Abstract
In the present study we focus on the nucleotide and the inferred amino acid variation occurring in humans and other primate species for mitochondrial NAD+-dependent succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase, a gene recently supposed to contribute to cognitive performance in humans. We determined 2527 bp of coding, intronic, and flanking sequences from chimpanzee, bonobo, gorilla, orangutan, gibbon, and macaque. We also resequenced the entire coding sequence on 39 independent chromosomes from Italian families. Four variable coding sites were genotyped in additional populations from Europe, Africa, and Asia. A test for constancy of the nonsynonymous vs. synonymous rates of nucleotide changes revealed that primates are characterized by largely variable d N /d S ratios. On a background of strong conservation, probably controlled by selective constraints, the lineage leading to humans showed a ratio increased to 0.42. Human polymorphic levels fall in the range reported for other genes, with a pattern of frequency and haplotype structure strongly suggestive of nonneutrality. The comparison with the primate sequences allowed inferring the ancestral state at all variable positions, suggesting that the c.538(C) allele and the associated functional variant is indeed a derived state that is proceeding to fixation. The unexpected pattern of human polymorphism compared to interspecific findings outlines the possibility of a recent positive selection on some variants relevant to new cognitive capabilities unique to humans.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahn J, Won T-W, Kaplan DE, Londin ER, Kuzmic P, Gelernter J, Gruen JR (2002) A detailed physical map of the 6p reading disability locus, including new markers and confirmation of recombination suppression. Hum Genet 111:339–349
Akaboshi S, Hogema BM, Novelletto A, Malaspina P, Salomons GS, Maropoulos GD, Jakobs C, Grompe M, Gibson KM (2003) Mutational spectrum of the succinate semialdehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH5A1) gene and functional analysis of 27 novel disease-causing mutations in patients with SSADH deficiency. Hum Mutat 22:442–450
Bamshad M, Wooding SP (2003) Signatures of natural selection in the human genome. Nat Rev Genet 4:99–111
Blasi P, Pilo Boyl P, Ledda M, Novelletto A, Gibson KM, Jakobs C, Hogema B, Akaboshi S, Loreni F, Malaspina P (2002) Structure of human succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase gene: identification of promoter region and alternatively processed isoforms. Mol Genet Metab 4:348–462
Busch KB, Fromm H (1999) Plant succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase. Cloning, purification, localization in mitochondria, and regulation by adenine nucleotides. Plant Physiol 121:589–597
Caceres M, Lachuer J, Zapala MA, Redmond JC, Kudo L, Geschwind DH, Lockhart DJ, Preuss TM, Barlow C (2003) Elevated gene expression levels distinguish human from non-human primate brains. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:13030–13035
Chambliss KL, Hinson DD, Trettel F, Malaspina P, Novelletto A, Jakobs C, Gibson KM (1998) Two exon-skipping mutations as the molecular basis of succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency (4-hydroxybutyric aciduria). Am J Hum Genet 63:399–408
Chimpanzee Sequencing, Analysis Consortium (2005) Initial sequence of the chimpanzee genome and comparison with the human genome. Nature 437:69–87
