Abstract
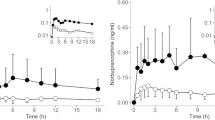
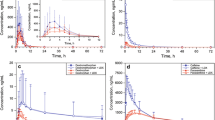
This pilot study was conducted to evaluate the potential of the new antidepressant moclobemide to inhibit the cytochrome enzyme P4502D6 (CYP2D6) using the cough suppressant dextromethorphan as a substrate in four extensive metabolizers (EM) of debrisoquine. The subjects received seven oral doses of 20 mg dextromethorphan at 4-h intervals over 2 days (1 and 2) and subsequently moclobemide (300 mg b.i.d.) for 9 days. On days 10 and 11, they received seven doses of 20 mg dextromethorphan in addition to moclobemide. During monotreatment and combined treatment, blood was collected on days 2 and 11, respectively, for determination of dextromethorphan and its demethylated metabolites using automated high- performance liquid chromatography with column switching. Concurrent administration of moclobemide markedly reduced the O-demethylation of dextromethorphan, whereas the N-demethylation of dextrorphan to hydroxymorphinan was not affected. The findings indicate that moclobemide can affect the pharmacokinetics of drugs that are mainly metabolized by CYP2D6.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Additional information
Received: 18 November 1996 / Final version: 10 March 1997
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Härtter, S., Dingemanse, J., Baier, D. et al. Inhibition of dextromethorphan metabolism by moclobemide. Psychopharmacology 135, 22–26 (1998). https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130050481
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s002130050481