Abstract
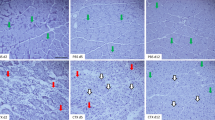
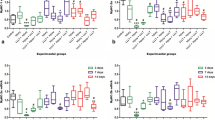
The purpose of this study was to examine the effect of ultrasound on inflammatory skeletal muscle in vitro and in vivo. C2C12 cells were cultured in medium with or without TNF-α or IL-1β. After stimulation with cytokines, the cells received ultrasound or sham exposure. Furthermore, the tibialis anterior (TA) muscle in C57BL/6 mice injured by cardiotoxin (CTX) were dissected after a series of ultrasound treatments and examined. Exposure of C2C12 cells to ultrasound resulted in down-regulation of cyclooxygenase-2 (COX-2) mRNA and protein expression induced by TNF-α or IL-1β, and up-regulated myogenin mRNA and protein depressed by TNF-α or IL-1β. In injured TA muscle induced by CTX, ultrasound caused increase of COX-2 mRNA at 1 day after ultrasound treatment, however, at day 5, reduction of COX-2 mRNA and protein. At day 5, ultrasound caused increase of myogenin mRNA and protein, increase of fast myosin protein, and increase of paired-box transcription factor 7 positive cells. At day 7, the cross-sectional area of myofibers in the ultrasound exposure side was significantly larger than that on the control side. In conclusion, ultrasound stimulation may be a better candidate as a medical remedy to promote myogenesis in inflammatory muscle states, such as muscle injury.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Acharyya, S., K. J. Ladner, L. L. Nelsen, J. Damrauer, P. J. Reiser, S. Swoap, et al. Cancer cachexia is regulated by selective targeting of skeletal muscle gene products. J. Clin. Invest. 114:370–378, 2004.
Agarwal, S., J. Deschner, P. Long, A. Verma, C. Hofman, C. H. Evans, et al. Role of NF-kappaB transcription factors in antiinflammatory and proinflammatory actions of mechanical signals. Arthritis Rheum. 50:3541–3548, 2004.
Allen, R. E., and L. K. Boxhorn. Regulation of skeletal muscle satellite cell proliferation and differentiation by transforming growth factor-beta, insulin-like growth factor I, and fibroblast growth factor. J. Cell. Physiol. 138:311–315, 1989.
Azuma, Y., M. Ito, Y. Harada, H. Takagi, T. Ohta, and S. Jingushi. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound accelerates rat femoral fracture healing by acting on the various cellular reactions in the fracture callus. J. Bone Miner. Res. 16:671–680, 2001.
Bondesen, B. A., S. T. Mills, K. M. Kegley, and G. K. Pavlath. The COX-2 pathway is essential during early stage of skeletal muscle regeneration. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 287:475–483, 2004.
Buckley, M. J., A. J. Banes, L. G. Levin, B. E. Sumpio, M. Sato, R. Jordan, et al. Osteoblasts increase their rate of division and align in response to cyclic, mechanical tension in vitro. Bone Miner. 4:225–236, 1988.
Chan, Y. S., K. Y. Hsu, C. H. Kuo, S. D. Lee, S. C. Chen, W. J. Chen, et al. Using low-intensity pulsed ultrasound to improve muscle healing after laceration injury: an in vitro and in vivo study. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 36:743–751, 2010.
Chan, C. W., L. Qin, K. M. Lee, W. H. Cheung, J. C. Cheng, and K. S. Leung. Dose-dependent effect of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound on callus formation during rapid distraction osteogenesis. J. Orthop. Res. 24:2072–2079, 2006.
Chandran, R., T. J. Knobloch, M. Anghelina, and S. Agarwal. Biomechanical signals upregulate myogenic gene induction in the presence or absence of inflammation. Am. J. Physiol. Cell Physiol. 293:267–276, 2007.
Claes, L., and B. Willie. The enhancement of bone regeneration by ultrasound. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 93:384–398, 2007.
Dalla-Bona, D. A., E. Tanaka, T. Inubushi, H. Oka, A. Ohta, H. Okada, et al. Cementoblast response to low- and high-intensity ultrasound. Arch. Oral Biol. 53:318–323, 2008.
Deasy, B. M., Z. Qu-Peterson, J. S. Greenberger, and J. Huard. Mechanisms of muscle stem cell expansion with cytokines. Stem Cells 20:50–60, 2002.
Eutwistle, A., D. H. Curtis, and R. J. Zalin. Myoblast fusion is regulated by a prostanoid of the one series independently of a rise in cyclic AMP. J. Cell Biol. 103:857–866, 1986.
Fong, Y., L. L. Moldawer, M. Marano, H. Wei, A. Barber, K. Manogue, et al. Cachectin/TNF or IL-1 alpha induces cachexia with redistribution of body proteins. Am. J. Physiol. 256:659–665, 1989.