Clark AG, Glanowski S, Nielsen R, Thomas PD, Kejariwal A, Todd MA, Tanenbaum DM, Civello D, Lu F, Murphy B, Ferriera S, Wang G, Zheng X, White TJ, Sninsky JJ, Adams MD, Cargill M (2003) Inferring nonneutral evolution from human-chimpanzee-mouse orthologous gene trios. Science 302:1960–1963
Cyranoski D (2002) Almost human. Nature 418:910–912
Deffenbacher KE, Kenyon JB, Hoover DM, Olson RK, Pennington BF, DeFries JC, Smith SD (2004) Refinement of the 6p21.3 quantitative trait locus influencing dyslexia: linkage and association analyses. Hum Genet 115:128–138
den Dunnen JT, Antonarakis SE (2000) Mutation nomenclature extensions and suggestions to describe complex mutations: a discussion. Hum Mutat 15:7–12 (Erratum: Hum Mutat 20:403, 2002)
Dennis C (2005) Chimp genome: branching out. Nature 437:17–19
Dervent A, Gibson KM, Pearl PL, Salomons GS, Jakobs C, Yalcinkaya C (2004) Photosensitive absence epilepsy with myoclonias and heterozygosity for succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase (SSADH) deficiency. Clin Neurophysiol 115:1417–1422
Dorus S, Vallender EJ, Evans PD, Anderson JR, Gilbert SL, Mahowald M, Wyckoff GJ, Malcom CM, Lahn BT (2004) Accelerated evolution of nervous system genes in the origin of Homo sapiens. Cell 119:1027–1040
Enard W, Przeworski M, Fisher SE, Lai CS, Wiebe V, Kitano T, Monaco AP, Paabo S (2002) Molecular evolution of FOXP2, a gene involved in speech and language. Nature 418:869–872
Evans PD, Anderson JR, Vallender EJ, Choi SS, Lahn BT (2004a) Reconstructing the evolutionary history of microcephalin, a gene controlling human brain size. Hum Mol Genet 3:1139–1145
Evans PD, Anderson JR, Vallender EJ, Gilbert SL, Malcom CM, Dorus S, Lahn BT (2004b) Adaptive evolution of ASPM, a major determinant of cerebral cortical size in humans. Hum Mol Genet 13:489–494
Evans PD, Gilbert SL, Mekel-Bobrov N, Vallender EJ, Anderson JR, Vaez-Azizi LM, Tishkoff SA, Hudson RR, Lahn BT (2005) Microcephalin, a gene regulating brain size, continues to evolve adaptively in humans. Science 309:1717–1720
Excoffier L, Smouse PE, Quattro JN (1992) Analysis of molecular variance inferred from metric distance among DNA haplotypes: application to human mitochondrial restriction data. Genetics 131:479–491
Excoffier L, Novembre J, Schneider S (2000) SIMCOAL: a general coalescent program for the simulation of molecular data in interconnected populations with arbitrary demography. J Hered 91:506–509
Fisher SE, DeFries JC (2002) Developmental dyslexia: genetic dissection of a complex cognitive trait. Nat Rev Neurosci 3:767–780
Gimelbrant AA, Skaletsky H, Chess A (2004) Selective pressures on the olfactory receptor repertoire since the human-chimpanzee divergence. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:9019–9022
Hill RS, Walsh CA (2005) Molecular insights into human brain evolution. Nature 437:64–67
Hudson RR, Bailey K, Skarecky D, Kwiatowski J, Ayala FJ (1994) Evidence for positive selection in the superoxide dismutase (Sod) region of Drosophila melanogaster. Genetics 136:1320–1340
Kimura M (1980) A simple method for estimating evolutionary rates of base substitutions through comparative studies of nucleotide sequences. J Mol Evol 16:111–120
King MC, Wilson AC (1975) Evolution at two levels in humans and chimpanzees. Science 188:107–116
Kitano T, Liu YH, Ueda S, Saitou N (2004) Human-specific amino acid changes found in 103 protein-coding genes. Mol Biol Evol 21:936–944
Kouprina N, Pavlicek A, Mochida GH, Solomon G, Gersch W, Yoon YH, Collura R, Ruvolo M, Barrett JC, Woods CG, Walsh CA, Jurka J, Larionov V (2004) Accelerated evolution of the ASPM gene controlling brain size begins prior to human brain expansion. PLoS Biol 2:E126
