Abstract
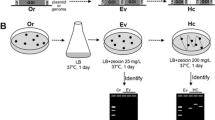
Boron is an industrially and biologically important element. However, the mechanisms of boron tolerance and its transport in bacteria and many other living systems are still not clearly understood. In this study, the boron resistance level of a boron-tolerant bacterium, Bacillus boroniphilus DSM 17376, was improved up to 300 mmol l−1 boron, by employing an in vivo evolutionary engineering strategy based on batch selection under continuous exposure to gradually increasing boron stress levels. The resistance was heterogeneous within the final mutant population which ranged from about 1- to 16-fold of the wild type resistance at 150 mmol l−1 boron stress level. Boron-resistant mutants had significant cross-resistance to iron and copper stresses, and were also cross-resistant to salt (NaCl) stress, suggesting a common resistance mechanism between these stress types. Additionally, highly boron-resistant mutants had up to 2.8-fold higher boron contents than the wild-type, when exposed to high levels of (150 mmol l−1) continuous boron stress throughout their cultivation. It was shown that evolutionary engineering is a successful approach to significantly increase bacterial boron resistance and investigate the complex mechanism of boron tolerance and transport in microbial systems.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed I, Fujiwara T (2010) Mechanism of boron tolerance in soil bacteria. Can J Microbiol 56:22–26
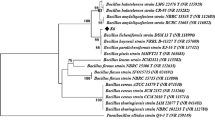
Ahmed I, Yokota A, Fujiwara T (2007a) A novel highly boron tolerant bacterium, Bacillus boroniphilus sp. nov., isolated from soil, that requires boron for its growth. Extremophiles 11:217–224
Ahmed I, Yokota A, Fujiwara T (2007b) Chimaereicella boritolerans sp nov., a boron-tolerant and alkaliphilic bacterium of the family Flavobacteriaceae isolated from soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57(Pt 5):986–992
Ahmed I, Yokota A, Fujiwara T (2007c) Gracibacillus boraciitolerans sp nov, a highly boron-tolerant and moderately halotolerant bacterium isolated from soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 57(Pt 4):796–802
Argust P (1998) Distribution of boron in the environment. Biol Trace Elem Res 66:131–143
Banuelos GS, LeDuc D, Johnson J (2010) Evaluating the tolerance of young hybrid poplar trees to recycled waters high in salinity and boron. Int J Phytoremediation 12:419–439
Bennett A, Rowe RI, Soch N, Eckhert CD (1999) Boron stimulates yeast (Saccharomyces cerevisiae) growth. J Nutr 129:2236–2238
Bolanos L, Redondo-Nieto M, Bonilla I, Wall LG (2002) Boron requirement in the Discaria trinervis (Rhamnaceae) and Frankia symbiotic relationship. Its essentiality for Frankia BCU110501 growth and nitrogen fixation. Physiol Plant 115:563–570
Bolanos L, Lukaszewski K, Bonilla I, Blevins D (2004) Why Boron? Plant Physiol Biochem 42:907–912
Bonilla I, Garcia-Gonzalez M, Mateo P (1990) Boron requirement in Cyanobacteria. Its possible role in early evolution of photosynthetic organisms. Plant Physiol 94:1554–1560
Çakar ZP, Seker UOS, Tamerler C, Sonderegger M, Sauer U (2005) Evolutionary engineering of multiple-stress resistant Saccharomyces cerevisiae. FEMS Yeast Res 5:569–578
Çakar ZP, Alkim C, Turanli B, Tokman N, Akman S, Sarikaya M, Tamerler C, Benbadis L, François JM (2009) Isolation of cobalt hyper-resistant mutants of Saccharomyces cerevisiae by in vivo evolutionary engineering approach. J Biotechnol 143:130–138
Chen GH (2004) Electrochemical technologies in wastewater treatment. Sep Purif Technol 38:11–41
Chen X, Schauder S, Potier N, van Dorsselaer A, Pelczer I, Bassler BL, Hughson FM (2002) Structural identification of a bacterial quorum-sensing signal containing boron. Nature 415:545–549
Daliparthy J, Barker AV, Mondal SS (1994) Potassium fractions with other nutrients in crops- a review focusing on the tropics. J Plant Nutr 17:1859–1886
Darmency V, Renaud P (2006) Tin-free radical reactions mediated by organoboron compounds. Radicals in Synthesis I: Methods and Mechanisms. Top Curr Chem 263:71–106
Dykhuizen DE, Hartl DL (1983) Selection in chemostats. Microbiol Rev 47:150–168
Gentz MC, Grace JK (2006) A review of boron toxicity in insects with an emphasis on termites. J Agric Urban Entomol 23:201–207
Grieve CM, Poss JA, Grattan SR, Suarez DL, Smith TE (2010) The combined effects of salinity and excess boron on mineral ion relations in broccoli. Sci Hortic 125:179–187
Guimaraes PMR, François J, Parrou JL, Teixeria JA, Domingues L (2008) Adaptive evolution of a lactose-consuming Saccharomyces cerevisiae recombinant. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:1748–1756
Hayes JE, Reid RJ (2004) Boron tolerance in barley is mediated by efflux of boron from the roots. Plant Physiol 136:3376–3382
Howe PD (1998) A review of boron effects in the environment. Biol Trace Elem Res 66:153–166
Kaya A, Karakaya HC, Fomenko DE, Gladyshev VN, Koc A (2009) Identification of a novel system for boron transport: Atr1 is a main boron exporter in yeast. Mol Cell Biol 29:3665–3674
Kazanskii AG, Mell H, Terukov EI, Forsh PA (2002) Effect of boron dopant on the photoconductivity of microcrystalline hydrogenated silicon films. Semiconductors 36:41–44
