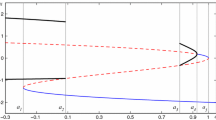
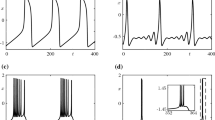
Abstract
A combination of asymptotic approaches provides a new analysis of the effect of small noise on the bursting cycle of a neuronal burster of elliptic type (type III). The analysis is applied to a stochastic model of an excitable spine, with an activity-dependent stem conductance, that exhibits conditional burst dynamics. First, we give an asymptotic approximation to the probability density for the state of the system. This density is used to compute several quantities which describe the influence of the noise on the transition from the silent to the active phase. Second, we also use a multiscale method to provide a reduced system for analysing the effect of noise on the transition out of the active phase. The combination of these two approaches results in a new framework for a quantitative description of how noise shortens the burst cycle, which measures the significant influence of small noise. For the stochastic spine model, this study suggests that small amplitude noise can significantly influence the activity-dependent morphological plasticity of dendritic spines. The techniques used in this paper combine probabilistic and asymptotic methods, and have been generalized for other noisy nonlinear systems.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Baer, S. M. and J. Rinzel (1991). Propagation of dendritic spikes mediated by excitable spines: a continuum theory. J. Neurophysiol. 65, 874–890.
Baer, S. M. and K. R. Zaremba (1998). Bursting oscillations in an idealized model for an activity-dependent spine, in Advance Topics in Biomathematics, L. Chen, S. Ruan and J. Zhu (Eds), Singapore: World Scientific.
Baer, S. M., T. Erneux and J. Rinzel (1989). The slow passage through a Hopf bifurcation: delay, memory effects and resonance. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 49, 55–71.
Ben-Jacob, E., D. J. Bergman, B. J. Matkowsky and Z. Schuss (1982). The lifetime of oscillatory steady states. Phys. Rev. A 26, 2805–2816.
Bertram, R. and A. Sherman (2000). Dynamical complexity and temporal plasticity in pancreatic beta-cells. J. Biosci. 25, 197–209.
Bertram, R., M. J. Butte, T. Kiemel and A. Sherman (1995). Topological and phenomenological classification of bursting oscillations. Bull. Math. Biol. 57, 413–439.
Chasman, L. (2000). Research Experience for Undergraduates Project, http://www.math.umn.edu/∼rachel/reu.
Chay, T. R. and H. S. Kang (1988). Role of single-channel stochastic noise on bursting clusters of pancreatic β-cells. Biophys. J. 54, 427–435.
Del Negro, C. A., C-F. Hsiao, S. H. Chandler and A. Garfinkel (1998). Evidence for a novel bursting mechanism in rodent trigeminal neurons. Biophys. J. 75, 174–182.
De Vries, G. (1998). Multiple bifurcations in a polynomial model of bursting oscillations. J. Nonlinear Sci. 8, 281–316.
De Vries, G. and A. Sherman (2000). Channel sharing in pancreatic beta-cells revisited: enhancement of emergent bursting by noise. J. Theor. Biol. 207, 513–530.
Ermentrout, G. B. and N. Kopell (1986). Parabolic bursting in an excitable system coupled with a slow oscillation. SIAM J. Appl Math. 46, 233–253.
Georgiou, M. and T. Erneux (1992). Pulsating laser oscillations depend on extremely-small-amplitude noise. Phys. Rev. A 45, 6636–42.
Golubitsky, M., K. Josic and T. J. Kaper (2001). An unfolding theory approach to bursting in fast-slow systems, in Global Analysis of Dynamical Systems, Festschrift Dedicated to Floris Takens for his 60th Birthday, H. Broer, B. Krauskopf and G. Vegter (Eds), Bristol: Institute of Physics.
Harris, K. M. and S. B. Kater (1994). Dendritic spines: cellular specializations imparting both stability and flexibility to synaptic function. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 17, 341–371.
Hille, B. (1992). Ionic Channels of Excitable Membranes, Sunderland, MA: Sinauer.
Hughes, D. and M. R. E. Proctor (1990). Chaos and the effect of noise in a model of three-wave mode coupling. Physica D 46, 163–176.
Izhikevich, E. M. (2000). Neural excitability, spiking and bursting. Int. J. Bifurcation Chaos 10, 1171–1266.
Keener, J. and J. Sneyd (1998). Mathematical Physiology, New York: Springer.
