Abstract
Pathogenic, dominant, de novo missense mutations in the glial fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) have been found in the three subtypes of infantile, juvenile and adult Alexander disease.
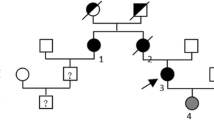
Here we describe four members of an Italian family (32 to 66-yearsold, 2 women and 2 men) affected by adult Alexander disease, the least common and the most clinically variable form.Direct sequencing of all coding regions of the GFAP gene, neurological examination and brain MRI were performed.
Two novel missense mutations were found involving two very close codons, c.[988C > G, 994G > A], leading to p.[Arg330Gly, Glu332Lys]. Clinically, two members exhibited pseudo-bulbar signs, gait ataxia and spasticity, one showed a severe cranial sensory symptomatology, and one subject was asymptomatic.Medulla and cervical cord atrophy was present in all of them on MRI.
Although adult Alexander disease shows a wide clinical variability, a more frequent pattern can be identified characterized by bulbar or pseudo-bulbar signs, gait ataxia, and spasticity, and including on MRI medulla and cervical cord atrophy. Our findings also confirm that the clinical spectrum of adult Alexander disease includes cases without overt neurological involvement and with minimal brain MRI alterations.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Alexander WS (1949) Progressive fibrinoid degeneration of fibrillary astrocytes associated with mental retardation in a hydrocephalic infant. Brain 72:373–381
Borrett D, Becker LE (1985) Alexander's disease – a disease of astrocytes. Brain 108:367–385
Brenner M, Johnson AB, Boesflug-Tanguy O, Rodriguez D, Goldman JE, Messing A (2001) Mutations in GFAP, encoding glial fibrillary acidic protein, are associated with Alexander disease. Nat Genet 27(1):117–120
Brockmann K, Meins M, Taubert A, Trappe R, Grond M, Hanefeld F (2003) A novel GFAP mutation and disseminated white matter lesions: adult Alexander disease? Eur Neurol 50:100–105
Caroli F, Biancheri R, Seri M, Rossi A, Pessagno A, Bugiani M, Corsolini F, Savasta S, Romano S, Antonelli C, Romano A, Pareyson D, Gambero P, Uziel G, Ravazzolo R, Ceccherini I, Filocamo M (2007) GFAP mutations and polymorphisms in 13 unrelated Italian patients affected by Alexander disease. Clin Genet 72(5):427–433
Dinda AK, Sarkar C, Roy S (1990) Rosenthal fibers: An immunohistochemical, ultrastructural and immunoelectron microscopy study. Acta Neuropathol 79:456–460
Fuchs E, Cleveland DW (1998) A structural scaffolding of intermediate filaments in health and disease. Science 279:514–519
Gorospe JR, Naidu S, Johnson AB, Puri V, Raymond GV, Jenkins SD, Pedersen RC, Lewis D, Knowles P, Fernandez R, De Vivi D, van der Knapp MS, Messing A, Brenner M, Hoffman EP (2002) Molecular findings in symptomatic and pre-simptomatic Alexander disease patients. Neurology 58:1494–1500
Habib M,Hassoun J, Ali-Cherif A, Alonzo B, Toga M, Khalil R (1984) Maladie d'Alexander de l'adulte. Rev Neurol 140:179–189
Head MW, Corbin E, Goldman JE (1993) Overexpression and abnormal modification of the stress proteins alpha B-crystallin and HSP27 in Alexander disease. Am J Pathol 143:1743–1753
Howard RS, Greenwood R, Gawler J, Scaravilli F, Marsden CD, Harding AE (1993) A familial disorder associated with palatal myoclonus, other brainstem signs, tetraparesis, ataxia and Rosenthal fibre formation. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 56(9):977–981
Hsiao VC, Tian R, Long H, Der Perng M, Brenner M, Quinlain RA, Goldman JE (2005) Alexander-disease mutation of GFAP causes filament disorganization and decreased solubility of GFAP. J Cell Sci 118(9):2057–2065
Iwaki T, Iwaki A, Tateishi J, Sakaki Y, Goldman JE (1993) Alpha B-crystallin and 27-kd heat shock protein are regulated by stress conditions in the central nervous system and accumulate in Rosenthal fibers. Am J Pathol 143:487–495