Lawrence CW (1991) Classical mutagenesis techniques. Methods Enzymol 194:456–464
Lewin JC (1966) Physiological studies of the boron requirement of the diatom, Cylindrotheca fusiformis Reimann and Lewin. J Exp Bot 17:473–479
Lindquist J (2010) A Five-Tube MPN Table (on-line). Available from: http://www.jlindquist.net/generalmicro/102dil3a.html. August 2010, last date accessed
Martinez-Ballesta MD, Bastias E, Zhu C, Schaffner AR, Gonzalez-Maro B, Gonzalez-Murua C, Carjaval M (2008) Boric acid and salinity effects on maize roots. Response of aquaporins ZmPIP1 and ZmPIP2, and plasma membrane H+-ATPase, in relation to water and nutrient uptake. Physiol Plant 132:479–490
Miwa K, Fujiwara T (2010) Boron transport in plants: co-ordinated regulation of transporters. Ann Bot 105:1103–1108
Miwa H, Ahmed I, Yokota A, Fujiwara T (2009) Lysinibacillus parviboronicapiens sp nov, a low-boron-containing bacterium isolated from soil. Int J Syst Evol Microbiol 59(Pt 6):1427–1432
Nielsen FH (2002) The nutritional importance and pharmacological potential of boron for higher animals and human. In: Goldbach HE, Rerkasem B, Wimmer MA, Brown PH, Thellier M, Bell RW (eds) Boron in plant and animal nutrition. Kluwer Academic/Plenum Publishers, New York, pp 37–50
Pahl MV, Culver BD, Vaziri ND (2005) Boron and the kidney. J Ren Nutr 15:362–370
Rowe RI, Eckhert CD (1999) Boron is required for zebrafish embryogenesis. J Exp Biol 202:1649–1654
Rowe RI, Bouzan C, Nabili S, Eckhert CD (1998) The response of trout and zebrafish embryos to low and high boron concentrations is U-shaped. Biol Trace Elem Res 66:262–270
Russek E, Colwell RR (1983) Computation of most probable numbers. Appl Environ Microbiol 45:1646–1650
Sauer U (2001) Evolutionary engineering of industrially important microbial phenotypes. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 73:130–166
Schubert DM (2003) Borates in industrial use. In: Roesky HW, Atwood DA (eds) Group 13 Chemistry III: Industrial Applications. Structure & Bonding, vol 105. Springer Verlag, Berlin, Heidelberg, New York, pp 1–40
Scialli AR, Bonde JP, Bruske-Hohlfeld I, Culver BD, Li YH, Sullivan FM (2010) An overview of male reproductive studies of boron with an emphasis on studies of highly exposed Chinese workers. Reprod Toxicol 29:10–24
Smith TE, Grattan SR, Grieve CM, Poss JA, Suarez DL (2010) Salinity’s influence on boron toxicity in broccoli: II. Impacts on boron uptake, uptake mechanisms and tissue ion relations. Agric Water Manage 97:783–791
Sonderegger M, Sauer U (2003) Evolutionary engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for anaerobic growth on xylose. Appl Environ Microbiol 69:1990–1998
Sonderegger M, Schümperli M, Sauer U (2005) Selection of quiescent Escherichia coli with high metabolic activity. Metab Eng 7:4–9
Steiner P, Sauer U (2003) Long-term continuous evolution of acetate resistant Acetobacter aceti. Biotechnol Bioeng 84:40–44
van Maris AJA, Winkler AA, Kuyper M, de Laat WTAM, van Dijken JP, Pronk JT (2007) Development of efficient xylose fermentation in Saccharomyces cerevisiae: xylose isomerase as a key component. Biofuels 108:179–204
Warington K (1923) The effect of boric acid and borax on the broad bean and certain other plants. Ann Bot 37:629–672
Weikert C, Sauer U, Bailey JE (1997) Use of a glycerol-limited, long-term chemostat for isolation of Escherichia coli mutants with improved physiological properties. Microbiology 143:1567–1574
White PJ, Brown PH (2010) Plant nutrition for sustainable development and global health. Ann Bot 105:1073–1080
Wiedemann B, Boles E (2008) Codon-optimized bacterial genes improve L-arabinose fermentation in recombinant Saccharomyces cerevisiae. Appl Environ Microbiol 74:2043–2050
Wisselink HW, Toirkens MJ, Berriel MRF, Winkler AA, van Dijken JP, Pronk JT, van Maris AJA (2007) Engineering of Saccharomyces cerevisiae for efficient anaerobic alcoholic fermentation of l-arabinose. Appl Environ Microbiol 73:4881–4891
Wisselink HW, Toirkens MJ, Wu Q, Pronk JT, van Maris AJA (2009) Novel evolutionary engineering approach for accelerated utilization of glucose, xylose, and arabinose mixtures by engineered Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains. Appl Environ Microbiol 75:907–914
Yermiyahu U, Ben-Gal A, Sarig P, Zipilevitch E (2007) Boron toxicity in grapevine (Vitis vinifera L.) in conjunction with salinity and rootstock effects. J Hortic Sci Biotechnol 82:547–554
Yermiyahu U, Ben-Gal A, Keren R, Reid RJ (2008) Combined effect of salinity and excess boron on plant growth and yield. Plant Soil 304:73–87
Acknowledgments
We thank Burcu Turanlı-Yıldız for technical assistance, and Ali Dinler for help with PCA. This work was supported by National Boron Research Institute (BOREN-2008-Ç0180, PI: Z.P. Çakar).
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Şen, M., Yılmaz, Ü., Baysal, A. et al. In vivo evolutionary engineering of a boron-resistant bacterium: Bacillus boroniphilus . Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 99, 825–835 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-011-9557-2
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10482-011-9557-2