Kuske, R. (1999). Probability densities for noisy delay bifurcations. J. Stat. Phys. 96, 797–816.
Kuske, R. (2000). Gradient particle solutions of Fokker-Planck equations for noisy delay bifurcations. SIAM J. Sci. Comp. 22, 351–367.
Kuske, R. and G. Papanicolaou (1998). Invariant measure for noise simplified dynamics. Physica D 120, 255–272.
Miller, J. P., W. Rall and J. Rinzel (1985). Synaptic amplification by active membrane in dendritic spines. Brain Res. 325, 325–330.
Muller, D., N. Toni and P. A. Buchs (2000). Spine changes associated with long-term potentiation. Hippocampus 10, 596–604.
Neu, J. C. (1979). Coupled chemical oscillators. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 37, 307–315.
Rall, W. and H. Agmon-Snir (1998). Cable theory for dendritic neurons, in Methods in Neuron Modeling, C. Koch and I. Segev (Eds), Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Rinzel, J. (1987). A formal classification of bursting mechanisms in excitable systems, in Mathematical Topics in Population Biology, Morphogenesis, and Neurosciences, Lecture Notes in Biomath, E. Teramoto and M. Yamaguti (Eds), Berlin: Springer.
Rinzel, J. and S. M. Baer (1988). Threshold for repetitive activity for a slow stimulus ramp: a memory effect and its dependence on fluctuations. Biophys. J. 54.
Rinzel, J. and W. C. Troy (1982). Bursting phenomena in a simplified Oregonator flow system model. J. Chem. Phys. 76, 1775–1789.
Schuss, Z. (1980). Theory and Applications of Stochastic Differential Equations, New York: Wiley.
Schuss, Z. and R. Eisenberg (2001). Diffusion: a Stochastic Dynamics Approach, Chapter 16, preprint.
Segev, I. and W. Rall (1988). Computational study of an excitable dendritic spine. J. Neurophysiol. 60, 499–523.
Sherman, A., J. Rinzel and J. Keizer (1988). Emergence of organized bursting in clusters of pancreatic β-cells by channel sharing. Biophys. J. 54, 411–425.
Maier, R. S. and D. L. Stein (1997). Limiting exit location distributions in the stochastic exit problem. SIAM J. Appl. Math. 57, 752–790.
McClintock, P. V.E. and F. Moss (1986). Stochastic postponement of critical onsets in a bistable system, in Noise in Physical Systems and 1/f Noise, A. D’Amico and P. Mazzetti (Eds), Amsterdam: Elsevier.
Rose, C. R., Y. Kovalchuk, J. Eilers and A. Konnerth (1999). Two-photon Na+ imaging in spines and fine dendrites of central neurons. Pflugers Arch. 439, 201–207.
Shardlow, T. (2000). Stochastic perturbations of the Allen-Cahn equation. Electron. J. Diff. Eqns 2000, 1.
Shepherd, G. M. (1996). The dendritic spine: a multifunctional integrative unit. J. Neurophysiol. 75, 2197–2210.
Shepherd, G. M., R. K. Brayton, J. P. Miller, I. Segev, J. Rinzel and W. Rall (1985). Signal enhancement in distal cortical dendrites by means of interaction between active dendritic spines. Proc. Natl Acad. Sci. 2192–2195.
Stocks, N. G., R. Mannella and P. V.E. McClintock (1989). Influence of random fluctuations on delayed bifurcations: the case of additive white noise. Phys. Rev. A 40, 5361–5369.
Stone, E. and D. Armbruster (1999). Noise and O(1) amplitude effects on heteroclinic cycles. Chaos 9, 499.
Wang, X-J., J. Rinzel and M. Arbib (1995). Oscillatory and bursting properties of neurons, in The Handbook of Brain Theory and Neural Networks, Cambridge, MA: MIT Press.
Wu, H.-Y. and S. M. Baer (1998). Analysis of an excitable dendritic spine with an activity-dependent stem conductance. J. Math. Biol. 36, 569–592.
Yuste, R., A. Majewska and K. Holthoff (2000). From form to function: calcium compartmentalization in dendritic spines. Nature Neurosci. 7, 653–659.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kuske, R., Baer, S.M. Asymptotic analysis of noise sensitivity in a neuronal burster. Bull. Math. Biol. 64, 447–481 (2002). https://doi.org/10.1006/bulm.2002.0279
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1006/bulm.2002.0279