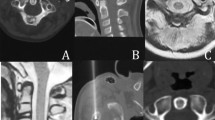
Abstract
Objective
To assess the clinical success and costs of computed tomography (CT)-guided radiofrequency ablation (RFA) of osteoblastoma (OB) and spinal osteoid osteoma (OO).
Materials and methods
Nineteen patients with OB and eight patients with spinal OO were treated with CT-guided RFA. The OBs were localized in the extremities (n = 10), the vertebral column (n = 2), and (juxta-)articular (n = 7). Dedicated procedural techniques included three-dimensional CT-guided access planning in all cases, overlapping RFA needle positions (median, two positions; range, 1–6 RF-electrode positions) within the OB nidus (multiple ablation technique, n = 15), and thermal protection in case of adjacent neural structure in four spinal OO. The data of eight operated OB and ten operated spinal OO patients were used for comparison. Long-term success was assessed by clinical examination and using a questionnaire sent to all operated and RFA-treated patients including visual analogue scales (VAS) regarding the effect of RFA on severity of pain and limitations of daily activities (0–10, with 0 = no pain/limitation up to 10 = maximum or most imaginable pain/limitation).
Results
All patients had a clear and persistent pain reduction until the end of follow-up. The mean VAS score for all spinal OO patients and all OB patients treated either with RFA or with surgical excision significantly decreased for severity of pain at night, severity of pain during the day, and both for limitations of daily and of sports activities.
Conclusions
RFA is an efficient method for treating OB and spinal OO and should be regarded as the first-line therapy after interdisciplinary individual case discussion.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Gangi A, Alizadeh H, Wong L, Buy X, Dietemann JL, Roy C. Osteoid osteoma: percutaneous laser ablation and follow-up in 114 patients. Radiology. 2007;242:293–301.
Motamedi D, Learch TJ, Ishimitsu DN, et al. Thermal ablation of osteoid osteoma: overview and step-by-step guide. Radiographics. 2009;29:2127–41.
Pourfeizi HH, Tabrizi A, Bazavar M, Sales JG. Clinical findings and results of surgical resection of thoracolumbar osteoid osteoma. Asian Spine J. 2014;8:150–5.
Lucas DR. Osteoblastoma. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2010;134:1460–6.
Papaioannou G, Sebire NJ, McHugh K. Imaging of the unusual pediatric ‘blastomas’. Cancer Imaging. 2009;9:1–11.
Orguc S, Arkun R. Primary tumors of the spine. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2014;18:280–99.
Mungo DV, Zhang X, O’Keefe RJ, Rosier RN, Puzas JE, Schwarz EM. COX-1 and COX-2 expression in osteoid osteomas. J Orthop Res. 2002;20:159–62.
Zileli M, Cagli S, Basdemir G, Ersahin Y. Osteoid osteomas and osteoblastomas of the spine. Neurosurg Focus. 2003;15(5):E5.
Boriani S, Amendola L, Bandiera S, et al. Staging and treatment of osteoblastoma in the mobile spine: a review of 51 cases. Eur Spine J. 2012;21:2003–10.
Gasbarrini A, Cappuccio M, Bandiera S, Amendola L, van Urk P, Boriani S. Osteoid osteoma of the mobile spine: surgical outcomes in 81 patients. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2011;36:2089–93.
Omlor GW, Lehner B, Wiedenhöfer B, Deininger C, Weber MA, Rehnitz C. Radiofrequency ablation in spinal osteoid osteoma. Options and limits. Orthopade. 2012;41:618–22.
Li Z, Zhao Y, Hou S, Mao N, Yu S, Hou T. Clinical features and surgical management of spinal osteoblastoma: a retrospective study in 18 cases. PLoS One. 2013;8:e74635. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0074635.
Rehnitz C, Sprengel SD, Lehner B, et al. CT-guided radiofrequency ablation of osteoid osteoma and osteoblastoma: clinical success and long-term follow-up in 77 patients. Eur J Radiol. 2012;81:3426–34.
Rehnitz C, Sprengel SD, Lehner B, et al. CT-guided radiofrequency ablation of osteoid osteoma: correlation of clinical outcome and imaging features. Diagn Interv Radiol. 2013;19:330–9.
Rimondi E, Mavrogenis AF, Rossi G, et al. Radiofrequency ablation for non-spinal osteoid osteomas in 557 patients. Eur Radiol. 2012;22:181–8.
Rosenthal DI, Hornicek FJ, Torriani M, Gebhardt MC, Mankin HJ. Osteoid osteoma: percutaneous treatment with radiofrequency energy. Radiology. 2003;229:171–5.