Kreitman M, Di Rienzo A (2004) Balancing claims for balancing selection. Trends Genet 20:300–304
Kumar S, Tamura K, Jakobsen B, Nei M (2001) MEGA2: Molecular Evolutionary Genetics Analysis software. Arizona State University, Tempe
Londin ER, Meng H, Gruen JR (2003) A transcription map of the 6p22.3 reading disability locus identifying candidate genes. BMC Genomics 4:25–33
Malaspina P, Roetto A, Trettel F, Jodice C, Blasi P, Frontali M, Carella M, Franco B, Camaschella C, Novelletto A (1996) Construction of a YAC contig covering human chromosome 6p22. Genomics 36:399–407
McDonald JH, Kreitman M (1991) Adaptive protein evolution at the Adh locus in Drosophila. Nature 351:652–654
Mekel-Bobrov N, Gilbert SL, Evans PD, Vallender EJ, Anderson JR, Hudson RR, Tishkoff SA, Lahn BT (2005) Ongoing adaptive evolution of ASPM, a brain size determinant in Homo sapiens. Science 309:1720–1722
Murphy TC, Amarnath V, Gibson KM, Picklo MJ Sr (2003) Oxidation of 4-hydroxy-2-nonenal by succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase (ALDH5A). J Neurochem 86:298–305
Pearl PL, Novotny EJ, Acosta MT, Jakobs C, Gibson KM (2003) Succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency in children and adults. Ann Neurol 54 (Suppl 6):S73–S80
Plomin R, Turic DM, Hill L, Turic DE, Stephens M, Williams J, Owen MJ, O’Donovan MC (2004) A functional polymorphism in the succinate-semialdehyde dehydrogenase (aldehyde dehydrogenase 5 family, member A1) gene is associated with cognitive ability. Mol Psychiatry 9:582–586
Rozas J, Rozas R (1999) DNAsp v.3: an integrated program for molecular population genetics and molecular evolution analysis. Bioinformatics 15:174–175
Sabeti PC, Reich DE, Higgins JM, Levine HZ, Richter DJ, Schaffner SF, Gabriel SB, Platko JV, Patterson NJ, McDonald GJ, Ackerman HC, Campbell SJ, Altshuler D, Cooper R, Kwiatkowski D, Ward R, Lander ES (2002) Detecting recent positive selection in the human genome from haplotype structure. Nature 419:832–837
Saito S, Iida A, Sekine A, Ogawa C, Kawauchi S, Higuchi S, Ohno M, Nakamura Y (2002) 906 variations among 27 genes encoding cytochrome P450 (CYP) anzymes and aldehyde dehydrogenases (ALDHs) in the Japanese population. J Hum Genet 47:419–444
Schneider S, Kueffer J-M, Roessli D, Excoffier L (1997) Arlequin ver.1.1: a software for population genetic data analysis. Genetics and Biometry Laboratory, University of Geneva, Geneva, Switzerland
Shi J, Xi H, Wang Y, Zhang C, Jiang Z, Zhang K, Shen Y, Jin L, Zhang K, Yuan W, Wang Y, Lin J, Hua Q, Wang F, Xu S, Ren S, Xu S, Zhao G, Chen Z, Jin L, Huang W (2003) Divergence of the genes on human chromosome 21 between human and other hominoids and variation of substitution rates among transcription units. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 100:8331–8336
Sophos NA, Vasiliou V (2003) Aldehyde dehydrogenase gene superfamily: the 2002 update. Chem Biol Interact 143–144:5–22
Stedman HH, Kozyak BW, Nelson A, Thesier DM, Su LT, Low DW, Bridges CR, Shrager JB, Minugh-Purvis N, Mitchell MA (2004) Myosin gene mutation correlates with anatomical changes in the human lineage. Nature 428:415–418
Stephens JC, Schneider JA, Tanguay DA, Choi J, Acharya T, Stanley SE, Jiang R, Messer CJ, Chew A, Han JH, Duan J, Carr JL, Lee MS, Koshy B, Kumar AM, Zhang G, Newell WR, Windemuth A, Xu C, Kalbfleisch TS, Shaner SL, Arnold K, Schulz V, Drysdale CM, Nandabalan K, Judson RS, Ruano G, Vovis GF (2001a) Haplotype variation and linkage disequilibrium in 313 human genes. Science 293:489–493 (Erratum: Science 293:1048, 2001)
