integrins associate with ErbB-2 in human carcinoma cell lines. Exp Cell Res. 236: 76–85, 1997
Riese DJ, Stern DF: Specificity within the EGF family/ErbB receptor family signaling network. Bioessays 20: 41–48, 1998
Comoglio PM, Trusolino L: Invasive growth: from development to metastasis. J Clin Invest 109: 857–862, 2002
Chung J, Yoon SO, Lipscomb EA, Mercurio AM: The Met receptor and alpha6 beta4 integrin can function independently to promote carcinoma invasion. J Biol Chem 279: 32287–32293, 2004
Gingras AC, Raught B, Sonenberg N: Regulation of translation initiation by FRAP/mTOR. Genes Dev 15: 807–826, 2001
Shaw RJ, Bardeesy N, Manning BD, Lopez L, Kosmatka M, DePinho RA, Cantley LC: The LKB1 tumor suppressor negatively regulates mTOR signaling. Cancer Cell 6: 91–99, 2004
Jauliac S, Lopez-Rodriguez C, Shaw LM, Brown LF, Rao A, Toker A: The role of NFAT transcription factors in integrin-mediated carcinoma invasion. Nat Cell Biol 4: 540–544, 2002
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lipscomb, E.A., Mercurio, A.M. Mobilization and activation of a signaling competent α6β4integrin underlies its contribution to carcinoma progression. Cancer Metastasis Rev 24, 413–423 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-005-5133-4
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10555-005-5133-4