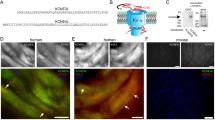
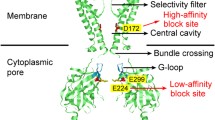
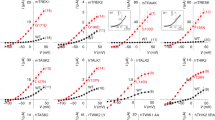
Abstract
Inward rectifier potassium (Kir) channels serve important functional and modulatory roles in a wide variety of cells. While the activity of several members of this channel family are tightly regulated by intracellular messengers such as adenosine triphosphate, G proteins, protein kinases and pH, other members are tonically active and activity is controlled only by the expression level of the protein. In a number of Kir channels, sequence motifs have been identified which determine how effectively the channel is trafficked to and from the plasma membrane. In this report, we identify a number of trafficking determinants in the Kir4.2 channel. Using mutational analysis, we found that truncation of the C terminus of the protein increased current density in Xenopus oocytes, although multiple mutations of the C terminus had no effect on current density. Instead, mutation of a unique region of the channel significantly increased current density. Selective mutation of a putative tyrosine phosphorylation site within this region mimicked the increase in current, suggesting that tyrosine phosphorylation of the protein increases channel retrieval from the membrane (or prevents trafficking to the membrane). Mutation of a previously identified trafficking determinant, K110N, also caused an increase in current density, and combining these mutations caused a multiplicative increase in current, suggesting that these two mutations increase current by independent mechanisms. These data demonstrate novel determinants of Kir4.2 channel expression.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Bond C.T., Pessia M., Xia X.M., Lagrutta A., Kavanaugh M.P., Adelman J.P. 1994. Cloning and expression of a family of inward rectifier potassium channels. Receptors Channels 2:183–191
Cohen N.A., Brenman J.E., Snyder S.H., Bredt D.S. 1996. Binding of the inward rectifier K+ channel Kir2.3 to PSD-95 is regulated by protein kinase A phosphorylation. Neuron 17:759–767
Derst C., Wischmeyer E., Preisig-Muller R., Spauschus A., Konrad M., Hensen P., Jeck N., Seyberth H.W., Daut J., Karschin A. 1998. A hyperprostaglandin E syndrome mutation in Kir1.1 (renal outer medullary potassium) channels reveals a crucial residue for channel function in Kir1.3 channels. J. Biol. Chem. 273:23884–23891
Flagg T.P., Yoo D., Sciortino C.M., Tate M., Romero M.F., Welling P.A. 2002. Molecular mechanism of a COOH-terminal gating determinant in the ROMK channel revealed by a Bartter’s disease mutation. J. Physiol. 544:351–362
Frindt G., Zhou H., Sackin H., Palmer L.G. 1998. Dissociation of K channel density and ROMK mRNA in rat cortical collecting tubule during K adaptation. Am. J. Physiol. 274:F525–F531
Horio Y., Hibino H., Inanobe A., Yamada M., Ishii M., Tada Y., Satoh E., Hata Y., Takai Y., Kurachi Y. 1997. Clustering and enhanced activity of an inwardly rectifying potassium channel, Kir4.1, by an anchoring protein, PSD-95/SAP90. J. Biol. Chem. 272:12885–12888
Inagaki N., Gonoi T., Clement J.P.T., Namba N., Inazawa J., Gonzalez G., Aguilar-Bryan L., Seino S., Bryan J. 1995. Reconstitution of I KATP: An inward rectifier subunit plus the sulfonylurea receptor. Science 270:1166–1170
Ishii M., Horio Y., Tada Y., Hibino H., Inanobe A., Ito M., Yamada M., Gotow T., Uchiyama Y., Kurachi Y. 1997. Expression and clustered distribution of an inwardly rectifying potassium channel, KAB-2/Kir4.1, on mammalian retinal Muller cell membrane: Their regulation by insulin and laminin signals. J. Neurosci. 17:7725–7735
Krapivinsky G., Gordon E.A., Wickman K., Velimirovic B., Krapivinsky L., Clapham D.E. 1995. The G-protein-gated atrial K+ channel IKACh is a heteromultimer of two inwardly rectifying K+-channel proteins. Nature 374:135–141
Kurschner C., Mermelstein P.G., Holden W.T., Surmeier D.J. 1998. CIPP, a novel multivalent PDZ domain protein, selectively interacts with Kir4.0 family members, NMDA receptor subunits, neurexins, and neuroligins. Mol. Cell. Neurosci. 11:161–172
Leipziger J., MacGregor G.G., Cooper G.J., Xu J., Hebert S.C., Giebisch G. 2000. PKA site mutations of ROMK2 channels shift the pH dependence to more alkaline values. Am. J. Physiol. 279:F919–F926
Lin D., Sterling H., Lerea K.M., Giebisch G., Wang W.H. 2002a. Protein kinase C (PKC)-induced phosphorylation of ROMK1 is essential for the surface expression of ROMK1 channels. J. Biol. Chem. 277:44278–44284
Lin D.H., Sterling H., Lerea K.M., Welling P., Jin L., Giebisch G., Wang W.H. 2002b. K depletion increases protein tyrosine kinase-mediated phosphorylation of ROMK. Am. J. Physiol. 283:F671–F677
Ma D., Zerangue N., Lin Y.F., Collins A., Yu M., Jan Y.N., Jan L.Y. 2001. Role of ER export signals in controlling surface potassium channel numbers. Science 291:316–319
