Abstract
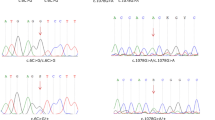
Cosegregation of markers on chromosome 5q12.3-q14.1 with profound congenital deafness in two Pakistani families (PKDF041 and PKDF141) defines a new recessive deafness locus, DFNB49. A maximum two-point lod score of 4.44 and 5.94 at recombination fraction θ=0 was obtained for markers D5S2055 and D5S424 in families PKDF041 and PKDF141, respectively. Haplotype analysis revealed an 11 cM linkage region flanked by markers D5S647 (74.07 cM) and D5S1501 (85.25 cM). Candidate deafness genes in this region include SLC30A5, OCLN, GTF2H2, and BTF3, encoding solute carrier family 30 (zinc transporter) member 5, occludin, RNA polymerase II transcription initiation factor, and basic transcription factor 3, respectively. Sequence analysis of the coding exons of SLC30A5 in DNA samples from two affected individuals of families PKDF041 and PKDF141 revealed no mutation. The mapping of DFNB49 further confirms the heterogeneity underlying autosomal recessive forms of nonsyndromic deafness.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed ZM, Riazuddin S, Bernstein SL, Ahmed Z, Khan S, Griffith AJ, Morell RJ, Friedman TB, Wilcox ER (2001) Mutations of the protocadherin gene PCDH15 cause Usher syndrome type 1F. Am J Hum Genet 69:25–34
Ahmed ZM, Smith TN, Riazuddin S, Makishima T, Ghosh M, Bokhari S, Menon PSN, Deshmukh D, Griffith AJ, Riazuddin S, Friedman TB, Wilcox ER (2002) Nonsyndromic recessive deafness DFNB18 and Usher syndrome type IC are allelic mutations of USHIC. Hum Genet 110:527–531
Ahmed ZM, Riazuddin S, Ahmad J, Bernstein SL, Guo Y, Sabar MF, Sieving P, Riazuddin S, Griffith AJ, Friedman TB, Belyantseva IA, Wilcox ER (2003a) PCDH15 is expressed in the neurosensory epithelium of the eye and ear and mutant alleles are responsible for both USH1F and DFNB23. Hum Mol Genet 12:3215–3223
Ahmed ZM, Riazuddin S, Riazuddin S, Wilcox ER (2003b) The molecular genetics of Usher syndrome. Clin Genet 63:431–444
Ben-Yosef T, Belyantseva IA, Saunders TL, Hughes ED, Kawamoto K, Van Itallie CM, Beyer LA, Halsey K, Gardner DJ, Wilcox ER, Rasmussen J, Anderson JM, Dolan DF, Forge A, Raphael Y, Camper SA, Friedman TB (2003) Claudin 14 knockout mice, a model for autosomal recessive deafness DFNB29, are deaf due to cochlear hair cell degeneration. Hum Mol Genet 12:2049–2061
Bork JM, Peters LM, Riazuddin S, Bernstein SL, Ahmed ZM, Ness SL, Polomeno R, Ramesh A, Schloss M, Srisailpathy CR, Wayne S, Bellman S, Desmukh D, Ahmed Z, Khan SN, Kaloustian VM, Li XC, Lalwani A, Riazuddin S, Bitner-Glindzicz M, Nance WE, Liu XZ, Wistow G, Smith RJ, Griffith AJ, Wilcox ER, Friedman TB, Morell RJ (2001) Usher syndrome 1D and nonsyndromic autosomal recessive deafness DFNB12 are caused by allelic mutations of the novel cadherin-like gene CDH23. Am J Hum Genet 68:26–37
Cohen MM, Gorlin RJ (1995) Epidemiology, etiology and genetic patterns. In: Gorlin RJ, Toriello HV, Cohen MM (eds) Hereditary hearing loss and its syndromes. Oxford University Press, Oxford, pp 43–61
De Kok YJ, Van der Maarel SM, Bitner-Glindzicz M, Huber I, Monaco AP, Malcolm S, Pembrey ME, Ropers HH, Cremers FP (1995) Association between X-linked mixed deafness and mutations in the POU domain gene POU3F4. Science 267:685–688
Delpire E, Lu J, England R, Dull C, Thorne T (1999) Deafness and imbalance associated with inactivation of the secretory Na-K-2Cl co-transporter. Nat Genet 22:192–195
Everett LA, Glaser B, Beck JC, Idol JR, Buchs A, Heyman M, Adawi F, Hazani E, Nassir E, Baxevanis AD, Sheffield VC, Green ED (1997) Pendred syndrome is caused by mutations in a putative sulphate transporter gene (PDS). Nat Genet 17:411–422
Friedman TB, Griffith AJ (2003) Human nonsyndromic sensorineural deafness. Annu Rev Genomics Hum Genet 4:341–402
Grimberg J, Nawoschik S, Belluscio L, McKee R, Turck A, Eisenberg A (1989) A simple and efficient non-organic procedure for the isolation of genomic DNA from blood. Nucleic Acids Res 17:8390
Hussain R, Bittles AH (1998) The prevalence and demographic characteristics of consanguineous marriages in Pakistan. J Biosoc Sci 30:261–275
Kubisch C, Schroeder BC, Friedrich T, Lutjohann B, El-Amraoui A, Marlin S, Petit C, Jentsch TJ (1999) KCNQ4, a novel potassium channel expressed in sensory outer hair cells, is mutated in dominant deafness. Cell 96:437–446