Kinoshita T, Imaizumi T, Miura Y, Fujimoto H, Ayabe M, Shoji H, Okamoto Y, Takashima H, Osame M, Nakagawa M (2003) A case of adult-onset Alexander disease with Arg416Trp human glial fibrillary acidic protein gene mutation. Neurosci Lett 350(3):169–172
Li R, Johnson AB, Salomons G, Goldman JE, Naidu S, Quinlan R, Cree B, Ruyle SZ, Banwell B, D'Hooghe M, Siebert JR, Rolf CM, Cox H, Reddy A, González Gutiérrez-Solana L, Collins A, Weller RO, Messing A, van der Knaap M, Brenner M (2005) Glial fibrillary acidic protein mutations in infantile, juvenile, and adult forms of Alexander disease. Ann Neurol 57(3):310–326
Messing A, Head M, Galles K, Galbreath E, Goldman J, Brenner M (1998) Fatal encephalopathy with astrocyte inclusions in GFAP transgenic mice. Am J Pathol 152:391–398
Namekawa M, Takiyama Y, Aoki Y, Takayashiki N, Sakoe K, Shimazaki H, Taguchi T, Tanaka Y, Nishizawa M, Saito K, Matsubara Y, Nakano I (2002) Identification of GFAP gene mutation in hereditary adult-onset Alexander’s disease. Ann Neurol 52:779–785
Okamoto Y, Mitsuyama H, Jonosono M, Hirata K, Arimura K, Osame M, Nakagawa M (2002) Autosomal dominant palatal myoclonus and spinal cord atrophy. J Neurol Sci 195:71–76
Probst EN, Hagel C, Weisz V, Nagel S, Wittkugel O, Zeumer H, Kohlschutter A (2003) Atypical focal MRI lesions in a case of juvenile Alexander’s disease. Ann Neurol 53:118–120
Rosenthal W (1898) Über eine eigentümliche, mit Syringomyelie komplizierte Geschwulst des Rückenmarks. Beitr path Anat 23:111
Russo LS Jr, Aron A, Anderson PJ (1976) Alexander’s disease: a report and a reappraisal. Neurology 26:607–614
Salvi F, Aoki Y, Della Nave R, Vella A, Pastorelli F, Scaglione C, Matsubara Y, Mascalchi M (2005) Adult Alexander’s disease without leukoencephalopathy. Ann Neurol 58 (5):813–814
Schwankhaus JD, Parisi JE, Gulledge WR, Chin L, Currier RD (1995) Hereditary adult-onset Alexander’s disease with palatal myoclonus, spastic paraparesis, and cerebellar ataxia. Neurology 45:2266–2271
Shiihara T, Sawaishi Y, Adachi M, Kato M, Hayasaka K (2004) Asymptomatic hereditary Alexander’s disease caused by a novel mutation in GFAP. J Neurol Sci 225(1–2):125–127
Seil FJ, Schochet SS, Earle KM (1968) Alexander’s disease in an adult: Report of a case. Arch Neurol 19:494–502
Spalke G, Mennel HD (1982) Alexander’s disease in an adult: clinicopathologic study of a case and review of the literature. Clin Neuropathol 1:106–112
Stumpf E, Masson H, Duquette A, Berthelet F, McNabb J, Lortie A, Lesage J, Montplaisir J, Brais B, Cossette P (2003) Adult Alexander disease with autosomal dominant transmission. Arch Neurol 60:1307–1312
Thyagarajan D, Chataway T, Li R, Gai WP, Brenner M (2004) Dominantlyinherited adult-onset leukodystrophy with palatal tremor caused by a mutation in the glial fibrillary acidic protein gene. Mov Disord 19(10):1244–1248
van der Knaap MS, Naidu S, Breiter SN, Blaser S, Stroink H, Springer S, Begeer JC, van Coster R, Barth PG, Thomas NH, Valk J, Powers JM (2001) Alexander disease: diagnosis with MR imaging. AJNR Am J Neuroradiol 22:541–542
van der Knaap MS, Ramesh V, Schiffmann, Blaser S, Kyllerman, Gholkar, Ellison DW, van der Voorn JP, van Dooren SJM, Jacobs C, Barkhof F, Salomons GS (2006) Alexander disease.Ventricular garlands and abnormalities of the medulla and spinal cord. Neurology 66:494–498
van der Knaap MS, Salomons GS, Li R, Franzoni E, Gutiérrez-Solana LG, Smit LME, Robinson R, Ferrie CD, Cree B, Reddy A, Thomas N, Banwell B, Barkhof F, Jakobs C, Johnson A, Messing A, Brenner M (2005) Unusual variants of Alexander's disease. Ann Neurol 57(3):327–338
Walls TJ, Jones RA, Cartlidge NEF, Saunders M (1984) Alexander’s disease with Rosenthal fibre formation in an adult. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry 47:399–403
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Balbi, P., Seri, M., Ceccherini, I. et al. Adult-onset Alexander disease. J Neurol 255, 24–30 (2008). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-007-0654-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00415-007-0654-0