Abstract
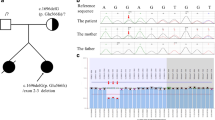
Bartter syndrome is a genetic disorder with hypokalemic metabolic alkalosis and is classified into five types. Type IV Bartter syndrome is a type of neonatal Bartter syndrome with sensorineural deafness and has been recently shown to be caused by mutations in the BSND gene. Owing to the rarity of this disease, only a limited number of mutations have been reported. We analyzed the BSND gene in a patient with type IV Bartter syndrome. The patient was delivered at 37 weeks, with normal body weight, and his neonatal course was uneventful. He was examined for developmental delay and polyuria at age 1 year 8 months and was found to have hypokalemia, metabolic alkalosis, hyperreninemic hyperaldosteronism, and sensorineural deafness. He developed end-stage renal failure at age 15 years, and renal transplantation was performed. We identified compound heterozygous mutations (Q32X and G47R) in the BSND gene. Each mutation was inherited from the parents. The Q32X mutation is a novel mutation and the first nonsense mutation identified in this gene. The mild perinatal clinical features of the patient were similar to those of a patient reported with a homozygous G47R mutation. However, the severity of renal failure suggested that factors other than this gene might affect the manifestation of renal abnormalities.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Hebert SC (2003) Bartter syndrome. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens 12:527–532
Naesens M, Steels P, Verberckmoes R, Vanrenterghem Y, Kuypers D (2004) Bartter’s and Gitelman’s syndromes: from gene to clinic. Nephron Physiol 96:65–78
Simon DB, Karet FE, Hamdan JM, DiPietro A, Sanjad SA, Lifton RP (1996) Bartter’s syndrome, hypokalaemic alkalosis with hypercalciuria, is caused by mutations in the Na-K-2Cl cotransporter NKCC2. Nat Genet 13:183–188
Simon DB, Karet FE, Rodriguez-Soriano J, Hamdan JH, DiPietro A, Trachtman H, Sanjad SA, Lifton RP (1996) Genetic heterogeneity of Bartter’s syndrome revealed by mutations in the K+ channel, ROMK. Nat Genet 14:152–156
Simon DB, Bindra RS, Mansfield TA, Nelson-Williams C, Mendonca E, Stone R, Schurman S, Nayir A, Alpay H, Bakkaloglu A, Rodriguez-Soriano J, Morales JM, Sanjad SA, Taylor CM, Pilz D, Brem A, Trachtman H, Griswold W, Richard GA, John E, Lifton RP (1997) Mutations in the chloride channel gene, CLCNKB, cause Bartter’s syndrome type III. Nat Genet 17:171–178
Birkenhager R, Otto E, Schurmann MJ, Vollmer M, Ruf EM, Maier-Lutz I, Beekmann F, Fekete A, Omran H, Feldmann D, Milford DV, Jeck N, Konrad M, Landau D, Knoers NV, Antignac C, Sudbrak R, Kispert A, Hildebrandt F (2001) Mutation of BSND causes Bartter syndrome with sensorineural deafness and kidney failure. Nat Genet 29:310–314
Watanabe S, Fukumoto S, Chang H, Takeuchi Y, Hasegawa Y, Okazaki R, Chikatsu N, Fujita T (2002) Association between activating mutations of calcium-sensing receptor and Bartter’s syndrome. Lancet 360:692–694
Landau D, Shalev H, Ohaly M, Carmi R (1995) Infantile variant of Bartter syndrome and sensorineural deafness: a new autosomal recessive disorder. Am J Med Genet 59:454–459
Estevez R, Boettger T, Stein V, Birkenhager R, Otto E, Hildebrandt F, Jentsch TJ (2001) Barttin is a Cl− channel beta-subunit crucial for renal Cl− reabsorption and inner ear K+ secretion. Nature 414:558–561
Schlingmann KP, Konrad M, Jeck N, Waldegger P, Reinalter SC, Holder M, Seyberth HW, Waldegger S (2004) Salt wasting and deafness resulting from mutations in two chloride channels. N Engl J Med 350:1314–1319
Miyamura N, Matsumoto K, Taguchi T, Tokunaga H, Nishikawa T, Nishida K, Toyonaga T, Sakakida M, Araki E (2003) Atypical Bartter syndrome with sensorineural deafness with G47R mutation of the beta-subunit for ClC-Ka and ClC-Kb chloride channels, barttin. J Clin Endocrinol Metab 88:781–786
Shalev H, Ohali M, Kachko L, Landau D (2003) The neonatal variant of Bartter syndrome and deafness: preservation of renal function. Pediatrics 112:628–633
Jeck N, Reinalter SC, Henne T, Marg W, Mallmann R, Pasel K, Vollmer M, Klaus G, Leonhardt A, Seyberth HW, Konrad M (2001) Hypokalemic salt-losing tubulopathy with chronic renal failure and sensorineural deafness. Pediatrics 108:E5
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by grants from the Ministry of Education, Science, Sports, and Culture of Japan.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kitanaka, S., Sato, U., Maruyama, K. et al. A compound heterozygous mutation in the BSND gene detected in Bartter syndrome type IV. Pediatr Nephrol 21, 190–193 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-005-2091-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00467-005-2091-6