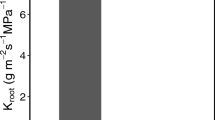Abstract
A common cylindropuntia in the northwestern Sonoran Desert, Opuntia acanthocarpa, was investigated for the following hypotheses: its lower elevational limit is set by high temperatures, so its seedlings require nurse plants; its upper elevational limit is set by freezing; spine shading is the least at intermediate elevations; and changes in plant size and frequency with elevation reflect net CO2 uptake ability. For four elevations ranging from 230 m to 1,050 m, the mean height of O. acanthocarpa approximately doubled and its frequency increased 14-fold. Nurse plants were associated with only 4% of O. acanthocarpa less than 20 cm tall at the two lower elevations compared with 57% at 1,050 m, where putative freezing damage was especially noticeable, suggesting that nurse plants protect from low temperature damage. Spine shading of the stem doubled from the lowest to the highest elevation. Net CO2 uptake, which followed a Crassulacean acid metabolism pattern, was maximal at day/night air temperatures of 25/15°C and was halved by 4 weeks of drought and by reducing the photosynthetic photon flux from 30 to 12 mol m–2 day–1. The root system of O. acanthocarpa was shallow, with a mean depth of only 9 cm for the largest plants. Root growth was substantial and similar for plants at 25/15°C and 35/25°C, decreasing over 70-fold at 15/5°C and 45/35°C. Based on cellular uptake of the vital stain neutral red, neither roots nor stems tolerated tissue temperatures below –5°C for 1 h while both showed substantial high temperature acclimation, roots tolerating 1 h at 61°C and stems 1 h at 70°C for plants grown at 35/25°C. The increase in height and frequency of O. acanthocarpa with elevation apparently reflected both a greater ability for net CO2 uptake and greater root growth and hence water uptake. This species achieves its greatest ecological success at elevations where it becomes vulnerable to low temperature damage.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Electronic Publication
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Nobel, P.S., Bobich, E.G. Plant frequency, stem and root characteristics, and CO2 uptake for Opuntia acanthocarpa: elevational correlates in the northwestern Sonoran Desert. Oecologia 130, 165–172 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1007/s004420100793
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s004420100793