Gebauer, D., and J. Correll. Pulsed low-intensity ultrasound: a new salvage procedure for delayed unions and nonunions after leg lengthening in 23 children. J. Pediatr. Orthop. 6:750–754, 2005.
Guttridge, D. C. Signaling pathways weigh in on decisions to make or break skeletal muscle. Curr. Opin. Clin. Nutr. Metab. Care 7:443–450, 2004.
Heckman, J. D., J. P. Ryaby, J. McCabe, J. J. Frey, and R. F. Kilcoyne. Acceleration of tibial fracture-healing by non-invasive, low-intensity pulsed ultrasound. J. Bone Joint Surg. Am. 74:26–34, 1994.
Inubushi, T., E. Tanaka, E. B. Rego, M. Kitagawa, A. Kawazoe, A. Ohta, et al. Effects of ultrasound on the proliferation and differentiation of cementoblast lineage cells. J. Periodontol. 79:1984–1990, 2008.
Iwata, A., S. Fuchioka, K. Hiraoka, M. Masuhara, and K. Kami. Characteristics of locomotion, muscle strength, and muscle tissue in regenerating rat skeletal muscles. Muscle Nerve 41:694–701, 2010.
Kokubu, T., N. Matsui, H. Fujioka, et al. Low intensity pulsed ultrasound exposure increases prostaglandin E2 production via the induction of cyclooxygenase-2 mRNA in mouse osteoblasts. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 256:284–287, 1999.
Lowe, D. A., and S. E. Alway. Stretch-induced myogenin, MyoD, and MRF4 expression and acute hypertrophy in quail slow-tonic muscle are not dependent upon satellite cell proliferation. Cell Tissue Res. 296:531–539, 1999.
Madhavan, S., M. Anghelina, B. Rath-Deschner, E. Wypasek, A. John, J. Deschner, et al. Biomechanical signals exert sustained attenuation of proinflammatory gene induction in articular chondrocytes. Osteoarthritis Cartilage 14:1023–1032, 2006.
Markert, C. D., M. A. Merrick, T. E. Kirby, and S. T. Devor. Nonthermal ultrasound and exercise in skeletal muscle regeneration. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 86:1304–1310, 2005.
Morioka, S., K. Goto, A. Kojima, T. Naito, Y. Matsuba, T. Akema, et al. Functional overloading facilitates the regeneration of injured soleus muscles in mice. J. Physiol. Sci. 58:397–404, 2008.
Naidu, P. S., D. C. Ludolph, R. Q. To, T. J. Hinterberger, and S. F. Konieczny. Myogenin and MEF2 function synergistically to activate the MRF4 promoter during myogenesis. Mol. Cell. Biol. 15:2707–2718, 1995.
Nakamura, T., S. Fujihara, T. Katsura, K. Yamamoto, T. Inubushi, K. Tanimoto, et al. Effects of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound on the expression and activity of hyaluronan synthase and hyaluronidase in IL-1b-stimulated synovial cells. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 38:3363–3370, 2010.
Nakamura, T., S. Fujihara, K. Yamamoto-Nagata, T. Katsura, T. Inubushi, and E. Tanaka. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound reduces the inflammatory activity of synovitis. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 39:2964–2971, 2011.
Pelosi, L., C. Giacinti, C. Nardis, G. Borsellino, E. Rizzuto, C. Nicoletti, et al. Local expression of IGF-1 accelerates muscle regeneration by rapidly modulating inflammatory cytokines and chemokines. FASEB J. 21:1393–1402, 2007.
Rantanen, J., O. Thorsson, P. Wollmer, T. Hurme, and H. Kalimo. Effect of therapeutic ultrasound on the regeneration of skeletal myofibers after experimental muscle injury. Am. J. Sport Med. 27:54–59, 1999.
Rauch, C., and P. T. Loughna. Cyclosporin-A inhibits stretch-induced changes in myosin heavy chain expression in C2C12 skeletal muscle cells. Cell Biochem. Funct. 24:55–61, 2006.
Rawls, A., M. R. Valdez, W. Zhang, J. Richardson, W. H. Klein, and E. N. Olson. Overlapping functions of the myogenic bHLH genes MRF4 and MyoD revealed in double mutant mice. Development 125:2349–2358, 1998.
Rego, E. B., T. Inubushi, M. Miyauchi, A. Kawazoe, E. Tanaka, T. Takata, and K. Tanne. Ultrasound stimulation attenuates root resorption of rat replanted molars and impairs tumor necrosis factor-α signaling in vitro. J. Periodontal Res. 46:648–654, 2011.