Stephens M, Smith NJ, Donnelly P (2001b) A new statistical method for haplotype reconstruction from population data. Am J Hum Genet 68:978–989
Tajima F (1989) Statistical methods to test for nucleotide mutation hypothesis by DNA polymorphism. Genetics 123:585–595
Thomas PD, Kejariwal A (2004) Coding single-nucleotide polymorphisms associated with complex vs. Mendelian disease: evolutionary evidence for differences in molecular effects. Proc Natl Acad Sci USA 101:15398–15403
Thomas PD, Campbell MJ, Kejariwal A, Mi H, Karlak B, Daverman R, Diemer K, Muruganujan A, Narechania A (2003) PANTHER: a library of protein families and subfamilies indexed by function. Genome Res 13:2129–2141
Thompson JD, Gibson T, Plewniak F, Jeanmougin F, Higgins DG (1997) The ClustalX windows interface: flexible strategies for multiple sequence alignment aided by quality analysis tools. Nucleic Acids Res 24:4876–4882
Wang YQ, Su B (2004) Molecular evolution of microcephalin, a gene determining human brain size. Hum Mol Genet 13:1131–1137
Wong CG, Bottiglieri T, Snead OC 3rd (2003) GABA, gamma-hydroxybutyric acid, and neurological disease. Ann Neurol 54 (Suppl 6):S3–S12
Yang Z (1997) PAML: a program package for phylogenetic analysis by maximum likelihood. CABIOS 13:555–556
Yang Z, Nielsen R (2000) Estimating synonymous and nonsynonymous substitution rates under realistic evolutionary models. Mol Biol Evol 17:32–43
Yang Z, Nielsen R (2002) Codon-substitution models for detecting molecular adaptation at individual sites along specific lineages. Mol Biol Evol 19:908–917
Ziyeh S, Berlis A, Korinthenberg R, Spreer J, Schumacher M (2002) Selective involvement of the globus pallidus and dentate nucleus in succinic semialdehyde dehydrogenase deficiency. Pediatr Radiol 32:598–600
Acknowledgments
We gratefully acknowledge Dr. A. Di Rienzo and two anonymous reviewers for their helpful comments on the first draft of this work. We thank Dr. M. Basile for computational support. This work was supported by grants MIUR 60% to Prof. Carla Jodice, PRIN 2003 and 60% to A.N., and CEGBA (Centro di Eccellenza Geni in campo Biosanitario e Agroalimentare) and European Commission (INPRIMAT, QLRI-CT-2002-01325) to M.R.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
[Reviewing Editor: Dr. Martin Kreitman]
Paola Blasi and Francesca Palmerio contributed equally to the work.
Appendix
Appendix
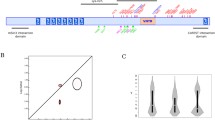
Alignment of sequences obtained in the present paper (see Materials and Methods) to human AL031230 is shown in Fig. A1. Noncoding and coding sequences are in lowercase and uppercase, respectively. Numbering refers to AL031230. Boundaries between noncontiguous genomic sequences concatenated here are shown. The arrow marks the first nucleotide of the mature peptide.
Alignment of sequences obtained in the present paper (see Materials and Methods) to human AL031230. Non coding and coding sequences are in lower and upper case, respectively. Numbering refers to AL031230. Boundaries between non-contiguous genomic sequences here concatenated are shown. The arrow marks the first nucleotide of the mature peptide.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Blasi, P., Palmerio, F., Aiello, A. et al. SSADH Variation in Primates: Intra- and Interspecific Data on a Gene with a Potential Role in Human Cognitive Functions. J Mol Evol 63, 54–68 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-005-0154-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00239-005-0154-8