Summary
-
1.
Field studies were conducted with second and third instar spiderlings of the orb weaver Nephila clavipes. The influences of prey type, prey condition, and web structure on feeding and predation were assessed.
-
2.
After emergence from the egg sac, spiderlings inhabited a communal, tangled web. Juveniles readily ate dead or immobile siblings and insect prey but did not attack live prey.
-
3.
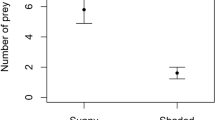
Communal web inhabitants were transferred to solitary, viscid spiral orbs built by spiderlings after dispersal. Some predatory responses were expressed by these subjects, while inhabitants of solitary orbs tested in communal webs did not attack prey. It is concluded that web structure influences predatory responses in early instars.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Austin AD, Anderson DT (1978) Reproduction and development of the spider Nephila edulis (Koch) (Araneidae: Araneae). Aust J Zool 26:501–518
Bristowe WS (1939, 1941) The comity of spiders, vols. 1 and 2. Royal Society, London
Browning HC (1941) The relationship of instar length to the external and internal environment in Tegenaria atrica (Arachnida). Proc Zool Soc London 111:303–317
Burch TL (1979) The importance of communal experience to survival for spiderlings of Araneus diadematus (Araneae: Araneidae). J Arachnol 7:1–18
Burgess JW (1979) Web-signal processing for tolerance and group predation in the social spider Mallos gregalis Simon. Anim Beh 27:157–164
Christenson TE, Goist KC (1979) Costs and benefits of male-male competition in the orb weaving spider, Nephila clavipes. Behav Ecol Sociobiol 5:87–92
Christenson TE, Wenzl PA (in press) Egg laying of the golden silk spider Nephila clavipes L. (Araneae: Araneidae): Functional analysis of the egg sac. Anim Behav
Christenson TE, Wenzl PA, Legum P (in press) Seasonal variation in egg hatching and certain egg parameters of the golden silk spider, Nephila clavipes. Psyche
Deevey GB (1949) The developmental history of Latrodectus mactans (Fabricus) at different rates of feeding. Am Midl Nat 52:189–219
Hill EM (1979) The effects of prey condition, web structure, and experience with orb residence on feeding responses in early instars of the orb weaving spider, Nephila clavipes. MS thesis, Tulane University, New Orleans, Louisiana
Moore CW (1977) The life cycle, habitat and variation in selected web parameters in the spider Nephila clavipes Koch (Araneidae). Am Midl Nat 98:95–108
Robinson MH, Mirick H (1971) The predatory behavior of the golden-web spider Nephila clavipes (Araneae: Araneidae). Psyche 78:123–139
Robinson MH, Robinson BC (1973) Ecology and behavior of the giant wood spider Nephila maculata (Fabricus) in New Guinea. Smithson Contrib Zool 149:1–76
Tolbert WW (1977) Aerial dispersal behavior of two orb weaving spiders. Psyche 84:13–27
Tretzel E (1961a) Biologie, Ökologie und Brutpflege von Coelotes terrestris (Wider) (Araneae, Agelenidae). I. Biologie und Ökologie. Z Morphol Oekol Tiere 49:658–745
Tretzel E (1961b) Biologie, Ökologie und Brutpflege von Coelotes terrestris (Wider) (Araneae, Agelenidae). II. Brutpflege. Z Morphol Oekol Tiere 50:375–542
Turnbull AL (1962) Quantitative studies of the food of Linyphia triangularis Clerck (Araneae: Linyphiidae). Can Entomol 94:1233–1249
Turnbull AL (1965) Effects of prey abundance on the development of the spider Agelenopsis potteri (Blackwell) (Araneae: Agelenidae). Can Entomol 97:141–147
Turnbull AL (1973) Ecology of the true spiders (Araneomorphae). Annu Rev Entomol 18:305–348
Vollrath F (1980) Male body size and fitness in the web-building spider, Nephila clavipes. Z Tierpsychol 53:61–78
Wise DH (1976) Variable rates of maturation in the spider, Neriene radiata (Linyphia marginata). Am Midl Nat 96:66–75
Witt PN (1975) The web as a means of communication. Biosci Commun 1:7–23
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Hill, E.M., Christenson, T.E. Effects of prey characteristics and web structure on feeding and predatory responses of Nephila clavipes spiderlings. Behav Ecol Sociobiol 8, 1–5 (1981). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00302838
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/BF00302838