Schmidt D, Clasen S, Schaefer JF, et al. CT-guided radiofrequency (RF) ablation of osteoid osteoma: clinical long-term results. Fortschr Röntgenstr. 2011;183:381–7.
Rybak LD, Gangi A, Buy X, La Rocca VR, Wittig J. Thermal ablation of spinal osteoid osteomas close to neural elements: technical considerations. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2010;195:W293–8.
Trotta B, Fox MG. Benign osteoid-producing bone lesions: update on imaging and treatment. Semin Musculoskelet Radiol. 2013;17:116–22.
Vanderschueren GM, Taminiau AH, Obermann WR, Bloem JL. Osteoid osteoma: clinical results with thermocoagulation. Radiology. 2002;224:82–6.
Pinto CH, Taminiau AH, Vanderschueren GM, Hogendoorn PC, Bloem JL, Obermann WR. Technical considerations in CT-guided radiofrequency thermal ablation of osteoid osteoma: tricks of the trade. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2002;179:1633–42.
Shrimpton P. Assessment of patient dose in CT. In: European guidelines for multislice computed tomography funded by the European Commission 2004: contract number FIGMCT2000-20078-CT-TIP. Luxembourg: Luxembourg: European Commission; 2004.
Albisinni U, Rimondi E, Malaguti MC, Ciminari R. Radiofrequency thermoablation in the treatment of osteoid osteoma. Radiology. 2004;232:304. author reply 304–305.
Jankharia B, Burute N. Percutaneous radiofrequency ablation for osteoid osteoma: how we do it. Indian J Radiol Imaging. 2009;19:36–42.
Bitsch RG, Rupp R, Bernd L, Ludwig K. Osteoid osteoma in an ex vivo animal model: temperature changes in surrounding soft tissue during CT-guided radiofrequency ablation. Radiology. 2006;238:107–12.
Dupuy DE, Hong R, Oliver B, Goldberg SN. Radiofrequency ablation of spinal tumors: temperature distribution in the spinal canal. AJR Am J Roentgenol. 2000;175:1263–6.
Klass D, Marshall T, Toms A. CT-guided radiofrequency ablation of spinal osteoid osteomas with concomitant perineural and epidural irrigation for neuroprotection. Eur Radiol. 2009;19:2238–43.
Rimondi E, Bianchi G, Malaguti MC, et al. Radiofrequency thermoablation of primary non-spinal osteoid osteoma: optimization of the procedure. Eur Radiol. 2005;15:1393–9.
Woertler K, Vestring T, Boettner F, Winkelmann W, Heindel W, Lindner N. Osteoid osteoma: CT-guided percutaneous radiofrequency ablation and follow-up in 47 patients. J Vasc Interv Radiol. 2001;12:717–22.
Ronkainen J, Blanco Sequeiros R, Tervonen O. Cost comparison of low-field (0.23 T) MRI-guided laser ablation and surgery in the treatment of osteoid osteoma. Eur Radiol. 2006;16:2858–65.
Vanderschueren GM, Obermann WR, Dijkstra SP, Taminiau AH, Bloem JL, van Erkel AR. Radiofrequency ablation of spinal osteoid osteoma: clinical outcome. Spine (Phila Pa 1976). 2009;34:901–4.
Laus M, Albisinni U, Alfonso C, Zappoli FA. Osteoid osteoma of the cervical spine: surgical treatment or percutaneous radiofrequency coagulation? Eur Spine J. 2007;16:2078–82.
Oliveira CR, Mendonça BB, Camargo OP, et al. Classical osteoblastoma, atypical osteoblastoma, and osteosarcoma. A comparative study based on clinical, histological, and biological parameters. Clinics (Sao Paulo). 2007;62:167–74.
Acknowledgments
The authors very much thank Professor Volker Ewerbeck, Heidelberg, for supporting this work and his fruitful comments. Also, we thank Dr. Wolfram Stiller, Heidelberg, for his help with calculating the radiation exposure of the CT-guided radiofrequency ablation.
Conflict of interest
No conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Electronic supplementary material
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Supplemental Fig. 1
(PDF 576 kb)
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Weber, MA., Sprengel, S.D., Omlor, G.W. et al. Clinical long-term outcome, technical success, and cost analysis of radiofrequency ablation for the treatment of osteoblastomas and spinal osteoid osteomas in comparison to open surgical resection. Skeletal Radiol 44, 981–993 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-015-2139-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00256-015-2139-z