Ma D., Zerangue N., Raab-Graham K., Fried S.R., Jan Y.N., Jan L.Y. 2002. Diverse trafficking patterns due to multiple traffic motifs in G protein-activated inwardly rectifying potassium channels from brain and heart. Neuron 33:715–729
Moral Z., Dong K., Wei Y., Sterling H., Deng H., Ali S., Gu R., Huang X.Y., Hebert S.C., Giebisch G., Wang W.H. 2001. Regulation of ROMK1 channels by protein-tyrosine kinase and -tyrosine phosphatase. J. Biol. Chem. 276:7156–7163
Nishida M., MacKinnon R. 2002. Structural basis of inward rectification. Cytoplasmic pore of the G protein-gated inward rectifier GIRK1 at 1.8 A resolution. Cell 111:957–965
Palmada M., Embark H.M., Wyatt A.W., Bohmer C., Lang F. 2003. Negative charge at the consensus sequence for the serum- and glucocorticoid-inducible kinase, SGK1, determines pH sensitivity of the renal outer medullary K+ channel, ROMK1. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 307:967–972
Palmer L.G., Antonian L., Frindt G. 1994. Regulation of apical K and Na channels and Na/K pumps in rat cortical collecting tubule by dietary K. J. Gen. Physiol. 104:693–710
Pearson W.L., Dourado M., Schreiber M., Salkoff L., Nichols C.G. 1999. Expression of a functional Kir4 family inward rectifier K+ channel from a gene cloned from mouse liver. J. Physiol. 514:639–653
Pessia M., Imbrici P., D’Adamo M.C., Salvatore L., Tucker S.J. 2001. Differential pH sensitivity of Kir4.1 and Kir4.2 potassium channels and their modulation by heteropolymerisation with Kir5.1. J. Physiol. 532:359–367
Pessia M., Tucker S.J., Lee K., Bond C.T., Adelman J.P. 1996. Subunit positional effects revealed by novel heteromeric inwardly rectifying K+ channels. EMBO J. 15:2980–2987
Pond L., Kuhn L.A., Teyton L., Schutze M.P., Tainer J.A., Jackson M.R., Peterson P.A. 1995. A role for acidic residues in di-leucine motif-based targeting to the endocytic pathway. J. Biol. Chem. 270:19989–19997
Schulte U., Hahn H., Konrad M., Jeck N., Derst C., Wild K., Weidemann S., Ruppersberg J.P., Fakler B., Ludwig J. 1999. pH gating of ROMK (Kir1.1) channels: Control by an Arg-Lys-Arg triad disrupted in antenatal Bartter syndrome. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 96:15298–15303
Shuck M.E., Piser T.M., Bock J.H., Slightom J.L., Lee K.S., Bienkowski M.J. 1997. Cloning and characterization of two K+ inward rectifier (Kir) 1.1 potassium channel homologs from human kidney (Kir1.2 and Kir1.3). J. Biol. Chem. 272:586–593
Stanfield P.R., Davies N.W., Shelton P.A., Sutcliffe M.J., Khan I.A., Brammar W.J., Conley E.C. 1994. A single aspartate residue is involved in both intrinsic gating and blockage by Mg2+ of the inward rectifier, IRK1. J. Physiol. 478:1–6
Sterling H., Lin D.H., Gu R.M., Dong K., Hebert S.C., Wang W.H. 2002. Inhibition of protein-tyrosine phosphatase stimulates the dynamin-dependent endocytosis of ROMK1. J. Biol. Chem. 277:4317–4323
Tanemoto M., Fujita A., Higashi K., Kurachi Y. 2002. PSD-95 mediates formation of a functional homomeric Kir5.1 channel in the brain. Neuron 34:387–397
Tucker S.J., Gribble F.M., Zhao C., Trapp S., Ashcroft F.M. 1997. Truncation of Kir6.2 produces ATP-sensitive K+ channels in the absence of the sulphonylurea receptor. Nature 387:179–183
Wald H., Garty H., Palmer L.G., Popovtzer M.M. 1998. Differential regulation of ROMK expression in kidney cortex and medulla by aldosterone and potassium. Am. J. Physiol. 275:F239–F245
Wang W.H., Lin D.H., Sterling H. 2002. Regulation of ROMK channels by protein tyrosine kinase and tyrosine phosphatase. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 12:138–142
Wei Y., Bloom P., Lin D., Gu R., Wang W.H. 2001. Effect of dietary K intake on apical small-conductance K channel in CCD: Role of protein tyrosine kinase. Am. J. Physiol. 281:F206–F212
Yan F., Lin C.W., Weisiger E., Cartier E.A., Taschenberger G., Shyng S.L. 2004. Sulfonylureas correct trafficking defects of ATP-sensitive potassium channels caused by mutations in the sulfonylurea receptor. J. Biol. Chem. 279:11096–11105
Zerangue N., Malan M.J., Fried S.R., Dazin P.F., Jan Y.N., Jan L.Y., Schwappach B. 2001. Analysis of endoplasmic reticulum trafficking signals by combinatorial screening in mammalian cells. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 98:2431–2436
Zerangue N., Schwappach B., Jan Y.N., Jan L.Y. 1999. A new ER trafficking signal regulates the subunit stoichiometry of plasma membrane KATP channels. Neuron 22:537–548
Acknowledgement
This work was supported by National Institutes of Health grants DK02773 (to W. L. P.) and NS048201 (to M. J. E.). We are indebted to Dr. Stan Misler for support and advice during experiments and for comments on the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pearson, W.L., Skatchkov, S.N., Eaton, M.J. et al. C-Terminal Determinants of Kir4.2 Channel Expression. J Membrane Biol 213, 187–193 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-006-0058-6
Received:
Revised:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s00232-006-0058-6