Leon PE, Raventos H, Lynch E, Morrow J, King MC (1992) The gene for an inherited form of deafness maps to chromosome 5q31. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 89:5181–5184
Li XC, Everett LA, Lalwani AK, Desmukh D, Friedman TB, Green ED, Wilcox ER (1998) A mutation in PDS causes non-syndromic recessive deafness. Nat Genet 18:215–217
Park HJ, Shaukat S, Liu XZ, Hahn SH, Naz S, Ghosh M, Kim HN, Moon SK, Abe S, Tukamoto K, Riazuddin S, Kabra M, Erdenetungalag R, Radnaabazar J, Khan S, Pandya A, Usami SI, Nance WE, Wilcox ER, Riazuddin S, Griffith AJ (2003) Origins and frequencies of SLC26A4 (PDS) mutations in east and south Asians: global implications for the epidemiology of deafness. J Med Genet 40:242–248
Peters LM, Anderson DW, Griffith AJ, Grundfast KM, San Agustin TB, Madeo AC, Friedman TB, Morell RJ (2002) Mutation of a transcription factor, TFCP2L3, causes progressive autosomal dominant hearing loss, DFNA28. Hum Mol Genet 11:2877–2885
Pieke-Dahl S, Moller CG, Kelley PM, Astuto LM, Cremers CWRJ, Gorin MB, Kimberling WJ (2000) Genetic heterogeneity of Usher syndrome type II: localisation to chromosome 5q. J Med Genet 37:256–262
Povey S, Lovering R, Bruford E, Wright M, Lush M, Wain H (2001) The HUGO Gene Nomenclature Committee (HGNC). Hum Genet 109:678–680
Saitou M, Furuse M, Sasaki H, Schulzke JD, Fromm M, Takano H, Noda T, Tsukita S (2000) Complex phenotype of mice lacking occludin, a component of tight junction strands. Mol Biol Cell 11:4131–4142
Schaffer AA (1996) Faster linkage analysis computations for pedigrees with loops or unused alleles. Hum Hered 46:226–235
Usami S, Abe S, Weston M D, Shinkawa H, Van Camp G, Kimberling WJ (1999) Nonsyndromic hearing loss associated with enlarged vestibular aqueduct is caused by PDS mutations. Hum Genet 104:188–192
Vahava O, Morell R, Lynch ED, Weiss S, Kagan ME, Ahituv N, Morrow JE, Lee MK, Skvorak AB, Morton CC, Blumenfeld A, Frydman M, Friedman TB, King MC, Avraham KB (1998) Mutation in transcription factor POU4F3 associated with inherited progressive hearing loss in humans. Science 279:1950–1954
Van Camp G, Willems PJ, Smith RJH (1997) Nonsyndromic hearing impairment unparalleled heterogeneity. Am J Hum Genet 60:758–764
Wayne S, Robertson NG, DeClau F, Chen N, Verhoeven K, Prasad S, Tranebjarg L, Morton CC, Ryan A F, Van Camp G, Smith RJH (2001) Mutations in the transcriptional activator EYA4 cause late-onset deafness at the DFNA10 locus. Hum Mol Genet 10:195–200
Weil D, Kussel P, Blanchard S, Levy G, Levi-Acobas F, Drira M, Ayadi H, Petit C (1997) The autosomal recessive isolated deafness, DFNB2, and the Usher 1B syndrome are allelic defects of the myosin-VIIA gene. Nat Genet 16:191–193
Weston MD, Luijendijk MWJ, Humphrey KD, Moller C, Kimberling WJ (2004) Mutations in the VLGR1 gene implicate G-protein signaling in the pathogenesis of Usher syndrome type II. Am J Hum Genet 74:357–366
Wilcox ER, Burton QL, Naz S, Riazuddin S, Smith TN, Ploplis B, Belyantseva I, Ben-Yosef T, Liburd NA, Morell RJ, Kachar B, Wu DK, Griffith AJ, Riazuddin S, Friedman TB (2001) Mutations in the gene encoding tight junction claudin-14 cause autosomal recessive deafness DFNB29. Cell 104:165–172
Xia J, Deng H, Feng Y, Zhang H, Pan Q, Dai H, Long Z, Tang B, Deng H, Chen Y, Zhang R, Zheng D, He Y, Xia K (2002) A novel locus for autosomal dominant nonsyndromic hearing loss identified at 5q31.1–32 in a Chinese pedigree. J Hum Genet 47:635–640
Acknowledgements
We are grateful to the families for their participation in this study. We thank Dr. Dennis Drayna and Dr. Robert Morell for their comments on this manuscript, and Sabiha Nazli and Muhammad Awais for their technical assistance. This study was supported by the Higher Education Commission, Islamabad, Pakistan; the Ministry of Science and Technology, Islamabad, Pakistan; and the International Center for Genetic Engineering and Biotechnology, Trieste, Italy under project CRP/PAK02-01 (contract no. 02/013). Part of this study in USA was supported by intramural funds from the National Institute on Deafness and Other Communication Disorders (1ZO1 DC000035-07 and 1ZO1 DC000039-07).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ramzan, K., Shaikh, R.S., Ahmad, J. et al. A new locus for nonsyndromic deafness DFNB49 maps to chromosome 5q12.3-q14.1. Hum Genet 116, 17–22 (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-004-1205-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00439-004-1205-8