Renno, A. C., R. L. Toma, S. M. Feitosa, K. Fernandes, P. S. Bossini, P. de Oliveira, et al. Comparative effects of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound and low-level laser therapy on injured skeletal muscle. Photomed. Laser Surg. 29:5–10, 2011.
Robertson, T. A., M. A. Maley, M. D. Grounds, and J. M. Papadimitriou. The role of macrophage in skeletal muscle regeneration with particular reference of chemotaxis. Exp. Cell Res. 207:321–331, 1993.
Sakai, N., N. Agata, M. Inoue-Miyazu, K. Kawakami, K. Kobayashi, M. Sokabe, et al. Involvement of PI3 K/Akt/TOR pathway in stretch-induced hypertrophy of myotube. Muscle Nerve 41:100–106, 2010.
Sant’Anna, E. F., R. M. Leven, A. S. Virdi, and D. R. Sumner. Effect of low intensity pulsed ultrasound and BMP-2 on rat bone marrow stromal cell gene expression. J. Orthop. Res. 23:646–652, 2005.
Schultz, E., D. L. Jaryszak, and C. R. Valliere. Response of satellite cells to focal skeletal muscle injury. Muscle Nerve 8:217–222, 1985.
Schutzle, U. B., M. J. Wakelam, and D. Pette. Prostaglandins and cyclic AMP stimulate creatine kinase synthesis but not fusion in cultured embryonic chick muscle cells. Biochem. Biophy. Acta. 805:204–210, 1984.
Seale, P., L. A. Sabourin, A. Girgis-Gabardo, A. Mansouri, P. Gruss, and M. E. Rudnicki. Pax7 is required for the specification of myogenic satellite cells. Cell 102:777–786, 2000.
Sena, K., R. M. Leven, K. Mazhar, D. R. Sumner, and A. S. Virdi. Early gene response to low-intensity pulsed ultrasound in rat osteoblastic cells. Ultrasound Med. Biol. 31:703–708, 2005.
Shimazaki, A., K. Inui, Y. Azuma, N. Nishimura, and Y. Yamano. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound accelerates bone maturation in distraction osteogenesis in rabbits. J. Bone Joint Surg. Br. 82:1077–1082, 2000.
Shiraishi, R., C. Masaki, A. Toshinaga, T. Okinaga, T. Nishihara, N. Yamanaka, T. Nakamoto, and R. Hosokawa. The effects of low-intensity pulsed ultrasound exposure on gingival cells. J. Periodontol. 82:1498–1503, 2011.
Signori, L. U., S. T. da Costa, A. F. Neto, R. M. Pizzolotto, C. Beck, G. Sbruzzi, et al. Haematological effect of pulsed ultrasound in acute muscular inflammation in rats. Physiotherapy 97:163–169, 2011.
St. Pierre, B. A., and J. G. Tidball. Differential response of macrophage subpopulations to soleus muscle reloading after rat hindlimb suspension. J. Appl. Physiol. 77:290–297, 1994.
Szelenyi, E. R., and M. L. Urso. Time-course analysis of injured skeletal muscle suggests a critical involvement of ERK1/2 signaling in the acute inflammatory response. Muscle Nerve 45:552–561, 2012.
Takakura, Y., N. Matsui, S. Yoshiya, H. Fujioka, H. Muratsu, M. Tsunoda, et al. Low-intensity pulsed ultrasound enhances early healing of medial collateral ligament injuries in rats. J. Ultrasound Med. 21:283–288, 2002.
Ten Broek, R. W., S. Grefte, and J. W. Von den Hoff. Regulatory factor and cell populations involved in skeletal muscle regeneration. J. Cell. Physiol. 224:7–16, 2010.
Yang, S., M. Alnaqeeb, H. Simpson, and G. Goldspink. Cloning and characterization of an IGF-1 isoform expressed in skeletal muscle subjected to stretch. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 17:487–495, 1996.
Zalin, R. J. The role of hormones and prostanoids in the in vitro proliferation and differentiation of human myoblasts. Exp. Cell Res. 172:265–281, 1987.
Zhou, S., A. Schmelz, T. Seufferlein, Y. Li, J. Zhao, and M. G. Bachem. Molecular mechanisms of low intensity pulsed ultrasound in human skin fibroblasts. J. Biol. Chem. 279:54463–54469, 2004.
Acknowledgments
We are grateful to Atsumi Ohta and Hiroshi Yoshiwara for providing the ultrasound devices and technical support for the experiments.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Associate Editor Konstantinos Konstantopoulos oversaw the review of this article.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nagata, K., Nakamura, T., Fujihara, S. et al. Ultrasound Modulates the Inflammatory Response and Promotes Muscle Regeneration in Injured Muscles. Ann Biomed Eng 41, 1095–1105 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-013-0757-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-013-0757-y